Abstract
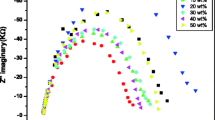
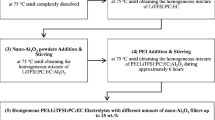
The ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of the solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes formed by dispersing a low particle-sized TiO2 ceramic filler in a poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO)-AgNO3 matrix are presented and discussed. The solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes are prepared by hot press method. The optimum conducting solid polymer electrolyte of polymer PEO and salt AgNO3 is used as host matrix and TiO2 as filler. From the filler concentration-dependent conductivity study, the maximum ionic conductivity at room temperature is obtained for 10 wt% of TiO2. The real part of impedance (Z′) and imaginary part of impedance (Z″) are analyzed using an LCR meter. The dielectric properties of the highest conducting solid polymer electrolyte are analyzed using dielectric permittivity (ε′), dielectric loss (ε″), loss tangent (tan δ), real part of the electric modulus (M′), and imaginary part of the electric modulus (M″). It is observed that the dielectric constant (ε′) increases sharply towards the lower frequencies due to the electrode polarization effect. The maxima of the loss tangent (tan δ) shift towards higher frequencies with increasing temperature. The peaks observed in the imaginary part of the electric modulus (M″) due to conductivity relaxation shows that the material is ionic conductor. The enhancement in ionic conductivity is observed when nanosized TiO2 is added into the solid polymer electrolyte.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Money BK, Hariharan K, Swenson J (2014) Relation between structural and conductivity relaxation in PEO and PEO based electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 262:785–789
Deraman SK, Mohamed NS, Subban RHY (2013) Conductivity and electrochemical studies on polymer electrolytes based on poly vinyl (chloride)—ammonium triflate-ionic liquid for proton battery. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:1459–1468
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolyte: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001 (18 pp)
Kumar Y, Hashmi SA, Pandey GP (2011a) Lithium ion transport and ion–polymer interaction in PEO based polymer electrolyte plasticized with ionic liquid. Solid State Ionics 201:73–80
Noor SAM, Ahmad A, Talib IA, Rahman MYA (2010) Morphology, chemical interaction, and conductivityof a PEO-ENR50 based on solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 16:161–170
Kim S, Park SJ (2009) Preparation and electrochemical properties of composite polymer electrolytes containing 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate salts. Electrochim Acta 54:3775–3780
Kumar KN, Kang M, Sivaiah K, Ravi M, Ratnakaram YC (2016) Enhanced electrical properties of polyethylene oxide (PEO) + polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): Li+ blended polymer electrolyte films with addition of Ag nanofiller. Ionics 22:815–825
Liu HK, Wang GX, Guo ZP, Wang JZ, Konstantinov K (2007) The impact of nanomaterials on Li-ion rechargeable batteries. J New Mat Electrochem 10:101–104
Ghosh A, Kofinas P (2008) PEO based block copolymer as solid state lithium nattery electrolyte. ECS Trans 11:131–137
Watanabe M, Nagano S, Sanui K, Ogata N (1986) Ionic conductivity of network polymers from poly(ethylene oxide) containing lithium perchlorate. Polym J 18:809–817
Fahmi EM, Ahmad A, Nazeri NNM, Hamzah H, Razali H, Rahman MYA (2012) Effect of LiBF4 salt concentration on the properties of poly (ethylene oxide)-based composite polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:5798–5804
Xue Z, Dan He D, Xie X Poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J of Mater Chem A 3:19218–19253
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly (ethylene oxide). Polymer 14:589
Kumer B, Scanlon LG (1994) Polymer-ceramic composite electrolyte. J Power Sources 52:261–268
Kumar B, Rodrigues SJ, Koka S (2002) The crystalline to amorphous transition in PEO-based composite electrolytes: role of lithium salts. Electrochim Acta 47:4125–4131
Pitawala HMJC, Dissanayake MAKL, Seneviratne VA (2007) Combined effect of Al2O3 nano-fillers and EC plasticizer on ionic conductivity enhancement in the solid polymer electrolyte (PEO)9 LiTf. Solid State Ionics 178:885–888
Scrosati B, Croce F, Persi L (2000) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J. Electrochemical Society 147:1718–1721
