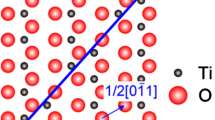
Abstract
In this work, a one-step solid-phase sintering process via TiO2 and Li2CO3 under an argon atmosphere, with ultra-fine titanium powder as the modifying agent, was used to prepare a nano-sized Li4Ti5O12/Ti composite (denoted as LTO–Ti) at 800 °C. The introduction of ultra-fine metal titanium powder played an important role. First, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrates that Ti4+ was partially changed into Ti3+, through the reduction of the ultra-fine metal titanium powder. Second, X-ray diffraction revealed that the ultra-fine metal titanium powder did not react with the bulk structure of Li4Ti5O12, while some pure titanium peaks could be seen. Additionally, the size of LTO–Ti particles could be significantly reduced from micro-scale to nano-scale. The structure and morphology of LTO–Ti were characterized by X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. Electrochemical tests showed a charge/discharge current of 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 C; the discharge capacity of the LTO–Ti electrode was 170, 161, 140, and 111 mAh g−1. It is believed that the designed LTO–Ti composite makes full use of both components, thus offering a large contact area between the electrolyte and electrode, high electrical conductivity, and lithium-ion diffusion coefficient during electrochemical processes. Furthermore, ultra-fine titanium powder, as the modifying agent, is amenable to large-scale production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li BH, Han CP, He YB, Yang C, Du HD, Yang QH, Kang FY (2012) Facile synthesis of Li4Ti5O12/C composite with super rate performance. Energy Environ Sci 5:9595–9602
Wang JS, Zhao F, Cao J, Liu Y, Wang BF (2015) Enhanced electrochemical performance of Cu2O-modified Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 21:2155–2160
Xiao CW, Ding Y, Zhang JT, Su XQ, Li GR, Gao XP, Shen PW (2014) Li4-xNaxTi5O12 with low operation potential as anode for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 248:323–329
Wang W, Yang X, Gu YX, Ding CF, Wan J (2015) Preparation and properties of bisphenol A sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Li4Ti5O12 -modified electrode. Ionics 21:885–893
Zhang QY, Zhang CL, Li B, Jiang DD, Kang SF, Li X, Wang YG (2013) Preparation and characterization of W-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for enhancing the high rate performance. Electrochim Acta 107:139–146
Prakash AS, Manikandan P, Ramesha K, Sathiya M, Tarascon JM, Shukla AK (2010) Solution-combustion synthesized nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 as high-rate performance Li-ion battery anode. Chem Mater 22:2857–2863
Raja MW, Mahanty S, Kundu M, Basu R (2009) Synthesis of nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 by a novel aqueous combustion technique. J Alloys Compd 468:258–226
Zhu YR, Yin LC, Yi TF, Liu HP, Xie Y, Zhu RS (2013) Electrochemical performance and lithium-ion intercalation kinetics of submicron-sized Li4Ti5O12 anode material. J Alloys Compd 547:107–112
Zheng SW, Xu YL, Zhao CJ, Liu HK, Qian XZ, Wang JH (2012) Synthesis of nano-sized Li4Ti5O12/C composite anode material with excellent high-rate performance. Mater Lett 68:32–35
Yan H, Zhu Z, Zhang D, Li W, Qi L (2012) A new hydrothermal synthesis of spherical Li4Ti5O12anode material for lithium-ion secondary batteries. J Power Sources 219:45–51
Wang YQ, Zhao J, Qu J, Wei FF, Song WG, Guo YG, Xu BM (2016) Investigation into the surface chemistry of Li4Ti5O12 nano-particles for lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:26008–26012
Jiang YM, Wang KX, Wu XY, Zhang HJ, Bartlett M, Chen JS (2014) Li4Ti5O12/TiO2 hollow spheres composed nanoflakes with preferentially exposed Li4Ti5O12 (011) facets for high-rate lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:19791–19796
Wang P, Zhang G, Cheng J, You Y, Li YK, Ding C, Gu JJ, Zheng XS, Zhang CF, Cao FF (2017) Facile synthesis of carbon-coated spinel Li4Ti5O12/rutile-TiO2 composites as an improved anode material in full lithium-ion batteries with LiFePO4@N-doped carbon cathode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:6138–6143
Tang YF, Huang FQ, Zhao W, Liu ZQ, Wan DY (2012) Synthesis of graphene-supported Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets for high rate battery application. J Mater Chem 22:11257–11260
Ma Y, Ding B, Ji G, Lee JY (2013) Carbon-encapsulated F-doped Li4Ti5O12 as a high rate anode material for Li+ batteries. ACS Nano 7:10870–10878
Li N, Zhou G, Li F, Wen L, Cheng HM (2013) A self-standing and flexible electrode of Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets with a N-doped carbon coating for high rate lithium ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 23:5429–5435
Yi TF, Xie Y, Zhu YR, Zhu RS, Shen HY (2013) Structural and thermodynamic stability of Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion battery. J Power Sources 222:448–454
Yi TF, Yang SY, Li XY, Yao JH, Zhu YR, Zhu RS (2014) Sub-micrometric Li4-xNaxTi5O12 (0≤x≤0.2) spinel as anode material exhibiting high rate capability. J Power Sources 246:505–511
