Abstract
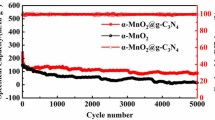
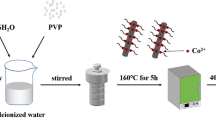
Spinel manganese-based oxide, as a promising cathode material for aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs), has attracted wide attention due to advantages of high voltage platform, and non-toxic and environmental friendliness. However, the poor conductivity and structural collapse due to the dissolution of Mn2+ limit the properties of the material. In this paper, the ZnMn2O4 nanoparticles with coating of Cu0-doped CuO (ZnMn2O4/CuO) were prepared by hydrothermal reaction and subsequent sintering process. The coating of Cu0-doped CuO displays a synergistic effect of two-phase composite, which effectively improves the conductivity and the charging/discharging electrochemical performance of the composite. As cathode materials for ZIBs, the ZnMn2O4/CuO composite shows a discharge-specific capacity of 150 mAh g−1 after an activation process at 300 mA g−1, it exhibits improved electrochemical performance than the pure ZnMn2O4. At a high current density of 2 A g−1, the composite displays a capacity of 118 mA h g−1, and the Coulomb efficiency of above 96% can be maintained throughout the cycles, indicating the high reversibility of charging and discharging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larcher D, Tarascon JM (2015) Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat Chem 7:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/Nchem.2085
Li Q, Liu Y, Guo SH, Zhou HS (2017) Solar energy storage in the rechargeable batteries. Nano Today 16:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2017.08.007
Li B, Xue J, Han C, Liu N, Ma K, Zhang R et al (2021) A hafnium oxide-coated dendrite-free zinc anode for rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. J Colloid Interface Sci 599:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.113
Chamoun M, Brant WR, Tai CW, Karlsson G, Noreus D (2018) Rechargeability of aqueous sulfate Zn/MnO2 batteries enhanced by accessible Mn2+ ions. Energy Storage Mater 15:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2018.06.019
Chen LN, An QY, Mai LQ (2019) Recent advances and prospects of cathode materials for rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Adv Mater Interfaces 6:1900387. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201900387
Chen S, Li K, Hui KS, Zhang JT (2020) Regulation of lamellar structure of vanadium oxide via polyaniline intercalation for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery. Adv Funct Mater 30:2003890. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202003890
Islam S, Alfaruqi MH, Putro DY, Park S, Kim S, Lee S et al (2021) In situ oriented mn deficient ZnMn2O4@C nanoarchitecture for durable rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Adv Sci 8:2002636. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202002636
Li CG, Zhang XD, He W, Xu GG, Sun R (2020) Cathode materials for rechargeable zinc-ion batteries: From synthesis to mechanism and applications. J Power Sources 449:227596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.227596
Li S, Qin L, Li L, Cheng H, Fang G, Liang S et al (2021) Porous structure ZnV2O4/C-N composite activating vanadium-based cathode in aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Mater Today Commun 27.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102271
Zhang SL, Yu NS, Zeng S, Zhou SS, Chen MH, Di JT et al (2018) An adaptive and stable bio-electrolyte for rechargeable Zn-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 6:12237–12243. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta04298e
Zhao SZXWYXLZZLC (2021) Manganese-based cathode materials for aqueous zinc ion batteries. Prog Chem 33:649–669
Tang F, Gao J, Ruan Q, Wu X, Wu X, Zhang T et al (2020) Graphene-wrapped MnO/C composites by mofs-derived as cathode material for aqueous zinc ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 353:136570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136570
Alfaruqi MH, Mathew V, Gim J, Kim S, Song J, Baboo JP et al (2015) Electrochemically Induced structural transformation in a gamma-MnO2 Cathode of a high capacity zinc-ion battery system. Chem Mater 27:3609–3620. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm504717p
Housel LM, Wang L, Abraham A, Huang JP, Renderos GD, Quilty CD et al (2018) Investigation of alpha-MnO2 tunneled structures as model cation hosts for energy storage. Accounts Chem Res 51:575–582. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00478
Wei CG, Xu CJ, Li BH, Du HD, Kang FY (2012) Preparation and characterization of manganese dioxides with nano-sized tunnel structures for zinc ion storage. J Phys Chem Solids 73:1487–1491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.11.038
Dai L, Wang Y, Sun L, Ding Y, Yao Y, Yao L et al (2021) Jahn–Teller distortion induced Mn 2+‐rich cathode enables optimal flexible aqueous high‐voltage Zn‐Mn batteries. Adv Sci 2004995. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202004995
Han M, Qin L, Liu Z, Zhang L, Li X, Lu B et al (2021) Reaction mechanisms and optimization strategies of manganese-based materials for aqueous zinc batteries. Mater Today Energy 20:100626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100626
Wang SQ, Chen JY, Elkholy AE, Liu XH, Li HL, Lin CF et al (2021) Transformation of spinel Zn2Mn4O8 center dot H2O to layered delta-MnO2-Based composite nanosheets with enhanced capacitance in aqueous electrolyte. Phys Status Solidi A 218:2000649. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.202000649
Chen LL, Yang ZH, Qin HG, Zeng X, Meng JL, Chen HZ (2019) Graphene-wrapped hollow ZnMn2O4 microspheres for high-performance cathode materials of aqueous zinc ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 317:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.05.147
