Abstract
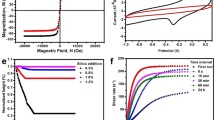
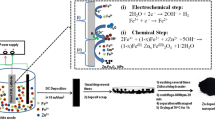
A new magnetic ionic liquid (MIL) based on 1-methylethyl ether-3-butylimidazole and [FeCl4]− is synthesized for application in electrolyte. It is found that the electrochemical performance of electrochemical cell based on MIL electrolyte can be improved by applying magnetic field. The enhanced electrochemical performance is attributed to formation of micro-domain in the mixed electrolyte under magnetic field. The ions of MIL can align along direction of magnetic field, providing efficient transmission path for migration of Li+ and Cl−. Under magnetic control, the MIL-based electrolyte does not only retain its wide electrochemical window characteristics, but also solve problem of limiting high viscosity of IL as electrolyte. The work provides a new method to design and prepare high-performance electrolyte for various electrochemical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Choi NS, Chen Z, Freunberger SA, Ji XL, Sun YK, Amine K, Yushin G, Nazar LF, Cho J, Bruce PG (2012) Challenges facing lithium batteries and electrical double-layer capacitors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:9994–10024
Gao TG, Matias I, Ribeiro APC, Martins LS (2020) Application of ionic liquids in electrochemistry-recent advances. Molecules 25:5812–5839
Hu AJ, Chen W, Li F, He M, Chen DJ, Li YY, Zhu J, Yan YC, Long JP, Hu Y, Lei TY, Li BH, Wang XF, Xiong J (2023) Nonflammable polyfluorides-anchored quasi-solid electrolytes for ultra-safe anode-free lithium pouch cells without thermal runaway. Adv Mater 35(51):2304762
Yang BR, Pan Y, Li T, Hu AJ, Li K, Li B, Yang L, Long JP (2024) High-safety lithium metal pouch cells for extreme abuse conditions by implementing flame-retardant perfluorinated gel polymer electrolytes. Energy Storage Mater 65:103124
Hu AJ, Chen W, Du XC, Hu Y, Lei TY, Wang HB, Xue LX, Li YY, Sun H, Yan YC, Long JP, Shu CZ, Zhu J, Li BH, Wang XF, Xiong J (2021) An artificial hybrid interphase for an ultrahigh-rate and practical lithium metal anode. Energy Environ Sci 14:4115–4124
Zhao C, Yan ZF, Zhou B, Pan Y, Hu AJ, He M, Liu J, Long JP (2023) Identifying the Role of Lewis-base sites for the chemistry in lithium-oxygen batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 62(32):e202302746
Li RJ, Fan YN, Zhao C, Hu AJ, Zhou B, He M, Chen JH, Yan ZF, Pan Y, Long JP (2023) Air-stable protective layers for lithium anode achieving safe lithium metal batteries. Small Methods 7(1):2201177
Kuhnel RS, Reber D, Remhof A, Figi R, Bleiner D, Battaglia C (2016) Water in salt electrolytes enable the use of cost effective aluminum current collectors for aqueous high voltage batteries. Chem Commun 52:10435–10438
Goodenough JB, Kim Y (2010) Challenges for rechargeable li batteries. Chem Mater 22:587–603
Mtj M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Hu L, Zhang Z, Amine K (2013) Fluorinated electrolytes for Li-ion battery: an FEC-based electrolyte for high voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite couple. Electrochem Commun 35:76–79
Xia J, Glazier SL, Petibon R, Dahn JR (2017) Improving linear alkyl carbonate electrolytes with electrolyte additives. J Electrochem Soc 164:A1239–A1250
Lee JT, Lin YW, Jan YS (2014) Allyl ethyl carbonate as an additive for lithium-ion battery electrolytes. J Power Sources 132:244–248
Yao W, Dai Q, Chen P, Zhong SW, Yan ZQ (2015) Influence of electrolyte additives on a cobalt oxide-based anode’s electrochemical performance and its action mechanism. RSC Adv 5:19145–19151
Wu X, Liu S, Wang N, Peng S, He ZX (2012) Influence of organic additives on electrochemical properties of the positive electrolyte for all-vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochim Acta 78:475–482
Tsunashima K, Yonekawa F, Sugiya M (2009) Lithium secondary batteries using a lithium nickelate based cathode and phosphonium ionic liquid electrolytes. Electrochem Solid State Lett 12:54–57
Egashira M, Todo H, Yoshimoto N, Morita M, Yamaki J (2007) Functionalized imidazolium ionic liquids as electrolyte components of lithium batteries. J Power Sources 174:560–564
Armand M, Endres F, MacFarlane DR, Ohno H, Scrosati B (2009) Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat Mater 8:621–629
Montanino M, Moreno M, Carewska M, Maresca G, Simonetti E, Lo PR, Alessandrini F, Appetecchi GB (2014) Mixed organic compound-ionic liquid electrolytes for lithium battery electrolyte systems. J Power Sources 269:608–615
Appetecchi GB, Moreno M, Simonetti E, Passerini S (2016) Ionic liquid electrolytes for safer lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 164:A6026–A6031
Hayashi S, Hamaguchi H (2004) Discovery of a magnetic ionic liquid FeCl4. Chem Lett 33:1590–1591
