Abstract
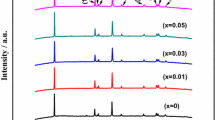
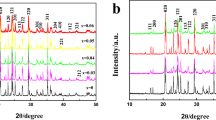
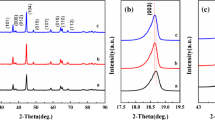
In this work, we have successfully in-situ synthesized Na+ and Co2+ co-doped Li0.9Na0.1Mn1-xCoxPO4/C nanoparticles on the surface of Li2.7Na0.3PO4 self-sacrificing template by the co-precipitation process combined with the hydrothermal method. The crystal lattice structure, crystal appearance and electrochemical parameters are characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), galvanostatic charge and discharge test, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). SEM analysis indicates that Li0.9Na0.1Mn0.9Co0.1PO4/C composite shows uniform porous structure and nanosized grain particles. The electrochemical measurements show that the double ions co-doping routine plays a vital influence on the rate capability and electrochemical lithium storage property of LiMnPO4 material. The initial discharge specific capacity of Li0.9Na0.1Mn0.9Co0.1PO4/C reaches 164.3 mAh/g (0.05 C) and 148.0 mAh/g (1 C), respectively. The excellent rate capability is attributed to the synergetic doping effect of Na+ and Co2+ on improving the Li-ion diffusion rate and broadening the Li-ion diffusion channels.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan Y, Zheng QJ, Lin DM (2014) Recent development of LiMnPO4 as cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries. Acta Chim Sin 72:537–551
Luo SH, Tang ZL, Lu JB, Zhang ZT (2008) Electrochemical properties of carbon-mixed LiFePO4 cathode material synthesized by the ceramic granulation method. Ceram Int 34:1349–1351
Martha SK, Markovsky B, Grinblat J (2009) LiMnPO4 as an advanced cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Electrochem Soc 156:A541–A552
Luo SH, Hu D, Liu H, Li J, Yi TF (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3/C using acid pickled iron oxide red for Li-ion batteries. J Hazard Mater 368:714–721
Bao S, Luo S, Yan S, Wang Z, Wang Q, Feng J, Wang Y, Yi T (2019) Nano-sized MoO2 spheres interspersed three-dimensional porous carbon composite as advanced anode for reversible sodium/potassium ion storage. Electrochim Acta 307:293–301
Bao L, Chen Y, Xu G, Yang T (2018) Hydrothermal synthesis of monodispersed LiMnPO4 (010) nanobelts and [001] nanorods and their applications in lithium-ion batteries. Eur J Inorg Chem (13):1533–1539
Hu XD, Sun XH, Yang M, Ji HM, Li XL, Cai S, Guo RS et al (2016) Sandwich nanostructured LiMnPO4/C as enhanced cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci 52(7):3597–3612
Long YF, Su J, Cui XR, Lv XY, Wen YX (2015) Enhanced rate performance of LiFePO4/C by co-doping titanium and vanadium. Solid State Sci 48:104–111
Li JZ, Luo SH, Wang Q et al (2018) Facile synthesis of carbon-LiMnPO4 nanorods with hierarchical architecture as a cathode for high-performance Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 289:415–421
Bezza I, Kaus M, Heinzmann R (2015) Mechanism of the delithiation/lithiation process in LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4: in situ and ex situ investigations on long-range and local structures. J Phys Chem C 119:9016–9024
Esmezjan L, Mikhailova D, Etter M, Cabana J, Grey CP, Indris S, Ehrenberg H (2019) Electrochemical lithium extraction and insertion process of sol-gel synthesized LiMnPO4 via two-phase mechanism. J Electrochem Soc 166(6):A1257–A1265
Xie Z, Chang K, Li B, Tang H, Fu X, Chang Z, Yuan XZ, Wang H (2016) Glucose-assisted synthesis of highly dispersed LiMnPO4 nanoparticles at a low temperature for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 189:205–214
Ragupathi V, Panigrahi P, Nagarajan GS (2019) Enhanced electrochemical performance of nanopyramid-like LiMnPO4/C cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci 495:143541
Pan X, Gao Z, Liu L, Xiao F, Xiao F, Xie S, Yi R (2019) Self-templating preparation and electrochemical performance of LiMnPO4 hollow microspheres. J Alloys Compd 783:468–477
Kwon NH, Yin H, Vavrova T, Lim JHW, Steiner U, Grobéty B, Fromm KM (2017) Nanoparticle shapes of LiMnPO4, Li+ diffusion orientation and diffusion coefficients for high volumetric energy Li+ ion cathode. J Power Sources 342:231–240
Wang L, Zhang H, Liu Q, Wang J, Ren Y, Zhang X, Yin G (2018) Modifying high-voltage olivine-type LiMnPO4 cathode via Mg substitution in high-orientation crystal. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1(11):5928–5935
Gutierrez A, Qiao R, Wang L (2014) High-capacity, aliovalently doped olivine LiMn1–3x/2Vx□x/2PO4 cathodes without carbon coating. Chem Mater 26(9):3018–3026
Vasquez FA, Calderon JA (2019) Vanadium doping of LiMnPO4 cathode material: correlation between changes in the material lattice and the enhancement of the electrochemcial performance. Electrochim Acta 325:134930
