Abstract
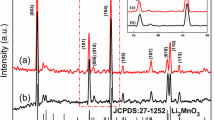
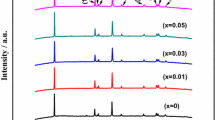
Lithium-ion battery cathode materials Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 and Li1.15Na0.05Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 were synthesized using different Na source through a facile ball-milling method. The XRD results reveal that all the cathode materials display a layered structure of solid solution. Charge/discharge tests demonstrate that the Li1.15Na0.05Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 electrode using LiAC and NaAC as raw materials shows an excellent electrochemical performance including high reversible discharge capacity (232 mAhg−1 at 0.2 C), enhanced rate capability (109 mAhg−1 at 5 C), and superior cycling stability (96.64% capacity retention after 80 cycles). Furthermore, EIS results also support that better raw materials can effectively decrease the charge transfer resistance and facilitate the Li diffusion coefficient of the as-prepared cathode material. It is also confirmed that the better electrochemical performance of the Na-doped sample Li1.15Na0.05Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 mainly come from the Na-doping process which stabilizes the host layered structure by suppressing the conversion from layered to spinel structure during cycling.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M, Tarascon JM (2008) Building better batteries. Nature 451(7179):652–657
Etacheri V, Marom R, Ran E (2011) Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ Sci 4(9):3243–3262
Nitta N, Wu F, Lee JT (2015) Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater Today 18(5):252–264
Whittingham MS (2004) Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Cheminform 35(50):4271–4301
Wei HH, Zhang Q, Xu QJ (2018) Baby diaper-inspired construction of 3D porous composites for long-term lithium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 28(3):1704440
Wang X, Xu QJ, Min YL (2018) Self-evaporating from inside to outside to construct cobalt oxide nanoparticles-embedded nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Chem Eng J 334:1642–1649
Wang J, He X, Paillard E (2016) Lithium- and manganese-rich oxide cathode materials for high-energy lithium ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 6(21)
Liu YJ, Gao YY, Lv J (2013) A facile method to synthesize carbon coated Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2, with improved performance. Mater Res Bull 48(11):4930–4934
Chong S, Wu Y, Chen Y (2017) A strategy of constructing spherical core-shell structure of Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2@Li1.2Ni0.4Mn0.4O2, cathode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. J Power Source 356:153–162
Lee DK, Park SH, Amine K (2006) High capacity Li[Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2 cathode materials via a carbonate co-precipitation method. J Power Sources 162(2):1346–1350
Li L, Wang L, Zhang X (2016) 3D reticular Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(2)
Zhang L, Wu B, Li N (2013) Rod-like hierarchical nano/micro Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 as high performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 240(1):644–652
He W, Yuan D, Qian J (2013) Enhanced high-rate capability and cycling stability of Na-stabilized layered Li1.2[Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54]O2 cathode material. J Mater Chem A 1(37):11397–11403
Guo H, Xia Y (2017) Stabilization effects of Al doping for enhanced cycling performances of Li-rich layered oxides. Ceram Int 43:13845–13852
Feng X, Gao Y, Ben L (2016) Enhanced electrochemical performance of Ti-doped Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 317:74–80
Song B, Zhou C (2014) Advances in sustain stable voltage of Cr-doped Li-rich layered cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 161:A1723–A1730
Chen H, Hu Q, Huang Z (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical study of Zr-doped Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2, as cathode material for Li-ion battery. Ceram Int 42:263–269
Liu X, Huang T, Yu A (2014) Fe doped Li1.2Mn0.6-x/2Ni0.2-x/2FexO2 (x≤0.1) as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 133:555–563
Liu YJ, Zhang ZQ, Fu Y (2016) Investigation the electrochemical performance of Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode material with ZnAl2O4 coating for lithium ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 685:523–532
Wang Z, Liu E (2013) Cycle performance improvement of Li-rich layered cathode material Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 by ZrO2 coating. Surf Coat Technol 235:570–576
Zou G, Yang X, Wang X (2014) Improvement of electrochemical performance for Li-rich spherical Li1.3[Ni0.35Mn0.65]O2+x modified by Al2O3. J Solid State Electrochem 18:1789–1797
Zheng J, Li J, Zhang ZR (2008) The effects of TiO2 coating on the electrochemical performance of Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 cathode material for lithium-ion battery. Solid State Ionics 179:1794–1799
Wu F, Zhang X (2015) Multifunctional AlPO4 coating for improving electrochemical properties of low-cost Li[Li0.2Fe0.1Ni0.15Mn0.55]O2 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:3773–3781
Lee SH, Koo BK (2008) Effect of Co3(PO4)2 coating on Li[Co0.1Ni0.15Li0.2Mn0.55]O2 cathode material for lithium rechargeable batteries. J Power Sources 184:276–283
Pang S, Wang Y (2016) The effect of AlF3 modification on the physicochemical and electrochemical properties of Li-rich layered oxide. Ceram Int 42:5397–5402
Jin X, Xu Q, Liu H (2014) Excellent rate capability of Mg doped Li[Li0.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54]O2 cathode material for lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta 136(8):19–26
Liu Y, Liu D, Zhang Z, Zheng S (2017) Investigation of the structural and electrochemical performance of Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 with Cr doping. Ionics (8):1–9
Li X, Xin HX, Liu Y (2015) Effect of niobium doping on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of lithium-rich layered Li[Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2 as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 5(56):45351–45358
Lübke M, Shin J, Marchand P (2015) Highly pseudocapacitive Nb-doped TiO2 high power anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3(45):22908–22914
Xie H, Du K, Hu G (2016) The role of sodium in LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 cathode material and its electrochemical behaviors. J Phys Chem C 120(6)
Yang Z, Guo X, Xiang W (2017) K-doped layered LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2, cathode material: towards the superior rate capability and cycling performance. J Alloys Compd 699:358–365
Wang D, Liu M, Wang X (2016) Facile synthesis and performance of Na-doped porous lithium-rich cathodes for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 6(62)
Chang ZR, Qi X, Wu F (2006) Preparation of co and Al coped LiNiO2 cathode material by using eutectic mixed lithium salt with lower melting point. Chem Eng 34:50–53
Wu XW, Li YH, Xiang YH (2016) The electrochemical performance of aqueous rechargeable battery of Zn/Na0.44MnO2 based on hybrid electrolyte. J Power Sources 336:35–39
Su MR, Wan HF (2018) Multi-layered carbon coated Si-based composite as anode for lithium-ion batteries. Powder Technol 323:294–300
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51504225 and 51404220) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150506 and BK20150535).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Tao, L., Wang, W. et al. Effects of raw materials on the electrochemical performance of Na-doped Li-rich cathode materials Li[Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2. Ionics 25, 959–968 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2696-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2696-y