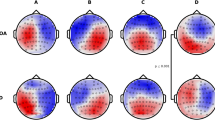
Abstract
Electroencephalography-based (EEG) microstate analysis is a promising and widely studied method in which spontaneous cerebral activity is segmented into sub second level quasi-stable states and analyzed. Currently it is being widely explored due to increasing evidence of the association of microstates with cognitive functioning and large-scale brain networks identified by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In our study using the four archetypal microstates (A, B, C and D), we investigated the changes in resting state EEG microstate dynamics in persons with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) and idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) compared to healthy controls (HC). Machine learning was applied to study its feasibility in differentiating between different groups using microstate statistics. We found significant differences in all parameters related to Microstate D (fronto-parietal network) in TLE patients and Microstate B (visual processing) in IGE patients compared to HCs. Occurrence, duration and time coverage of Microstate B was highest in IGE when compared to the other groups. We also found significant deviations in transition probabilities for both epilepsy groups, particularly into Microstate C (salience network) in IGE. Classification accuracy into clinical groups was found to exceed 70% using microstate parameters which improved on incorporating neuropsychological test differences. To the best of our knowledge, the current study is the first to compare and validate the use of microstate features to discriminate between two disparate epilepsy syndromes (TLE, IGE) and HCs using machine learning suggesting that resting state EEG microstates can be used for endophenotyping and to study resting state dysfunction in epilepsy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algin DI, Erdinç OO (2020) Impaired visual habituation in idiopathic generalized epilepsy with photosensitivity patients. Archiv Neuropsychiatr. https://doi.org/10.29399/npa.23047
Al Zoubi O, Mayeli A, Tsuchiyagaito A et al (2019) EEG microstates temporal dynamics differentiate individuals with mood and anxiety disorders from healthy subjects. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2019.00056
Ahmadi N, Pei Y, Carrette E, Aldenkamp AP, Pechenizkiy M (2020) EEG-based classification of epilepsy and PNES: EEG microstate and functional brain network features. Brain Inform. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-020-00107-z
Asadi-Pooya A, Fattahi D, Abolpour N, Boostani R, Farazdaghi M, Sharifi M (2023) Epilepsy classification using artificial intelligence: a web based application. Epilepsia Open. https://doi.org/10.1002/epi4.12800
Basri A, Muhammad A (2021) Classification of seizure types using Random Forest Classifier. Adv Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.12913/22998624/140542
Bernasconi N, Andermann F, Arnold DL, Bernasconi A (2003) Entorhinal Cortex MRI assessment in temporal, extratemporal, and idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia 44:1070–1074. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1528-1157.2003.64802.x
Bocquillon P, Dujardin K, Betrouni N, Phalempin V, Houdayer E, Bourriez J, Derambure P, Szurhaj W (2009) Attention impairment in temporal lobe epilepsy: a neurophysiological approach via analysis of the P300 wave. Hum Brain Mapp. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20666
Brechet L, Brunet D, Birot G, Gruetter R, Michel CM, Jorge J (2019) Capturing the spatiotemporal dynamics of self-generated, task-initiated thoughts with EEG and fMRI. Elsevier NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.029
Brissart H, Forthoffer N, Maillard L (2019) Attention disorders in adults with epilepsy. Determinants and Therapeutic strategies. Elsevier Revue Neurologique. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2019.01.394
Britz J, Van De Ville D, Michel CM (2010) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.052
Buonfiglio M et al (2021) Differences in visual information processing style between Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy with and without photosensitivity. Elsevier Epilepsy Behav. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.108183
Cai Y, Chen S, Chen Y, Li J, Chang DW, Zhao F, Cai PD (2019) Altered resting-state EEG microstate in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss patients with tinnitus. Front Neurosci Audit Cognit Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00443
Chowdhury FA, Elwes RD, Koutroumanidis M, Morris RG, Nashef L, Richardson MP (2014) Impaired cognitive function in idiopathic generalized epilepsy and unaffected family members: an epilepsy endophenotype. Epilepsia. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12604
Custo A, VanDeVille D, Wells WM, Tomescu MI, Brunet D, Michel CM (2017) Electroencephalographic resting-state networks: source localization of microstates. Brain Connect. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2016.0476