Khalfaouy RE, Addaou A, Laajeb A (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Na-substituted LiMnPO4 as a cathode material for improved lithium ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 775:836–844
Zhu YR, Zhang R, Deng L, Yi TF (2015) Lithium-ion insertion kinetics of Na-doped LiFePO4 as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Metall Mater Trans E 2(1):33–38
Rajammal K, Sivakumar D (2017) Na-doped LiMnPO4 as an electrode material for enhanced lithium ion batteries. Bull Mater Sci 40(1):171–175
Chen W, Fang H (2019) Communication-aluminum doping in LiMnPO4 with an unexpected charge compensation. J Electrochem Soc 166(13):A2752–A2754
Zhang J, Luo SH, Sui LL, Sun YY (2018) Co-precipitation assisted hydrothermal method to synthesize Li0.9Na0.1Mn0.9Ni0.1PO4/C nanocomposite as cathode for lithium ion battery. J Alloys Compd 768:991–994
Zhang J, Luo S, Wang Q (2017) Yttrium doping at Mn-site to improve electrochemical kinetics activity of sol-gel synthesized LiMnPO4/C as cathode for lithium ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 21(11):3189–3194
Zhang J, Luo S, Chang L (2016) In-situ growth of LiMnPO4 on porous LiAlO2 nanoplates substrates from AAO synthesized by hydrothermal reaction with improved electrochemical performance. Electrochim Acta 193:16–23
Dinh HC, Mho S, Kang Y (2013) Large discharge capacities at high current rates for carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanocrystalline cathodes. J Power Sources 244:189–195
Ouyang C, Shi S, Wang Z (2004) First-principles study of Li ion diffusion in LiFePO4. Phys Rev B 69(10):104303
Morgan D, Van der Ven A, Ceder G (2004) Li conductivity in LixMPO4 (M= Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) olivine materials. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 7(2):A30–A32
Yang G, Ni H, Liu H, Gao P, Ji H, Roy S (2011) The doping effect on the crystal structure and electrochemical properties of LiMnxM1-xPO4(M=Mg, V, Fe, Co, Gd). J Power Sources 196(10):4747–4755
Ma F, Zhang X, He P, Zhang X, Wang P, Zhou H (2011) Synthesis of hierarchical and bridging carbon-coated LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4 nano-structure as cathode material with improved performance for lithium ion battery. J Power Sources 359(15):408–414
Wang RJ, Zheng JY, Feng XM, Ge Y (2020) Highly [010]-oriented, gradient Co-doped LiMnPO4 with enhanced cycling stability as cathode for Li-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 24:511–519
Zhang J, Luo SH, Ren QX, Zhang DJ, Qin Y (2020) Tailoring the sodium doped LiMnPO4/C orthophosphate to nanoscale as a high-performance cathode for lithium ion battery. Appl Surf Sci 530:146628
Huang QY, Wu Z, Su J, Long YF, Lv XY, Wen YX (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ti–Fe co-doped LiMnPO4/C as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram Int 42:11348–11354
Ramar V, Balaya P (2013) Enhancing the electrochemical kinetics of high voltage olivine LiMnPO4 by isovalent co-doping. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:17240–17249
Li R, Fan CL, Zhang WH, Tan MC (2019) Structure and performance of Na+ and Fe2+ co-doped Li1-xNaxMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nanocapsule synthesized by a simple solvothermal method for lithium ion batteries. Ceram Int 45:10501–10510
Lv XY, Cui XR, Long YF, Su J, Wen YX (2015) Optimization of titanium and vanadium co-doping in LiFePO4/C using response surface methodology. Ionics 21(9):2447–2455
Su J, Liu ZZ, Long YF, Yao H, Lv XY, Wen YX (2015) Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiMnPO4/C prepared by microwave-assisted solvothermal method. Electrochim Acta 173:559–565
Sronsri C, Noisong P, Danvirutai C (2016) Synthesis, characterization and vibrational spectroscopic study of Co, Mg co-doped LiMnPO4. Spectrochim Acta A 153:436–444
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Fund of China (Nos. 51874079, 51674068), Liaoning Province Ordinary Higher Education Institutions Intercollegiate Cooperation Project (No. 202010), Liaoning Province Education Department Science and Technology Research Project (No. 202006), Scientific Research Fund of Shenyang Medical College (No. 20201006), Science and Technology Fund of Shenyang Medical College (No. 20195076), Supported by the Program for Guangdong Introducing Innovative and Entrepreneurial Teams (No. 2016ZT06G025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Luo, SH., Ren, QX. et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Na+ and Co2+ co-doped Li0.9Na0.1Mn1-xCoxPO4/C cathode material for Li-ion battery. Ionics 27, 3251–3257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04102-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04102-0