Abstract
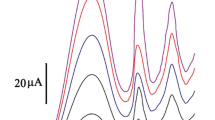
A sensitive determination of Hg(II) in different water samples has been carried out using stripping voltammetric technique based on poly xylenol orange film modified electrode. The modified poly xylenol orange (PXO) film was fabricated on the paraffin-impregnated graphite electrode (PIGE) using electro polymerization method by applying the potential between − 0.4 V to 0.8 V at a scan rate of 50 mV/s for 30 segments in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.0) containing 5 × 10−4 M of xylenol orange. The PXO film modified electrode was characterized by DRS-UV, SEM, and differential pulse voltammetry techniques. The xylenol orange film electrode was used to preconcentrate Hg(II) ions through complexation; the complexed metal ions were then reduced electrochemically followed by stripping anodically from the surface of the modified electrode. The obtained linear concentration range for Hg(II) was from 0.13 to 20.5 μg/L with a limit of detection is 0.043 μg/L.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drasch GA, Mercury, Seile HG, Sigel A (1994) Handbook on metals in clinical and analytical chemistry. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Krystek P, Ritsema R (2004) Determination of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in shark fillets. Appl Organomet Chem 18:640–645
Gu Z, Zhao M, Sheng Y, Bentolila A, Tang Y (2011) Detection of mercury ion by infrared fluorescent protein and its hydrogel-based paper assay. Anal Chem 83:2324–2329
Tchounwou PB, Ayensu WK, Ninashvili N, Sutton D (2003) Environmental exposure to mercury and its toxicopathologic implications for public health. Environ Toxicol 18:149–175
Nylander M, Friberg L, Lind B (1987) Mercury concentrations in the human brain and kidneys in relation to exposure from dental amalgam fillings. Swed Dent J 11:179–184
Cuvin-Aralar MLA, Furness RW (1991) Mercury and selenium interaction: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 21:348–364
Chen J, Chakravarty P, Davidson G, Wren D, Locked M, Zhou Y, Brown G Jr, Cizdziel J (2015) Simultaneous determination of mercury and organic carbon in sediment and soils using a direct mercury analyzer based on thermal decomposition–atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Anal Chim Acta 871:9–17
Khan N, Jamila N, Choi JY, Nho EY, Hwang IM, Kim KS (2016) Determination of mercury and aluminum concentrations in aromatic spices by direct mercury analyzer and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. World Appl Sci J 34:743–749
Daniel Pro¨Frock, Andreas Prange Helmholtz Zentrum Geesthacht–Zentrum Fu¨R Material Und Ku¨Stenforschung (2012) Inductively coupled plasma– mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for quantitative analysis in environmental and life sciences: a review of challenges, solutions, and trends. Appl Spectrosc 8:843–868
Lu Y, Yu J, Ye W, Yao X, Zhou P, Zhang H, Zhao S, Jia L (2016) Spectrophotometric determination of mercury(II) ions based on their stimulation effect on the peroxidase-like activity of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Microchim Acta 183:2481–2489
Abdelhamid HN, Wu H-F (2015) Reduced graphene oxide conjugate thymine as a new probe for ultrasensitive and selective fluorometric determination of mercury(II) ions. Microchim Acta 182:1609–1617
Gao C, Huang X-J (2013) Voltammetric determination of mercury(II). Trends Anal Chem 51:1–12
Chena L, Li Z, Menga Y, Zhanga P, Sua Z, Liua Y, Huanga Y, Zhoua Y, Xiea Q, Yao S (2014) Sensitive square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions at Bi/Nafion/overoxidized 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate-tethered polypyrrole/glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B 191:94–101
Bernalte E, Marín Sμnchez C, Pinilla Gil E (2012) High-throughput mercury monitoring in indoor dust microsamples by bath ultrasonic extraction and anodic stripping voltammetry on gold nanoparticles-modified screen-printed electrodes. Electroanalysis 25:289–294
Keawkim K, Chuanuwatanakul S, Chailapakul O, Motomizu S (2013) Determination of lead and cadmium in rice samples by sequential injection/ anodic stripping voltammetry using a bismuth film/crown ether/Nafion modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Food Control 3:14–21
Ding L, Liu Y, Zhai J, Bond AM, Zhang J (2014) Direct electrodeposition of graphene-gold nanocomposite films for ultrasensitive voltammetric determination of mercury(II). Electroanalysis 26:121–128
Padamadathil K, Sindhu R, Talasila P, Ajayaghosh A (2014) Electrochemical synthesis of a gold atomic cluster–chitosan nanocomposite film modified gold electrode for ultra-trace determination of mercury. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8529–8535
Ting SL, Ee SJ, Ananthanarayanan A, Leong KC, Chen P (2015) Graphene quantum dots functionalized gold nanoparticles for sensitive electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. Electrochim Acta 172:7–11
Lee S, Bong S, Ha J, Kwak M, Park S-K, Piao Y (2015) Electrochemical deposition of bismuth on activated graphene-nafion composite for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of trace heavy metals. Sensors Actuators B 215:62–69