DaCruz JR, Favrod O, Roinishvili M, Chkonia E, Brand A, Mohr C, Figueiredo P, Herzog MH (2020) EEG microstates are a candidate endophenotype for schizophrenia. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16914-1
D’Croz-Baron DF, Baker M, Michel CM, Karp T (2019) EEG microstates analysis in young adults with autism spectrum disorder during resting-state. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2019.00173
Englot DJ, Morgan VL, Chang C (2020) Impaired vigilance networks in temporal lobe epilepsy: mechanisms and clinical implications. Epilepsia. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16423
Ghosh A, Pahari P, Basak P, Maulik U, Sarkar A (2022) Epileptic-seizure onset detection using PARAFAC model with cross-wavelet transformation on multi-channel EEG. Phys Eng Sci Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-022-01127-1
Hao Z, Zhai X, Cheng D, Pan Y, Dou W (2022) EEG Microstate-specific functional connectivity and stroke-related alterations in brain dynamics. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.848737
Hudson JM, Flowers KA, Walster KL (2014) Attentional control in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuropsychol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnp.12008
Jeyaraj MK, Menon RN, Justus S, Alexander A, Sarma PS, Radhakrishnan K (2013) A critical evaluation of the lateralizing significance of material-specific memory deficits in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Behav. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.06.011
Jiang Y, Ming YZ, Hu Y, Wang K (2021) Altered resting-state electroencephalography microstates in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: a prospective case-control study. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.710952
Kamiya K, Amemiya S, Suzuki Y, Kunii N, Kawai K, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, Saito N, Aoki S, Ohtomo K (2016) Machine learning of DTI structural brain connectomes for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy. MagnReson Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.2015-0027
Khanna A, Pascual-Leone A, Farzan F (2014) Reliability of resting-state microstate features in electroencephalography. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114163
Khanna A, Pascual-Leone A, Michel CM, Farzan F (2015) Microstates in resting-state EEG: current status and future directions. Neurosci Biobehav. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.010
Kill JB, Ciarelli PM, Côco KF (2022) Analysis of EEG microstates to predict epileptic seizures in an online approach. Res Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-021-00197-6
Khosla A, Khandnor P, Chand T (2021) EEG-based automatic multi-class classification of epileptic seizure types using recurrence plots. Expert Syst. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12923
Koenig T, Lehmann D, Merlo MCG, Kochi K, Hell D, Koukkou M (1999) A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06449-8
Koenig T, Prichep L, Lehmann D, Sosa PV, Braeker E, Kleinlogel H et al (2002) Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2002.1070
Koenig T, Studer D, Hubl D, Melie L, Strik WK (2005) Brain connectivity at different time-scales measured with EEG. Philos Trans R Soc B: Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1649
Lariviere S, Royer J, Cruces RR et al (2022) Structural network alterations in focal and generalized epilepsy assessed in a worldwide ENIGMA study follow axes of epilepsy risk gene expression. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31730-5
Lehmann D, Pascal LF, Galderisi S, Herrmann WM, Kinoshita T, Koukkou M, Mucci A, Pascual-Marqui RD, Saito N, Wackermann J, Winterer G, Koenig T (2004) EEG microstate duration and syntax in acute, medication-naïve, first-episode schizophrenia: a multi-center study. Psychiatr Res Neuroimag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2004.05.007
Lehmann D, Skrandies W (1980) Reference-free identification of components of checkerboard-evoked multichannel potential fields. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(80)90419-8
Lehmann D, Ozaki H, Pal I (1987) EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(87)90025-3
Li X, Hou Y, Ren Y, Tian X, Song Y (2017) Alterations of theta oscillation in executive control in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2017.12.017
Liu H, Tang H, Wei W, Wang G, Du Y, Ruan J (2021) Altered peri-seizure EEG microstate dynamics in patients with absence epilepsy. Elsevier Seizure. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2021.03.020
Menon V, Uddin LQ (2010) Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0262-0
Michel CM, Koenig T (2018) EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: a review. Elsevier NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.11.062
Murphy M, Stickgold R, Ongur D (2020) EEG microstate abnormalities in early course psychosis. Biol Psychiatr: Cognit Neurosci Neuroimag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.07.006
