Abstract
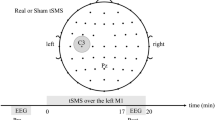
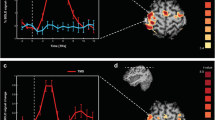
Continuous theta-burst stimulation (cTBS) induces long-lasting inhibitory effects on cortical excitability. Although cTBS has been reported to modulate neural oscillations and functional connectivity, it is still unclear how cTBS affects brain dynamics that could be captured by the resting-sate EEG microstate sequences. This study aims to investigate how cTBS over the left motor cortex affects brain dynamics. We applied 40 s-long cTBS over the left motor cortex of 28 healthy participants. Before and in multi-sessions up to 90 min after cTBS, their performance in a Nine-Hole Peg Test (NHPT), that measures the hand dexterity, and resting state EEG were recorded. Resting-sate EEG data were clustered into four microstates (namely A, B, C, and D) using k-means clustering algorithms. cTBS-induced changes in NHPT performance, microstate dynamics and functional connectivity networks were comprehensively assessed. As compared with baseline, the completion time of NHPT became shorter immediately after cTBS, suggesting cTBS-induced motor function improvement. After cTBS, the topography of microstate B revealed a greater change compared with other three topographies. Importantly, cTBS-induced decrease in completion time of NHPT correlated with cTBS-induced decrease of the mean occurrence of microstate B. Functional connectivity analysis further revealed that cTBS led to an increase of the node efficiency at C4 electrode in microstate B. These results indicated the specific modulation of cTBS over the motor cortex on the dynamics of microstate B. This work provided the evidence of the association between B and motor function, and it also implies the modulation of cTBS over the motor network.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data archiving is not mandated but data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Andreaou C, Faber PL, Leicht G, Schoettle D, Polomac N, Hanganu-Opatz IL et al (2014) Resting-state connectivity in the prodromal phase of schizophrenia: insights from EEG microstates. Schizophr Res 152:513–520
Avenanti A, Coccia M, Ladavas E, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG (2012) Low-frequency rTMS promotes use-dependent motor plasticity inchronic stroke: a randomized trial. Neurology 78:256–264
Britz J, Van De Ville D, Michel CM (2010) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 52:1162–1170
Brodbeck V, Kuhn A, von Wegner F, Morzelewski A, Tagliazucchi E, Borisov S et al (2012) EEG microstates of wakefulness and NREM sleep. Neuroimage 62(3):2129–2139
Brodie SM, Meehan S, Borich MR, Boyd LA (2014) 5 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the ipsilesional sensory cortex enhances motor learning after stroke. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00143
Cai Y, Chen S, Chen Y, Li J, Wang CD, Zhao F et al (2019) Altered resting-state EEG microstate in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss patients with tinnitus. Front Neurosci 13:443. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00443
Chen R, Classen J, Gerloff C, Celnik P, Wassermann EM, Hallett M et al (1997) Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 48(5):1398–1403
Chun SW, Rogasch NC, Hoy KE, Fitzgeral PB (2015) Measuring brain stimulation induced changes in cortical properties using TMS-EEG. Brain Stimul 8(6):1010–1020
Croce P, Zappasodi F, Capotosto P (2018) Offline stimulation of human parietal cortex differently affects resting EEG microstates. Sci Rep 8:1287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19698-z
Croce P, Quercia A, Costa S, Zappasodi F (2020) EEG microstates associated with intra- and inter-subject alpha variability. Sci Rep 10(1):2469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58787-w
Cui RQ, Huter D, Lang W, Deecke L (1999) Neuroimage of voluntary movement: topography of the Bereitschafts potential, a 64-channel DC current source density study. Neuroimage 9(1):124–134
Daskalakis ZJ, Farzan F, Barr MS, Maller JJ, Chen R, Fitzgerald PB (2008) Long-interval cortical inhibition from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: a TMS-EEG study. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(12):2860–2869
