Abstract
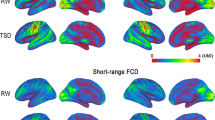
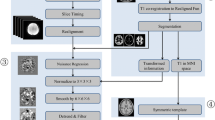
A better understanding of the neural mechanism of sleep initiation is helpful for sleep health. Our current study aimed to develop a new paradigm that is suitable for using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) to investigate the inability to initiate sleep. We recruited 28 subjects from nearby communities, in addition to traditionally resting-state eyes-closed condition (EC), they were further asked to try-to-sleep (TTS) in the MRI scanner. Independent component analysis (ICA) was used to extract the large-scale brain networks. No significant difference was found between EC and TTS in the amplitude of brain activity, nor the functional connectivity. However, under the condition of TTS, there was a significant negative correlation between functional connectivity and sleep quality. The results suggesting that the stronger the functional connectivity between the visual network and default mode network, the worse the sleep quality. The results of our research presented here suggested the increased integration among the visual thought-related networks of poor sleepers during sleep onset. More importantly, this study attempt to combine the sleep latency test with resting-state fMRI, and it may help us to investigate the neural mechanism of sleep initiation problem.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ (1989) The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psych Res 28:193–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Calhoun VD, Adali T, Pearlson GD, Pekar JJ (2001) A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 14:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.1048
Carskadon MA, Dement WC, Mitler MM, Roth T, Westbrook PR, Keenan S (1986) Guidelines for the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT): a standard measure of sleepiness. Sleep 9:519–524. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/9.4.519
Chen MC, Chang C, Glover GH, Gotlib IH (2014) Increased insula coactivation with salience networks in insomnia. Biol Psychol 97:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.12.016
Delamillieure P et al (2010) The resting state questionnaire: an introspective questionnaire for evaluation of inner experience during the conscious resting state. Brain Res Bull 81:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.11.014
Harvey AG (2000) Pre-sleep cognitive activity: a comparison of sleep-onset insomniacs and good sleepers. British J Clin Psychol 39:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466500163284
Harvey AG, Payne S (2002) The management of unwanted pre-sleep thoughts in insomnia: distraction with imagery versus general distraction. Behav Res Therapy 40:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(01)00012-2
Huang X, Long Z, Lei X (2019) Electrophysiological signatures of the resting-state fMRI global signal: a simultaneous EEG-fMRI study. J Neurosci Methods 311:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.09.017
Jafri MJ, Pearlson GD, Stevens M, Calhoun VD (2008) A method for functional network connectivity among spatially independent resting-state components in schizophrenia. NeuroImage 39:1666–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.11.001
Jaumally BA et al (2020) Excessive daytime sleepiness in cancer patients. Sleep Breath. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02151-9
Killgore WD, Schwab ZJ, Kipman M, Deldonno SR, Weber M (2013) Insomnia-related complaints correlate with functional connectivity between sensory-motor regions. NeuroReport 24:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e32835edbdd
Lei X, Zhao Z, Chen H (2013) Extraversion is encoded by scale-free dynamics of default mode network. NeuroImage 74:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.020
Lei X, Wang Y, Yuan H, Chen A (2015) Brain Scale-free Properties in Awake Rest and NREM Sleep: a Simultaneous EEG/fMRI Study. Brain Topogr 28:292–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-014-0399-x
Marques DR, Gomes AA, Clemente V, Moutinho dos Santos J (2015) Default-mode network activity and its role in comprehension and management of psychophysiological insomnia: a new perspective. New Ideas Psychol 36:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newideapsych.2014.08.001
Marques DR, Gomes AA, Caetano G, Castelo-Branco M (2018) Insomnia disorder and brain’s default-mode network. Current Neurol Neurosci Rep 18:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-018-0861-3
Naomi B, Thomas R, Leon R, Andreski P (1996) Sleep Disturbance and Psychiatric Disorders: A Longitudinal Epidemiological Study of Young Adults. Biol Psychiatry 39:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(95)00188-3
Perlis ML, Giles DE, Mendelson WB, Bootzin RR, Wyatt JK (1997) Psychophysiological insomnia: the behavioural model and a neurocognitive perspective. J Sleep Res 6:179–188
Raichle ME (2015) The brain’s default mode network. Annu Rev Neurosci 38:433–447. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014030
Regen W et al. (2016) Objective sleep disturbances are associated with greater waking resting-state connectivity between the retrosplenial cortex/hippocampus and various nodes of the default mode network. J Psychiatry Neurosci 41:295-303. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.14029041:140290
Riemann D, Spiegelhalder K, Feige B, Voderholzer U, Berger M, Perlis M, Nissen C (2010) The hyperarousal model of insomnia: a review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Med Rev 14:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2009.04.002
Rosch PJ (1994) Insomnia, psychological assessment and management, Charles M. Morin, Guilford Press, New York, 1993. 238. 10:69-70 https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.2460100113
Sateia MJ (2014) International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest 146:1387–1394. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-0970
Tzourio-Mazoyer N et al (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15:273–289. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0978
Woods H, Marchetti LM, Biello S, Espie C (2009) The clock as a focus of selective attention in those with primary insomnia: An experimental study using a modified Posner paradigm. Behav Res Ther 47(3):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2008.12.009
Yan C, Zang YF (2010) DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for “Pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Front Syst Neurosci 4:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2010.00013
Yu S, Guo B, Shen Z, Wang Z, Kui Y, Hu Y, Feng F (2018) The imbalanced anterior and posterior default mode network in the primary insomnia. J Psychiatr Res 103:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.05.013
Zang YF et al (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2006.07.002
Zhou X, Lei X (2018) Wandering minds with wandering brain networks. Neurosci Bull 34:1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-018-0278-7
Zung WWK (1965) A self-rating depression scale. Arch General Psych 12:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720310065008
Zung WWK (1971) Rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics 12:371–372
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant number 31971028), Major Project of Medicine Science and Technology of PLA (AWS17J012), and Chongqing Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project (CYS19119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Dong, X. & Lei, X. Hard to initiate sleep: a new paradigm for resting-state fMRI. Cogn Neurodyn 15, 825–833 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09659-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09659-6