Jae-Geun K, Dong QS, Min-Sik P, Goojin J, Yoon-Uk H, Minsu S, Young-Jun K, Jung HK, Shi XD (2013) Controlled Ag-driven superior rate-capability of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for lithium rechargeable batteries. Nano Res 6(5):365–372
Krajewski M, Michalsk M, Hamankiewicz B, Ziolkowska D, Korona KP, Jasinski JB, Kaminska M, Lipinska L, Czerwinski A (2014) Li4Ti5O12 modified with Ag nanoparticles as an advanced anode material in lithium-ion. J Power Sources 245:764–771
Liu Z, Zhang N, Wang Z, Sun K (2012) Highly dispersed Ag nanoparticles (<10 nm) deposited on nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 demonstrating high-rate charge/discharge capability for lithium-ion battery. J Power Sources 205:479–482
Zhao B, Ran R, Liu M, Shao Z (2015) A comprehensive review of Li4Ti5O12-based electrodes for lithium-ion batteries: the latest advancements and future perspectives. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 98:1–71
Mohamed H, Amrollahi GM (2012) Surface Ti3+-containing (blue) Titania: a unique photocatalyst with high activity and selectivity in visible light-stimulated selective oxidation. ACS Catal 2:2641–2647
Mukai K, Kato Y (2015) Role of oxide ions in thermally activated lithium diffusion of Li[Li1/3Ti5/3]O4: X-ray diffraction measurements and raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 119:10273–10281
Feng X, Zou H, Xiang H, Guo X, Zhou T, Wu Y, Xu W, Yan P, Wang C, Zhang JG, Yu Y (2016) Ultrathin Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets as anode materials for lithium and sodium storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:16718–16726
Wang DD, Shan ZQ, Na R, Huang WL, Tian JH (2016) Solvothermal synthesis of hedgehog-like mesoporous rutile TiO2 with improved lithium storage properties. J Power Sources 377:1–7
Xu GB, Li W, Yang LW, Wei XL, Ding JW, Zhong JX, Chu PK (2015) Highly-crystalline ultrathin Li4Ti5O12 nanosheets decorated with silver nanocrystals as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 276:247–254
Zhang QY, Lu HS, Zhong HX, Yan XD, Zhang CYOYLZ (2015) W6+ & Br− codoped Li4Ti5O12 anode with super rate performance for Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:13706–13716
Zhang QY, Liu Y, Lu HS, Tang DP, Ouyang CY, Zhang LZ (2016) Ce3+-doped Li4Ti5O12 with CeO2 surface modification by a sol-gel method for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 189:147–157
Li GL, Li J, Li G, Jiang GB (2015) N and Ti3+ co-doped 3D anatase TiO2 superstructures composed of ultrathin nanosheets with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. J Mater Chem A 3:22073–22080
Yan B, Li MS, Li XF, Bai ZM, Yang JW, Xiong DB, Li DJ (2015) Novel understanding of carbothermal reduction enhancing electronic and ionic conductivity of Li4Ti5O12 anode. J Mater Chem A 3:11773–11781
Huang S, Wen Z, Zhang J, Gu Z, Xu X (2006) Li4Ti5O12/Ag composite as electrode materials for lithium-ion battery. Solid State Ionics 177:851–855
Huang S, Wen Z, Zhang J, Gu Z, Yang X (2007) Improving the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12/Ag composite by an electroless deposition method. Electrochim Acta 52:3704–3708
Wang W, Guo YY, Liu LX, Wang SX, Yang XJ, Guo H (2014) Gold coating for a high performance Li4Ti5O12 nanorod aggregates anode in lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 245:624–629
Ge H, Li N, Li DY, Dai CS, Wang DL (2008) Electrochemical characteristics of spinel Li4Ti5O12 discharged to 0.01 V. Electrochem Commun 10:719–722
Ge H, Li N, Li DY, Dai CS, Wang DL (2009) Study on the theoretical capacity of spinel lithium Titanate induced by low-potential intercalation. J Phys Chem C 113:6324–6326
Yi TF, Yang SY, Xie Y (2015) Recent advances of Li4Ti5O12 as a promising next generation anode material for high power lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:5750–5777
Chen S, Xin Y, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Zhou H, Qi L (2014) Self-supported Li4Ti5O12 nanosheet arrays for lithium ion batteries with excellent rate capability and ultralong cycle life. Energy Environ Sci 7:1924–1930
Kim C, Norberg NS, Alexander CT, Kostecki R, Cabana J (2013) Mechanism of phase propagation during lithiation in carbon-free Li4Ti5O12 battery electrodes. Adv Funct Mater 23:1214–1222
Ji MD, Xu YL, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Liu D, Zhao CJ, Qian XZ, Zhao CH (2014) Preparation and electrochemical performance of La3+and F− co-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 263:296–303
Dong SY, Wang XY, Shen LF, Li HS, Wang J, Nie P, Wang JJ, Zhang XG (2015) Trivalent Ti self-doped Li4Ti5O12: a high performance anode material forlithium-ion capacitors. J Electroanal Chem 757:1–7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51572058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 488 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, W., Xu, Y., Yan, B. et al. Titanium-modified Li4Ti5O12 with a synergistic effect of surface modifying, bulk doping, and size reducing. Ionics 24, 1019–1027 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2278-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2278-4