Ding L, Shou G, Yuan H, Urbano D, Cha YH (2014) Lasting modulation effects of rTMS on neural activity and connectivity as revealed by resting-state EEG. IEEE Trans Biomd Eng 61(7):2070–2080
Duc NT, Lee B (2019) Microstate functional connectivity in EEG cognitive tasks revealed by a multivariate Gaussian hidden Markov model with phase locking value. J Neural Eng 16(2):026033. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ab0169
Farzan F, Vernet M, Shafi MMD, Rotenberg A, Daskalakis ZJ, Pascual-Leone A (2016) Characterizing and modulating brain circuitry through transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with electroencephalography. Front Neural Circuits 10:73. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2016.00073
Giordano GM, Koenig T, Mucci A, Vignapiano A, Amodio A, Di Lorenzo G et al (2018) Neurophysiological correlates of Avolition-apathy in schizophrenia: a resting-EEG microstates study. Neuroimage Clin 20:627–636
Gordon PC, Desideri D, Belardinelli P, Zrenner C, Ziemann U (2018) (2018) Comparison of cortical EEG responses to realistic sham versus real TMS of human motor cortex. Brain Stimul 11(6):1322–1330
Huang YZ, Edwards MJ, Rounis E, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC (2005) Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron 45(2):201–206
Huang YZ, Chen RS, Rothwell JC, Wen HY (2007) The aftereffect of human theta burst stimulation is NMDA receptor dependent. Clin Neurophysiol 118(5):1028–1032
Jin JN, Wang X, Li Y, Jin F, Liu ZP, Yin T (2017) The effects of rTMS combined with motor training on functional connectivity in alpha frequency band. Front Behav Neurosci 11:234. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00234
Khanna A, Pascual-Leone A, Michel CM, Farzan F (2015) Microstates in resting-state EEG: current status and future directions. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 49:105–113
Kimiskidis VK (2016) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) coupled with electroencephalography (EEG): biomarker of the future. Rev Neurol (pairs) 172(2):123–126
Kindle J, Hubl D, Strik WK, Dierks T, Koenig T (2011) Resting-state EEG in schizophrenia: auditory verbal hallucinations are related to shortening of specific microstates. Clin Neurophysiol 122:1179–1182
Leodori G, Thirugnanasambandam N, Conn H, Popa T, Berardelli A, Hallett M (2019) Intracortical inhibition and surround inhibition in the motor cortex: a TMS-EEG study. Front Neurosci 13:612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00612
Lezzi E, Suppa A, Conte A, Agostino R, Nardella A, Berardelli A (2010) (2010) Theta-burst stimulation over primary motor cortex degrades early motor learning. Eur J Neurosci 31(3):585–592
Meehan SK, Dao E, Linsdell MA, Boyd LA (2011) Continuous theta burst stimulation over the contralesional sensory and motor cortex enhances motor learning post-stroke. Neurosci Lett 500(1):26–30
Michel CM, Koenig T (2018) EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: a review. Neuroimage 180:577–593
Milz P, Pascual-Marqui RD, Achermann P, Kochi K, Faber PL (2017) The EEG microstate topography is predominantly determined by intracortical sources in the alpha band. Neuroimage 162:353–361
Musso F, Brinkmeyer J, Mobascher A, Warbrick T, Winterer G (2010) Spontaneous brain activity and EEG microstates. A novel EEG/fMRI analysis approach to explore resting-state networks. Neuroimage 52(4):1149–1161
Ortiz E, Stingl K, Münßinger J, Braun C, Preissl H, Belardinelli P (2012) Weighted phase lag index and graph analysis: Preliminary investigation of functional connectivity during resting state in children. Comput Math Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/186353
Qiu S, Yi W, Wang S, Zhang C, He H (2020) The lasting effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on resting state EEG in healthy subjects. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(4):832–841
Sebastianelli L, Versace V, Martignago S, Brigo F, Trinka E, Saltuari L et al (2017) Low-frequency rTMS of the unaffected hemisphere in stroke patients: a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand 136(6):585–605