Wieczorek W, Florjancyk Z, Stevens JR (1995) Composite polyether based solid electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 40:2251–2258
Verma ML, Sahu HD (2015) Ionic conductivity and dielectric behavior of PEO-based silver ion conducting nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 21:3223–3231
Verma ML, Minakshi M, Singh NK (2014a) Synthesis and characterization of solid polymer electrolyte based on activated carbon for solid state capacitor. Electrochim Acta 137:497–503
Polu AR, Rhee HW (2016) Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on structural, thermal, mechanical and ionic conductivity studies of PEO12–LiTDI solid polymer electrolyte. J Ind Eng Chem 37:347–353
Johan MR, Ting LM (2011) Structural, thermal and electrical properties of nano manganese-composite polymer electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:4737–4748
Mohapatra SR, Thakur AK, Choudhary RNP (2008) Studies on PEO-based sodium ion conducting composite polymer films. Ionics 14:255–262
Polu AR, Rhee HW (2015) Nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide)/POSS-PEG (n = 13.3) hybrid nanoparticles for lithium ion batteries. J Ind Eng Chem 31:323–329
Kumar KK, Ravi M, Pavani Y, Bhavani S et al (2011b) Investigations on the effect of complexation of NaF salt with polymer blend (PEO/PVP) electrolytes on ionicconductivity and optical energy band gaps. Physica B 406:1706–1712
Karuppasamy K, Antony R, Thanikaikarasan S et al (2013) Combined effect of nanochitosan and succinonitrile on structural, mechanical, thermal, and electrochemical properties of plasticized nanocomposite polymer electrolytes (PNCPE) for lithium batteries. Ionics 19:747–755
Angulakshmi N, Yoo DJ et al (2013) MgAl2SiO6-incorporated poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Ionics DOI. doi:10.1007/s11581-013-0985-z
Prabakaran P, Manimuthu RP, Gurusamy S (2016) Influence of barium titanate nanofiller on PEO/PVdF-HFP blend-based polymer electrolyte membrane for Li-battery applications. J Solid State Electrochem DOI. doi:10.1007/s10008-016-3477-z
Singh NK, Verma ML, Minakshi M (2015) PEO nanocomposite polymer electrolyte for solid state symmetric capacitors. Bull Mater Sci 38:1577–1588
Karuppasamy K, Thanikaikarasan S, Antony R et al (2012) Effect of nanochitosan on electrochemical, interfacial and thermal properties of composite solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics. doi:10.1007/s11581-012-0678-z
Genova FKM, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Vijaya N et al (2015) Lithium ion-conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on PVA-PAN doped with lithium nitrate. Polym-Plast Technol Eng. doi:10.1080/03602559.2015.1050523
Meng C, Liu C, Chen L, Hu C, Fan S (2010) Highly flexible andall-solid-state paper like polymer supercapacitors. Nano Lett 10:4025–4031
Laxmi N, Chandra S (2001) Proton conducting composites of heteropolyacid hydrates (phosphomolybdic and phosphotungstic acids) dispersed with insulating Al2O3. Phys Status Solidi (a) 186:395
Verma ML, Minakshi M, Singh NK (2014b) Structural and electrochemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte for electrochemical devices. Ind Eng Chem Res. doi:10.1021/ie502615w
Xu D, Sridhar V, Mahapatra SP, Kim JK (2009) Dielectric properties of exfoliated graphite reinforced flouroelastomer composites. J Appl Polym Sci 111:1358–1368
Al-Saleh MH, Al-Anid HK, Husain YA, El-Ghanem HM, Jawad S (2013) Impedance characteristics and conductivity of CNT/ABS nanocomposites. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:385305 (8pp)
Maier J (2004) Ionic transport in nano-sized systems. Solid State Ionics 175:7–12
Sharma JP, Sekhon SS (2007) Nanodispersed polymer gel electrolytes: conductivity modification with the addition of PMMA and fumed silica. Solid State Ionics 178:439–445
Saikia D, Chen-Yang YW, Chen YT, Li YK, Lin SI (2009) LiNMR spectroscopy and ion conduction mechanism of composite gel polymer electrolyte: a comparative study with variation of salt and plasticizer with filler. Electrochim Acta 54:1218–1227
Agrawal RC, Gupta RK (1999) Superionic solids: composite electrolyte phase—an overview. J Mater Sci 34:1131–1162
Croce F, Persi L, Scrosati B, Serraino-Fiory F, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2001) Role of the ceramic fillers in enhancing the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 46:2457–2461
