Abstract
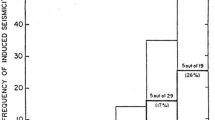
From December 3, 2005 to May 18, 2006, a water injection-induced seismicity test was conducted on DuPont test well 1# for about six months by China Earthquake Administration. To the vertical injected well, 11 water injection processes were conducted on four depth intervals, including middle Shahejie3, the top of the upper Shahejie3, the bottom of the upper Shahejie3 and Shahejie2, with the vertical span from 1 464 m to 3 034 m. Monitoring stations has been run throughout the procedure. From the recorded data, there were 5 090 events being picked out manually, 274 events located. It indicates that the energy of seismic signal is very small, and the largest magnitude is no more than M L0.5. And also, the major energy is centered on the vertical component, while amplitude of the other horizontal components is very small. From the start of water injection, the number of seismic events varied with time. And the event was most frequent in the period of upper Shahejie3 injection. The distribution of events extended from the injected well to the outside with time, and the direction of events distribution rotated in different injected interval. Of which, in the low permeability interval, events trend close to the direction of principal compressive stress direction; while in higher permeability interval, they trend close to the predominant seepage direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHEN Guo-guang, XU Jie, MA Zong-jin, et al. 2004. Recent tectonic stress field and major earthquakes of the Bohai sea basin [J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 17(4): 438–446.
CHENG Shi and LIU Wen-tai. 1992. Another earthquake events induced by water injection in China [J]. Earthquake, 1: 63–66 (in Chinese).
Crosson R S. 1972. Small earthquakes, structure, and tectonics of the Puget Sound region [J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 62: 1 133–1 171.
Davis S D and Pennington W D. 1989. Induced seismic deformation in the Cogdell oil field of west Texas [J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 79:1 477–1 494.
DONG Rui-shu and JIANG Xiu-qin. 1985. Focal mechanism solutions and stress field character in Bo Hai region [J]. Seismological Research of Northeast China, 1(1): 55–62 (in Chinese).
Evans K F, Moria H, Niitsuma H, et al. 2005. Micro-seismicity and permeability enhancement of hydrogeologic structures during massive fluid injections into granite at 3 km depth at the Soultz HDR site [J]. Geophys J Int, 160: 388–412.
FENG Xue-cai, CUI Zhong-yuan, JIA Wen-shan. 1985. The relationship between regional structural activity induced by water injection and earthquake [J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1(3): 67–71 (in Chinese).
GAO Jian-li, DING Jian-min, LIANG Guo-ping, et al. 1987. Crustal stress varies versus depth in North China basin [J]. Earthquake Research in China, 3(4): 82–89 (in Chinese).
GAO Jian-li, DING Jian-min, LIANG Guo-ping, et al. 1992. In-situ stress regime in China sea and ambient regions [J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 5(3): 523–538.
GONG Hong-qing. 1983. Discussion on reservoir earthquake control and its possibility [J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 4: 54–58 (in Chinese).
Harjes H-P, Bram K, Duerbaum H-J, et al. 1997. Origin and nature of crustal reflections: Results from integrated seismic measurements at the KTB super-deep drilling site [J]. J Geophys Res, 102(B8): 18 267–18 288.
Healy J H, Rubey W W, Griggs D T, et al. 1968. The Denver earthquakes [J]. Science, 161: 1 301–1 304.
House L. 1987. Locating micro-earthquakes induced by hydraulic fracturing in crystalline rock [J]. Geophys Res Lett, 14(9): 919–921.
LI Ping, LU Liang-ye, LU Zao-xun, et al. 2001. A 3D finite element simulation research on the relationship between crustal stress and earthquake activity in Liaoning and its vicinity [J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 14(1): 25–37.
LIU Yi-ming, HE Jing-hao, CHEN Jia-geng, et al. 1984. Exploitation and Seismic Activity in Renqiu Oil Field[A]. In: China Earthquake Administration institute eds. Induced Earthquakes in China [C]. Beijing: Seismologial Press, 183–188 (in Chinese).