Zhao G, Si Y, Wang H, Liu G (2016) A portable electrochemical detection system based on graphene/ionic liquid modified screen-printed electrode for the detection of cadmium in soil by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:54–64
Fua X-C, Wub J, Nie L, Xie C-G, Liua J-H, Huang X-J (2012) Electropolymerized surface ion imprinting films on a gold nanoparticles/single-wall carbon nanotube nanohybrids modified glassy carbon electrode for electrochemical detection of trace mercury(II) in water. Anal Chim Acta 720:29–37
Yi H (2003) Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of mercury using multi-walled carbon nanotubes film coated glassy carbon electrode. Anal Bioanal Chem 377:770–774
Faller C, Yu N, Stojko G, Henze G, Brainina Kh Z (1999) Stripping voltammetric determination of mercury at modified solid electrodes: determination of mercury traces using PDC/Au(III) modified electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 396:195–202
Yuan S, Peng D, Song D, Gong J (2013) Layered titanate nanosheets as an enhanced sensing platform for ultrasensitive stripping voltammetric detection of mercury(II). Sensors Actuators B 181:432–438
Li Z, Xia S, Wang J, Bian C, Tong J (2016) Determination of trace mercury in water based on N-octylpyridinium ionic liquids preconcentration and stripping voltammetry. J Hazard Mater 301:206–213
Wei J, Yang D, Chen H, Gao Y, Li H (2014) Stripping voltammetric determination of mercury(II) based on SWCNT-PhSH modified gold electrode. Sensors Actuators B 190:968–974
Afkhami A, Madrakian T, Sabounchei SJ, Rezaei M, Samiee S, Pourshahbaz M (2012) Construction of a modified carbon paste electrode for the highly selective simultaneous electrochemical determination of trace amounts of mercury(II) and cadmium(II). Sensors Actuators B 161:542–548
Zhou N, Chen H, Li J, Chen L (2013) Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric detection of mercury(II) using an ITO electrode modified with 5-methyl-2- thiouracil, graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180:493–499
Guha KS, Mascarenhas RJ, Thomas T, D’Souza OJ (2014) Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Hg2+ at poly(Eriochrome Black T)-modified carbon paste electrode. Ionics 20:849–856
Tamer U, lay Oymak T, Ertas N (2007) Voltammetric determination of mercury(II) at poly(3-hexylthiophene) film electrode. Effect of halide ions. Electroanalysis 19:2565–2570
Yoo K-S, Woo S-B, Jyoung J-Y (2003) Trace mercury determination by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using polythiophene-quinoline/glassy carbon modified electrode. Bull Kor Chem Soc 24:27–31
Zejli H, Sharrock P, Hidalgo-Hidalgo de Cisneros JL, Naranjo-Rodriguez I, Khalid Temsamani R (2005) Voltammetric determination of trace mercury at a sonogel–carbon electrode modified with poly-3-methylthiophene. Talanta 68:79–85
Senthil Kumar S, Sriman Narayanan S (2008) Mechanically immobilized nickel aquapentacyanoferrate modified electrode as an amperometric sensor for the determination of BHA. Talanta 76:54–59
Manikandan R, Narayanan SS (2017) Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead (II) using poly xylenol orange modified electrode. Electroanalysis 29:609–615
Liva L, Nakiboglu N (2018) Voltammetric determination of boron using poly xylenol orange-modified pencil graphite electrode. Anal Lett 51:170–185
Fernandez E, Vidal L, Costa-García A, Canals A (2016) Mercury determination in urine samples by gold nanostructured screen-printed carbon electrodes after vortex-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquideliquid microextraction. Anal Chim Acta 915:49–55
Punrat E, Chuanuwatanakul S, Kaneta T, Motomizu S, Chailapakul O (2014) Method development for the determination of mercury(II) by sequential injection/anodic stripping voltammetry using an in situ gold-film screen-printed carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 727:78–83
Borgo SD, Jovanovski V, Hocevar S (2013) Antimony film electrode for stripping voltammetric measurement of Hg(II) in the presence of Cu(II). Electrochim Acta 88:713–717
Somé IT, Sakira AK, Mertens D, Ronkart SN, Kauffmann J-M (2016) Determination of groundwater mercury (II) content using a disposable gold modified screen printed carbon electrode. Talanta 152:335–340
Hezard T, Fajerwerg K, Evrard D, Collière V, Behra P, Gros P (2012) Gold nanoparticles electrodeposited on glassy carbon using cyclic voltammetry: application to Hg(II) trace analysis. J Electroanal Chem 664:46–52
Alves GMS, Magalhães JMCS, Salaün P, van den Berg CMG, Soares HMVM (2011) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of arsenic, copper, lead and mercury in unpolluted fresh waters using a vibrating gold microwire electrode. Anal Chim Acta 703:1–7
Jovanovski V, Hrastnik NI, Hočevar SB (2015) Copper film electrode for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of trace mercury and lead. Electrochem Commun 57:1–4
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, for financial support and National Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Madras, for recording DRS-UV spectra and SEM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manikandan, R., Deepa, P.N. & Narayanan, S.S. Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Hg(II) using poly xylenol orange film modified electrode. Ionics 25, 1387–1394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2704-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2704-2