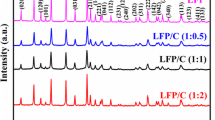
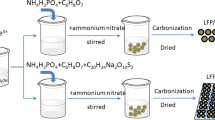
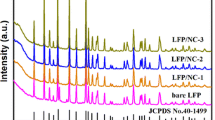
Abstract
LiFePO4/carbon (LFP/C) composites with different carbon contents are obtained through a carbothermic reduction process using glucose as carbon source. The effect of carbon content on the performance of LFP is investigated through structure and electrochemical characterization analysis. It is obvious that LFP/C composites significantly enhance the electrochemical performance compared with the unmodified LFP as the carbon content increases. In particular, LFP/C with 15% carbon content (LFP/C-15) exhibits the highest initial discharge specific capacity and the most superior capacity retention rate, with a discharge capacity of 160.7 mAh g−1 and a capacity retention rate of 82.1% after 100 cycles at 0.1 C. Moreover, the discharge capacity is already very close to the theoretical specific capacity of LiFePO4 (170 mAh g−1). However, when the carbon content reaches 20%, the electrochemical performance decreases instead, indicating that excessive carbon content has the opposite effect on the improvement of material performance. Hence, the carbon content plays a crucial role in the future improvement of the material properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang X, Tu J, Lei M, Zuo Z, Wu B, Zhou H (2016) Selection of carbon sources for enhancing 3D conductivity in the secondary structure of LiFePO4/C cathode. Electrochimica Acta 193:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.068
Gao C, Zhou J, Liu G, Wang L (2017) Synthesis of F-doped LiFePO4/C cathode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries using co-precipitation method with hydrofluoric acid source. J Alloys Compd 727:501–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.149
Hong S-A, Kim DH, Chung KY, Chang W, Yoo J, Kim J (2014) Toward uniform and ultrathin carbon layer coating on lithium iron phosphate using liquid carbon dioxide for enhanced electrochemical performance. J Power Sources 262:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.132
Lim J, Gim J, Song J, Nguyen DT, Kim S, Jo J, Mathew V, Kim J (2016) Direct formation of LiFePO4/graphene composite via microwave-assisted polyol process. J Power Sources 304:354–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.11.069
Schmuch R, Wagner R, Hörpel G, Placke T, Winter M (2018) Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat Energy 3:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-018-0107-2
Tian Z, Liu S, Ye F, Yao S, Zhou Z, Wang S (2014) Synthesis and characterization of LiFePO4 electrode materials coated by graphene. App Surf Sci 305:427–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.03.106
Wang Q, Peng D, Chen Y, Xia X, Liu H, He Y, Ma Q (2018) A facile surfactant-assisted self-assembly of LiFePO4/graphene composites with improved rate performance for lithium ion batteries. J of Electroanal Chem 818:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.04.030
Adepoju AA, Williams QL (2020) High C-rate performance of LiFePO4/carbon nanofibers composite cathode for Li-ion batteries. Curr App Phys 20:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.09.014
Du G, Zhou Y, Tian X, Wu G, Xi Y, Zhao S (2018) High-performance 3D directional porous LiFePO4/C materials synthesized by freeze casting. App Surf Sci 453:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.142
Huang C, Ai D, Wang L, He X (2013) Rapid synthesis of LiFePO4 by coprecipitation. Chem Lett 42:1191–1193. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.130436
Wei X, Guan Y, Zheng X, Zhu Q, Shen J, Qiao N, Zhou S, Xu B (2018) Improvement on high rate performance of LiFePO4 cathodes using graphene as a conductive agent. Appl Surf Sci 440:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.201
Li D, Huang Y, Sharma N, Chen Z, Jia D, Guo Z (2012) Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 by Mo-substitution and graphitic carbon-coating via a facile and fast microwave-assisted solid-state reaction. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:3634–3639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp24062a
Shi M, Kong L-B, Liu J-B, Yan K, Li J-J, Dai Y-H, Luo Y-C, Kang L (2015) A novel carbon source coated on C-LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 22:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1549-1
Wang X, Huang Y, Jia D, Guo Z, Ni D, Miao M (2010) Preparation and characterization of high-rate and long-cycle LiFePO4/C nanocomposite as cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 16:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1269-4
Yi X, Zhang F, Zhang B, Yu W-J, Dai Q, Hu S, He W, Tong H, Zheng J, Liao J (2018) (010) facets dominated LiFePO4 nano-flakes confined in 3D porous graphene network as a high-performance Li-ion battery cathode. Ceram In 44:18181–18188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.026
Gong H, Xue H, Wang T, He J (2016) In-situ synthesis of monodisperse micro-nanospherical LiFePO4 /carbon cathode composites for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sour 318:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.03.100
Su C, Bu X, Xu L, Liu J, Zhang C (2012) A novel LiFePO4/graphene/carbon composite as a performance-improved cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta 64:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.01.014
Tian X, Zhou Y, Wu G, Wang P, Chen J (2017) Controllable synthesis of porous LiFePO4 for tunable electrochemical Li-insertion performance. Electrochimica Acta 229:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.093
Wu K, Hu G, Du K, Peng Z, Cao Y (2015) Improved electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/graphene/carbon composite synthesized from FePO4·2H2O/graphene oxide. Ceram Int 41:13867–13871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.130
Yang C-C, Hsu Y-H, Shih J-Y, Wu Y-S, Karuppiah C, Liou T-H, Lue SJ (2017) Preparation of 3D micro/mesoporous LiFePO4 composite wrapping with porous graphene oxide for high-power lithium ion battery. Electrochimica Acta 258:773–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.126
Liu T, Cao F, Ren L, Li X, Sun S, Sun X, Zang Z, Niu Q, Wu J (2017) A theoretical study of different carbon coatings effect on the depolarization effect and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode. J Electroanal Chem 807:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.11.021
Zhang K, Lee JT, Li P, Kang B, Kim JH, Yi GR, Park JH (2015) Conformal coating strategy comprising N-doped carbon and conventional graphene for achieving ultrahigh power and cyclability of LiFePO4. Nano Lett 15:6756–6763. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02604
Ni J, Zhao Y, Chen J, Gao L, Lu L (2014) Site-dependent electrochemical performance of Mg doped LiFePO4. Electrochem Commun 44:4–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.04.004
Liu Y, Gu Y-J, Luo G-Y, Chen Z-L, Wu F-Z, Dai X-Y, Mai Y, Li J-Q (2020) Ni-doped LiFePO4/C as high-performance cathode composites for Li-ion batteries. Ceram Int 46:14857–14863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.011
Khan S, Raj RP, Mohan TVR, Bhuvaneswari S, Varadaraju UV, Selvam P (2019) Electrochemical performance of nano-LiFePO4 embedded ordered mesoporous nitrogenous carbon composite as cathode material for Li-ion battery applications. J Electroanal Chem 848:113242–113251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhao, R., Xia, Y. et al. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/carbon cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 28, 4579–4585 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04715-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04715-z