LU Shou-an, SU Luan-sheng, CHEN Zheng-pin, et al. 1987. Induced earthquakes by injection and leaking water in Well Jiao7, Shandong Province: Macroscopic phenomena on ground surface and characteristics of earthquake swarm activity [J]. Seismology and Geology, 9(3): 79–83 (in Chinese).
Reservoir Earthquake Research Group, Wuhan Earthquake Team. 1977. Earthquake induced by water injection in deep well [J]. Earthquake Front, 3: 21–23 (in Chinese).
Reservoir Earthquake Work Team, Wuhan Institute of Seismology. 1978. Earthquake induced by water injection in rocky mountains, America [J]. Earthquake Front, 6: 7–8 (in Chinese).
Rutledge J T, Phillips W S, Mayerhofer M J. 2004. Faulting induced by forced fluild injection and fluid flow forced by faulting: An interpretation hydraulic-fracturing micro-seismicity, Carthage Cotton Valley Gas Field, Texas [J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 94(5): 1 817–1 830.
Segall P. 1989. Earthquakes triggered by fluid extraction [J]. Geology, 17(10): 942–946.
SHANG Hong-kuan, CHANG Bao-qi, LIU Xiao-nian. 1986. Induced Earthquake Countermeasure [A]. In: GUO Zeng-jian, CHEN Xin-lian eds. Earthquake Countermeasure [C]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 40–47 (in Chinese).
Sminchak J and Gupta N. 2003. Aspects of induced seismic activity and deep-well sequestration of carbon dioxide [J]. Environmental Geosciences, 10(2): 81–89.
SUN Ye and TAN Cheng-xuan. 1995. An analysis of present-day regional tectonic stress field and crustal movement trend in China [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1(3): 1–12 (in Chinese).
TU Yi-min and CHEN Yun-tai. 2002. The acurate location of the injection-induced micro-earthquakes in German continental deep drilling program [J]. Acta Seimologica Sinica, 15(6): 616–627 (in Chinese).
WEI Bai-lin, GUO Qin-hua, LI Chun-qing. 1999. The cause of the Sanshui earthquakes [J]. Earthquake Research in China, 15(3):247–256 (in Chinese).
XIE Fu-ren, CUI Xiao-feng, ZHAO Jian-tao. 2003. Analysis of global tectonic stress field [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(suppl.): 22–30 (in Chinese).
XU Ze-kui. 1989. Geological structure of the Luocheng region and earthquakes induced by injecting to mine salt [J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 11(3): 96–98 (in Chinese).
XU Zhong-huai, WANG Su-yun, HUANG Yü-rui, et al. 1989. China tectonic stress field deduced by amounts of earthquakes [J]. Chinese J Geophys, 32(6): 636–647 (in Chinese).
XU Zhong-huai, YAN Ming, ZHAO Zhong-he. 1983. Orientation of tectonic stress field in North China deduced by amounts of micro-earthquakes [J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 5(3): 268–279 (in Chinese).
Yerkes R F and Castle R O. 1976. Seismicity and faulting attributable to fluid extraction [J]. Engineering Geology, 10(24): 151–167.
ZHANG Bao-hong and QIU Ze-hua. 1994. On study of fluid injection earthquake [J]. Geosciences, 8(3): 329–333 (in Chinese).
ZHAO Gen-mo and ZHANG De-yuan. 1995. Study on Earthquake Induced by Water Injection [M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 46–48 (in Chinese).
ZONG Guo-hong, XIAO Huan-qin, LI Chang-bao, et al. 1999. Evolution of Jiyang depression and its tectonic implications [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 5(3): 275–282 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Collaborative Project between China and America “Temporary Seismic Activity Monitoring and Analysis for DuPont Test Well 1#, Dongying, Shandong Province”.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xc., Guo, B., Qü, Gs. et al. Analysis of injection-induced failure for DuPont test 1#, Dongying, Shandong Province. Acta Seimol. Sin. 20, 290–301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-007-0290-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-007-0290-x