Abstract
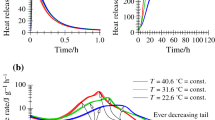
The auto efficiently hydration heat arrangement and the non-contacting electrical resistivity device were used to test the thermology effect and the resistivity variation of Portland cement hydration. The structure forming model of Portland cement initial hydration was established through the systematical experiments with different cements, the amount of mixing water and the chemical admixture. The experimental results show that, the structure forming model of cement could be divided into three stages, i e, solution-solution equilibrium period, structure forming period and structure stabilizing period. Along with the increase of mixing water, the time of inflexion appeared is in advance for thermal process of cement hydration and worsened for the structure forming process. Comparison with the control specimen, adding Na2SO4 makes the minimum critical point lower, the flattening period shorter and the growing slope after stage one steeper. So the hydration and structure forming process of Portland cement could be described more exactly by applying the thermal model and the structure-forming model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J Skalny, J F Young. Hydration Mechanism of Portland Cement[C]. In:Translation Florilegium of the 7th International Congress on the Chemical of Cement (I). Peking: China Building Industry Press, 1985: 169–214(in Chinese)
Kondo R L & diamond M. A Review of the Mechanisms of Set-retardation in Portland Cement Pastes Containing Organic Admixtures[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1972, 2(3):415–433
Taylor H F. Cement Chemistry[M]. London: Academic Press, 1990
Huang Xuehui, Zheng Jian and Ma Baoguo. Effect of Admixtures on Heat of Hydration of Fresh Cement[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2003, 25(1): 26–29 (in Chinese)
Ma Baoguo, Zhang Pingjun, Xu Chanjuan, et al. Analysis of Hydration Heat and Crack-resistance of High Micro-slag in Mass Concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2003, 25(11): 18–21 (in Chinese)
Ma Baoguo, Dong Rongzhen, Zhang Li. Research of the Initial Hydration Process and Structure Formation of Portland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the “973” project (2001CB610704-3)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, R., Ma, B., Wei, J. et al. Model analysis of initial hydration and structure forming of Portland cement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 22, 757–759 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-006-4757-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-006-4757-8