Lage-Estebanez I, Olmo LD, López R, Jose M (2018) Molecular modeling and physicochemical properties of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-FeX4 and -Fe2X7 (X=Cl and Br) magnetic ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 256:175–182
Mohammad RA, Mohammad AZ, Meysam Y, Morteza T, Saeid A (2020) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of tributyl(carboxymethyl) phosphonium bromotrichloroferrate as a new magnetic ionic liquid for the preparation of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones and 4H-pyrimidobenzothiazoles. Res Chem Intermed 46:3945–3960
Feng XT, Zhang W, Zhang TH, Yao S (2018) Systematic investigation for extraction and separation of polyphenols in tea leaves by magnetic ionic liquids. J Sci Food Agric 98:4550–4560
Sajid M (2019) Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation: a literature review. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 113:210–223
Kowsari E, Mohammadi M (2016) Synthesis of reduced and functional graphene oxide with magnetic ionic liquid and its application as an electromagnetic-absorbing coating. Compos Sci Technol 126:106–114
Mirmohseni A, Dorraji MSS, Hosseini MG (2012) Influence of metal oxide nanoparticles on pseudocapacitive behavior of wet-spun polyaniline-multiwall carbon nanotube fibers. Electrochim Acta 70:182–192
Chen C (2018) A functionalised ionic liquid: 1-(3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl)-3-methyl imidazolium chloride. Phys Chem Liq 48:298–306
Tao L, Lu J, Hu B, Chen J, Xu S, Liu F, He D (2014) Synthesis and characterisation of new polymeric ionic liquid poly(imidazolium chloride-4,6-dinitrobenzene-1,3-diyl). Mater Res Innovations 19:65–68
Haddad B, Mokhtar D, Goussem M, Belarbi EH, Kiefer J (2017) Influence of methyl and propyl groups on the vibrational spectra of two imidazolium ionic liquids and their non-ionic precursors. J Mol Struct 1134:582–590
Chen CC (2010) A functionalised ionic liquid: 1-(3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl)-3-methyl imidazolium chloride. Phys Chem Liq 48:298–306
Melissa SS, Eric RS, Eric VP, Freeman RG (2001) Ionic liquids based on FeCl3 and FeCl2 raman scattering and ab initio calculations. Inorg Chem 40:2298–2304
Wang G, Zhou F, Lu Z, Dong X (2019) Controlled synthesis of CoFe2O4/MoS2 nanocomposites with excellent sedimentation stability for magnetorheological fluid. J Ind Eng Chem 70:439–446
Suarez PAZ, Selbach VM, Dullius JEL, Einloft S, Dupont J (1997) Enlarged electrochemical window in dialkyl imidazolium cation based room temperature air and water stable molten salts. Electrochim Acta 42:2533–2535
Liew CW, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2016) Investigation of ionic liquid-doped ion conducting polymer electrolytes for carbon-based electric double layer capacitors. Mater Design 92:829–835
Bonhote P, Dias AP, Papageorgiou N, Kalyanasundaram K (1996) Highly conductive ambient temperature molten salt. Inorg Chem 35:1168–1178
Du X, Wang CY, Chen MM, Wang JJ (2009) Electrochemical performances of nanoparticle Fe3O4 activated carbon supercapacitor using KOH electrolyte solution. J Phys Chem C 113:2643–2646
Zhang HT, Zhang SJ, Zhang XX (2016) Experimental discovery OF magnetoresistance and its memory effect in methylimidazolium-type iron-containing ionic liquids. Chem Mater 28(23):8710–8714
Nykaza JR, Ye YH, Nelson RL, Jackson AC, Beyer FL, Davis EM, Page K, Sharick S, Wineye KI, Elabd YA (2016) Polymerized ionic liquid d iblock copolymers: impact of water/ion clustering on ion conductivity. Soft Matter 12:1133–1144
Abel GS, Imanol DP, Pedro M (2014) Anion-π and halide-halide nonbonding interactions in a new ionic liquid based on imidazolium cation with three dimensional magnetic ordering in the solid state. Am Chem Socity 53:8384–8396
Burba CM, Chang HC (2019) The nature of cation-anion interactions in magnetic ionic liquids as revealed using high-pressure Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 73:511–519
Funding
This study is financially supported by the Shanxi Province and Shanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (202104021301059, YDZJSX2021A026, TZLH20230818009, 202204021301049) and Special Fund for Science and Technology Innovation Teams of Shanxi Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ning Gu: Conceptualization, investigation, roles/writing—original draft.
Xiaolin Li: Conceptualization, investigation.
Miao Gao: Formal analysis, investigation.
Zixuan Liu: Formal analysis.
Qichao Liu: Review and editing.
Yang Cao: Writing—review and editing.
Youyi Sun: Roles/writing, original draft; funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, N., Li, X., Gao, M. et al. Facile synthesis of magnetic ionic liquid with magnetic tuning electrochemical performance. Ionics 30, 2783–2791 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-024-05466-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-024-05466-9