Abstract
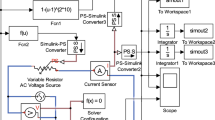
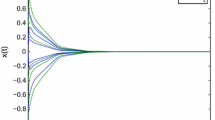
This paper addresses the stability problem on the memristive neural networks with time-varying impulses. Based on the memristor theory and neural network theory, the model of the memristor-based neural network is established. Different from the most publications on memristive networks with fixed-time impulse effects, we consider the case of time-varying impulses. Both the destabilizing and stabilizing impulses exist in the model simultaneously. Through controlling the time intervals of the stabilizing and destabilizing impulses, we ensure the effect of the impulses is stabilizing. Several sufficient conditions for the globally exponentially stability of memristive neural networks with time-varying impulses are proposed. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the theoretical results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baæinov D, Simeonov PS (1989) Systems with impulse effect: stability, theory, and applications. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Cantley KD, Subramaniam A, Stiegler HJ (2011) Hebbian learning in spiking neural networks with nanocrystalline silicon TFTs and memristive synapses. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 10:1066–1073
Chen WH, Zheng WX (2009) Global exponential stability of impulsive neural networks with variable delay: an LMI approach. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 56:1248–1259
Chua L (1971) Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory 18:507–519
Chua L, Kang SM (1976) Memristive devices and systems. Proc IEEE 64:209–223
Filippov A (1960) Differential equations with discontinuous right-hand side. Matematicheskii Sbornik 93:99–128
Guan ZH, Hill DJ, Yao J (2006) A hybrid impulsive and switching control strategy for synchronization of nonlinear systems and application to Chua’s chaotic circuit. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 16:229–238
Guo Z, Wang J, Yan Z (2013) Global exponential dissipativity and stabilization of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Neural Netw 48:158–172
He X, Li C, Huang T, Peng M (2013a) Codimension two bifurcation in a simple delayed neuron model. Neural Comput Appl 23:2295–2300
He X, Li C, Huang T (2013b) Bogdanov–Takens singularity in tri-neuron network with time delay. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24:1001–1007
Hu J, Wang J (2010) Global uniform asymptotic stability of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time delays. In: The 2010 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), pp 1–8
Hu C, Jiang H, Teng Z (2010) Impulsive control and synchronization for delayed neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21:67–81
Hu W, Li C, Wu S (2012) Stochastic robust stability for neutral-type impulsive interval neural networks with distributed time-varying delays. Neural Comput Appl 21:1947–1960
Kim KH, Gaba S, Wheeler D (2011) A functional hybrid memristor crossbar-array/CMOS system for data storage and neuromorphic applications. Nano Lett 12:389–395
Liu B, Liu X (2007) Robust stability of uncertain discrete impulsive systems[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 54:455–459
Liu X, Shen X, Zhang H (2011) Intermittent impulsive synchronization of chaotic delayed neural networks. Differ Equ Dyn Syst 19:149–169
Lu J, Ho D, Cao J (2010) A unified synchronization criterion for impulsive dynamical networks. Automatica 46:1215–1221
Lu J, Ho DWC, Cao J (2011) Exponential synchronization of linearly coupled neural networks with impulsive disturbances. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22:329–336
Lu J, Kurths J, Cao J (2012) Synchronization control for nonlinear stochastic dynamical networks: pinning impulsive strategy. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23:285–292
Strukov DB, Snider GS, Stewart DR (2008) The missing memristor found. Nature 453:80–83
Tour JM, He T (2008) The fourth element. Nature 453:42–43
Wang G, Shen Y (2013) Exponential synchronization of coupled memristive neural networks with time delays. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-013-1349-3
Wang X, Li C, Huang T, Duan S (2012) Predicting chaos in memristive oscillator via harmonic balance method. Chaos 22:4
Wen S, Zeng Z (2012) Dynamics analysis of a class of memristor-based recurrent networks with time-varying delays in the presence of strong external stimuli. Neural Process Lett 35:47–59
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T (2012a) Adaptive synchronization of memristor-based Chua’s circuits. Phys Lett A 376:2775–2780
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T (2012b) Exponential stability analysis of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 97:233–240
Wu A, Zeng Z (2012a) Dynamic behaviors of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Neural Networks 36:1–10
Wu A, Zeng Z (2012b) Exponential stabilization of memristive neural networks with time delays. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Sys 23(12):1919–1929
Wu AL, Wen S, Zeng Z (2012) Synchronization control of a class of memristor-based recurrent neural networks. Inf Sci 183:106–116
Yang Z, Xu D (2005) Stability analysis of delay neural networks with impulsive effects. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 52:517–521
Yang Z, Xu D (2007) Stability analysis and design of impulsive control systems with time delay. IEEE Trans Autom Control 52:1448–1454
Zhang H, Guan Z, Ho D (2006) On synchronization of hybrid switching and impulsive networks. In: 2006 45th IEEE conference on decision and control, IEEE pp 2765–2770
Zhang G, Shen Y, Sun J (2012) Global exponential stability of a class of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 97:149–154
Acknowledgments
This publication was made possible by NPRP Grant # NPRP 4-1162-1-181 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors. This work was also supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 61374078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, J., Li, C. & Huang, T. Stability of delayed memristive neural networks with time-varying impulses. Cogn Neurodyn 8, 429–436 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-014-9286-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-014-9286-0