Chung SH, Wang Y, Persi L, Croce F, Greenbaum SG, Scrosati B, Plichta E (2001) Enhancement of ion transport in polymer electrolytes by addition of nanoscale inorganic oxides. J Power Sources 97:644
Ravi M, Song S, Gu K, Tang J, Zhang Z (2015) Electrical properties of biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone): lithium thiocyanate complexed polymer electrolyte films. Mater Sci Eng B 195:74–83
Shyly PM, Karuppasamy K, Linda T, Thiravetyan P, Balakumar S et al (2012) Ionic conductivity and dielectric studies of chitin nanofiber (CNF) incorporated PMMA based polymer electrolytes. IOSR J Appl Phys 1:47–51
Zamri SFM, Latif FA et al (2014) Ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of LiBF4 doped PMMA/ENR 50 filled acid modified SiO2 electrolytes. Procedia Technol 15:850–856
Tripathi SK, Gupta A, Jain A, Kumari M (2013) Electrochemical studies on nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Indian J Pure & Appl Phys 51:358–361
Reicha FM, El-Hiti M, El-Sonabati AZ, Diab MA (1991) Conducting polymers. V. Electrical conductivity of polymer complexes of bis-2,6-diaminopyridinesulphoxide-copper halides. J. Phys. D. Appl Phys 24:369
Aziz SB (2013) Li+ ion conduction mechanism in poly (ecaprolactone)- based polymer electrolyte. Iran Polym J 22:877–883
Nithya H, Selvasekarapandian S, Kumar DA et al (2011) Thermal and dielectric studies of polymer electrolyte based on P(ECH-EO). Mater Chem Phys 126:404–408
Liew CW, Ramesh S, Durairaj R (2012) Impact of low viscosity ionic liquid on PMMA–PVC–LiTFSI polymer electrolytes based on AC -impedance, dielectric behavior, and HATR–FTIR characteristics. J Mater Res 27:2996–3004
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2011) Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy and ion conduction in poly (ethylene oxide)-blend saltsmontmorillonite nanocomposite electrolytes. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 49:204–213
Kumar TV, Chary AS, Bhardwaj S, Awasthi AM, Reddy SN (2013) Dielectric relaxation, ionic conduction and complex impedance studies on NaNO3 fast ion conductor. Int J Mater Sci Appl 2:173–178
Gurusiddappa J, Madhuri W, Suvarna RP, Dasan KP (2016) Conductivity and dielectric behavior of polyethylene oxide-lithium perchlorate solid polymer electrolyte films. Indian Journal of Advances in Chemical Science 4:14–19
Sikkanthar S, Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S et al (2016) Structural, electrical conductivity, and transport analysis of PAN–NH4Cl polymer electrolyte system. Ionics 22:1085–1094
Kumar M, Srivastava N (2014) Conductivity and dielectric investigation of NH4I-doped synthesized polymer electrolyte system. Ionics. doi:10.1007/s11581-014-1294-x
Ramlli MA, Isa MIN (2014) Conductivity study of carboxyl methyl cellulose solid biopolymer electrolytes (SBE) doped with ammonium fluoride. Res J Recent Sci 3:59–66
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Arof AK (2010) Influence of silver ion reduction on electrical modulus parameters of solid polymer electrolyte based on chitosansilver triflate electrolyte membrane. Express Polym Lett 4:300–310
Dutta A, Sinha TP, Jena P, Adak S (2008) Ac conductivity and dielectric relaxation in ionically conducting soda-lime-silicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:3952–3957
Kumar M, Tiwari T, Chauhan JK, Srivastava N (2014) Erratum on ‘Understanding the ion dynamics and relaxation behavior from impedance spectroscopy of NaI doped Zwitterionic polymer system’. Mater Res Express 1:049601
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2009) Studies of dielectric and electrical properties of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 115:557–561
Raghu S, Archana K, Sharanappa C, Ganesh S, Devendrappa H (2015) The physical and chemical properties of gamma ray irradiated polymer electrolyte films. J. Non-Cryst Solids 426:55–62
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the kind support of the management of Shri Shankaracharya Technical Campus (SSTC). Helpful discussions with Prof. R C Agrawal (School of Studies in Physics Pt. RSU, Raipur, Chattishgarh, India) and Dr. Manickam Minakshi (School of Engineering and Information Technology, Murdoch University, Australia) is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, M.L., Sahu, H.D. Study on ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of PEO-based solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 23, 2339–2350 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2063-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2063-4