Wu XW, Xiang YH, Peng QJ, Wu XS, Li YH, Tang F et al (2017) Green-low-cost rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries using hollow porous spinel ZnMn2O4 as the cathode material. J Mater Chem A 5:17990–17997. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta00100b
Zhang N, Cheng FY, Liu YC, Zhao Q, Lei KX, Chen CC et al (2016) Cation-deficient spinel ZnMn2O4 Cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)(2) Electrolyte for rechargeable aqueous Zn-Ion battery. J Am Chem Soc 138:12894–12901. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b05958
Chen L, Yang Z, Qin H, Zeng X, Meng J (2019) Advanced electrochemical performance of ZnMn2O4/N-doped graphene hybrid as cathode material for zinc ion battery. J Power Sources 425:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.04.010
Wang D, Zhou WW, Zhang Y, Wang YL, Wu GG, Yu K et al (2016) A novel one-step strategy toward ZnMn2O4/N-doped graphene nanosheets with robust chemical interaction for superior lithium storage. Nanotechnology. 27:045405. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/4/045405
Zhou L, Wu HB, Zhu T, Lou XW (2012) Facile preparation of ZnMn2O4 hollow microspheres as high-capacity anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem 22:827–829. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm15054e
Zhu L, Yang X-X, Xiang Y-H, Kong P, Wu X-W (2020) Neurons-system-like structured SnS2/CNTs composite for high-performance sodium-ion battery anode. Rare Met 40:1383–1390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01555-6
Yang SN, Zhang MS, Wu XW, Wu XS, Zeng FH, Li YT et al (2019) The excellent electrochemical performances of ZnMn2O4/Mn2O3: the composite cathode material for potential aqueous zinc ion batteries. J Electroanal Chem 832:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.10.051
Gou L, Mou KL, Fan XY, Zhao MJ, Wang Y, Xue D et al (2020) Mn2O3/Al2O3 cathode material derived from a metal-organic framework with enhanced cycling performance for aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Dalton Trans 49:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9dt03995c
JinleiMeng ZY, Chen L, Qin H, Cui F, Jiang Y, Zeng X (2020) Energy storage performance of CuO as a cathode material for aqueous zinc ion battery. Mater Today Energy 15:100370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2019.100370
Meng JL, Yang ZH, Chen LL, Qin HG, Cui F, Jiang YA et al (2020) Energy storage performance of CuO as a cathode material for aqueous zinc ion battery. Mater Today Energy 15:100370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2019.100370
Nesbit HW, Banerjee D (1998) Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am Miner 83:305–315
Di Castro V, Polzonetti G (1989) XPS study of MnO oxidation. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 48:117–123
Fang Q, Chen CS, Yang Z, Chen XA, Chen XH, Liu TG (2020) Synthetization and electrochemical performance of pomegranate-like ZnMn2O4 porous microspheres. J Alloy Compd 826:154084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154084
Sun T, Nian Q, Zheng S, Shi J, Tao Z (2020) Layered Ca028 MnO2 .0.5H2 O as a high performance cathode for aqueous zinc-ion battery. Small 16:e2000597. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202000597
Sun TJ, Nian QS, Zheng SB, Yuan XM, Tao ZL (2020) Water cointercalation for high-energy-density aqueous zinc-ion battery based potassium manganite cathode. J Power Sources 478:228758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228758
Liu NN, Wu X, Yin YY, Chen AS, Zhao CY, Guo ZK et al (2020) Constructing the efficient ion diffusion pathway by introducing oxygen defects in Mn2O3 for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Acs Appl Mater Inter 12:28199–28205. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c05968
Dodoo-Arhin D, Leoni M, Scardi P, Garnier E, Mittiga A (2010) Synthesis, characterisation and stability of Cu2O nanoparticles produced via reverse micelles microemulsion. Mater Chem Phys 122:602–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.03.053
Zhao QH, Chen X, Wang ZQ, Yang LY, Qin RZ, Yang JL et al (2019) Unravelling H+/Zn2+ Synergistic intercalation in a novel phase of manganese oxide for high-performance aqueous rechargeable battery. Small 15:1904545. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201904545
Rajkumar S, Elanthamilan E, Balaji TE, Sathiyan A, Jafneel NE, Merlin JP (2020) Recovery of copper oxide nanoparticles from waste SIM cards for supercapacitor electrode material. J Alloy Compd 849:156582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156582
Knight JC, Therese S, Manthiram A (2015) Chemical extraction of Zn from ZnMn2O4-based spinels. J Mater Chem A 3:21077–21082. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta06482a
Zhang N, Cheng F, Liu Y, Zhao Q, Lei K, Chen C et al (2016) Cation-deficient spinel ZnMn2O4 cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)2 electrolyte for rechargeable aqueous Zn-Ion Battery. J Am Chem Soc 138:12894–12901. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b05958
Zhao S, Han B, Zhang DT, Huang Q, Xiao L, Chen LB et al (2018) Unravelling the reaction chemistry and degradation mechanism in aqueous Zn/MnO2 rechargeable batteries. J Mater Chem A 6:5733–5739. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta01031e
Funding
This work was supported by the Opening Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Green Processing of Sugar Resources (No. GXTZY202004), the Natural Science Key Foundation of Guangxi Province (No. 2019GXNSFDA245025), the High Levels of Innovation Team and Excellence Scholars Program in Colleges of Guangxi, and the Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Guangxi University of Science and Technology (No. 16Z02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, L., Zhu, Q., Li, L. et al. Improved electrochemical performance of ZnMn2O4/CuO composite as cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Ionics 27, 4783–4792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04235-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04235-2