Seitzman BA, Abell M, Bartley SC, Erickson MA, Bolbecker AR, Hetrick WP (2017) Cognitive manipulation of brain electric microstates. Neuroimage 146:533–543
Shafi MM, Westover MB, Oberman L, Cash SS, Pascual-Leone A (2014) Modulation of EEG functional connectivity networks in subjects undergoing repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr 27(1):172–191
Sikka A, Jamalabadi H, Krylova M, Alizadeh S, van der Meer JN, Danyeli L et al (2020) Investigating the temporal dynamics of electroencephalogram (EEG) microstates using recurrent neural networks. Hum Brain Mapp 41(9):2334–2346
Smailovic U, Koenig T, Laukka EJ, Kalpouzos G, Andersson T, Winblad B et al (2019) EEG time signature in Alzheimer´s disease: functional brain networks falling apart. Neuroimage Clin 24:102046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102046
Smith YA, Hong E, Presson C (2000) Normative and validation studies of the nine-hole peg test with children. Percept Mot Skills 90:823–843
Strelets V, Faber PL, Golikova J, Novototsky-Vlasov V, Koenig T, Gianotti LR et al (2003) Chronic schizophrenics with positive symptomatology have shortened EEG microstate durations. Clin Neurophysiol 114(11):2043–2051
Strens LH, Oliviero A, Bloem BR, Gerschlager W, Rothwell JC, Brown P (2002) The effects of subthreshold 1 Hz repetitive TMS on cortico-cortical and interhemispheric coherence. Clin Neurophysiol 113(8):1279–1285
Thut G, Pascual-Leone A (2010) A review of combined TMS-EEG studies to characterize lasting effects of repetitive TMS and assess their usefulness in cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Brain Topogr 22(4):219–232
Vinck M, Oostenveld R, van Wingerden M, Battaglia F, Pennartz CM (2011) An improved index of phase-synchronization for electrophysiological data in the presence of volume-conduction, noise and sample-size bias. Neuroimage 55(4):1548–1565
Xu M, Xiao X, Wang Y, Qi H, Jung TP, Ming D (2018) A brain computer interface based on miniature event-related potentials induced by very small lateral visual stimuli. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(5):1166–1175
Xu J, Pan Y, Zhou S, Zou G, Liu J, Su Z et al (2020) EEG microstates are correlated with brain functional networks during slow-wave sleep. Neuroimage 15(215):116786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116786
Yi W, Qiu S, Wang K, Qi H, Zhang L, Zhou P et al (2014) Evaluation of EEG oscillatory patterns and cognitive process during simple and compound limb motor imagery. PLoS ONE 9(12):e114853. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114853
Yuan H, Zotev V, Phillips R, Drevets WC, Bodurka J (2012) Spatiotemporal dynamics of the brain at rest–exploring EEG microstates as electrophysiological signatures of BOLD resting state networks. Neuroimage 60(4):2062–2072
Zanesco AP, King BG, Skwara AC, Saron CD (2020) Within and between-person correlates of the temporal dynamics of resting EEG microstates. Neuroimage 211:116631
Zappasodi F, Croce P, Giodani A, Assenza G, Giannantoni NM, Profice P et al (2017) Prognostic value of EEG microstates in acute stroke. Brian Topogr 30(5):698–710
Zhang Y, Xu P, Guo D, Yao D (2013) Prediction of SSVEP-based BCI performance by the resting-state EEG network. J Neural Eng 10(6):066017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/10/6/066017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 81701785, 62006014, 62020106015, 61976209, 61906188); the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS (XDB32040200); the CAS International Collaboration Key Project (173211KYSB20190024); and the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (4214078). The authors would like to thank the subjects for participating in these experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [SQ], [SW], [WP], [WY], [CZ], and [JZ]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [SQ] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, S., Wang, S., Peng, W. et al. Continuous theta-burst stimulation modulates resting-state EEG microstates in healthy subjects. Cogn Neurodyn 16, 621–631 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09726-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09726-6