Musaeus CS, Nielsen MS, Høgh P (2019) Microstates as disease and progression markers in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00563
Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1995) Segmentation of brain electrical activity into microstates: model estimation and validation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.391164
Patrikelis P et al (2022) Selective impairment of auditory attention processing in idiopathic generalized epilepsies: Implications for their cognitive pathophysiology. Appl Neuropsychol Adult. https://doi.org/10.1080/23279095.2020.1852566
Peters SK, Dunlop DKJ (2016) Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: a central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Front Syst Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2016.00104
Piorecka V, Piorecky M et al (2018) EEG microstates analysis in patients with epilepsy. Lekar Technika 48(3):96–102
Poulsen AT, Pedroni A, Langer N, and Hansen LK (2018) Microstate EEGlab toolbox: an introductory guide. https://doi.org/10.1101/289850
Raghu S, Sriraam N, Temel Y, Rao SV, Kubben PL (2020) EEG based multi-class seizure type classification using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Neural Netw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.017
Raj KV, Rajagopalan SS, Bhardwaj S, Panda R et al (2018) Machine learning detects EEG microstate alterations in patients living with temporal lobe epilepsy. Elsevier Seizure. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2018.07.007
Ricci L, Croce P, Pulitano P, Boscarino M, Zappasodi F, Narducci F, Lanzone J, Sancetta B, Mecarelli O et al (2022) Levetiracetam modulates EEG microstates in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Topogr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-022-00911-2
Roy S, Asif U, Jianbin T, Harrer S (2020) Seizure type classification using EEG signals and machine learning: setting a benchmark. IEEE Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPMB50085.2020.9353642
Schumacher J, Peraza LR, Firbank M, Thomas AJ et al (2019) Dysfunctional brain dynamics and their origin in Lewy body dementia. Brain J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz069
Skrandies W (2007) The effect of stimulation frequency and retinal stimulus location on visual evoked potential topography. Brain Topogr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-007-0026-1
Strigaro G et al (2012) Defective visual inhibition in photosensitive idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsia. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03411.x
Tomescu MI, Rihs TA, Roinishvili M, Karahanoglu FI, Schneider M, Menghetti S et al (2015) Schizophrenia patients and 22q11. 2 deletion syndrome adolescents at risk express the same deviant patterns of resting state EEG microstates: a candidate endophenotype of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res Cogn. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scog.2015.04.005
VandeVille D, Britz J, Michel CM (2010) EEG microstate sequences in healthy humans at rest reveal scale-free dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1007841107
Vaudano AE, Ruggieri A, Avanzini P, Gessaroli G, Cantalupo G, Coppola A, Sisodiya SM, Meletti S (2017) Photosensitive epilepsy is associated with reduced inhibition of alpha rhythm generating networks. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx009
Verhoeven T, Coito A, Plomp G, Thomschewski A, Pittau F, Trinka E et al (2018) Automated diagnosis of temporal lobe epilepsy in the absence of interictal spikes. NeuroImage Clin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.09.021
Villa AEP, Tetko IV (2010) Cross frequency coupling in mesio temporal EEG recordings of epileptic patients. J Physiol Paris. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphysparis.2009.11.024
Wei Y, Ramautar JR, Colombo MA, Bart H, Someren EJW (2018) EEG microstates indicate heightened somatic awareness in insomnia: toward objective assessment of subjective mental content. Front Psych. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00395
Wu X, Yang Z, Zhang T, Zhang L, Qiao L (2023) An end-to-end seizure prediction approach using long short-term memory network. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2023.1187794
Yang L, He J, Liu D, Zheng W, Song Z (2022) EEG microstate features as an automatic recognition model of high-density epileptic EEG using support vector machine. Brain Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121731
Yu H, Zhu L, Cai L, Wang J, Liu C, Shi N, Liu J (2020) Variation of functional brain connectivity in epileptic seizures: an EEG analysis with cross-frequency phase synchronization. Cognit Neurodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09551-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
SA, A., C, S., P, D. et al. Resting state EEG microstate profiling and a machine-learning based classifier model in epilepsy. Cogn Neurodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10095-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10095-z