Abstract
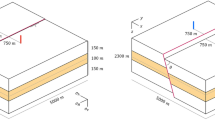
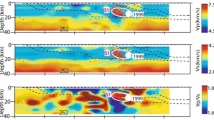
In this paper, crust medium is treated as Maxwell medium, and crust model includes hard inclusion, soft inclusion, deep-level fault. The stress concentration and its evolution with time are obtained by using three-dimensional finite element method and differential method. The conclusions are draw as follows: (1) The average stress concentration and maximum shear stress concentration caused by non-heterogeneous of crust are very high in hard inclusion and around the deep fault. With the time passing by, the concentration of average stress in the model gradually trends to uniform. At the same time, the concentration of maximum shear stress in hard inclusion increases gradually. This character is favorable to transfer shear strain energy from soft inclusion to hard inclusion. (2) When the upper mantle beneath the inclusion upheave at a certain velocity of 1 cm/a, the changes of average stress concentration with time become complex, and the boundary of the hard and soft inclusion become unconspicuous, but the maximum shear stress concentration increases much more in the hard inclusion with time at a higher velocity. This feature make for transformation of energy from the soft inclusion to the hard inclusion. (3) The changes of average stress concentration and maximum shear stress concentration with time around the deep-level fault result in further accumulation of maximum shear stress concentration and finally cause the deep-level fault instable and accelerated creep along fault direction. (4) The changes of vertical displacement on the surface of the model, which is caused by the accelerated creep of the deep-level fault, is similar to that of the observation data before Xingtai strong earthquake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu F T, Qu K X, Wu H, et al. 1986. Seismic tomography of North China region. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 29(5): 442–449 (in Chinese)
Song Z P, Yin X C, Chen X Z. 1998. The quantitative study of stress concentration of the inclusion model. Seismological Research, 21(3): 247–255 (in Chinese)
Sun R M, Zhao Y L, Mei S R. 1993. ST image in Bohai sea and its adjacent. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 36(1): 44–54 (in Chinese)
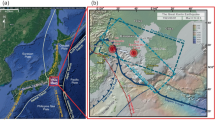
Shao X Z, Zhang J R, Zhang S Y, et al. 1993. Study of structure in Xingtai area by method of converted waves of earthquake. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 36(5): 609–619 (in Chinese)
Teng J W, Wang G Z, Liu D H, et al. 1975. Crust structure of the central part of the North China plain and the Xingtai earthquake. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 18(3): 196–207 (in Chinese)
Wang C Y, Zhang X K, Lin Z Y, et al. 1994. Characteristic of crustal structure in the Shulu fault basin and it vicinity. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 7(4): 587–594
Yin J Y, Mei S R. 1998. The crustal stress state and its significance in three dimensional simulation. Earthquake, 18(3): 226–232 (in Chinese)
Zeng R S, Zhu L P, He Z Q, et al. 1991. A seismic source model of the large earthquake in North China extensional basin and discussion on the genetic process of the extensional basin and earthquakes. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 34(3): 288–300 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, LX., Zhu, YQ., Zhang, SQ. et al. The relationship between the deep-level structure in crust and brewing of strong earthquakes in Xingtai area. Acta Seimol. Sin. 12, 647–658 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-999-0065-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-999-0065-7