Abstract
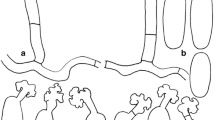
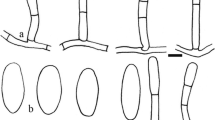
The powdery mildew fungus Leveillula taurica (Erysiphales) is reported for the first time from the monocot Triglochin maritima (Juncaginaceae), a widespread salt marsh plant that causes economic losses because of its high toxicity to young livestock. This is the first report of an erysiphaceous fungus on a member of the Juncaginaceae. Morphological data, obtained by light and scanning electron microscopy, and ITS sequence data provided evidence that this fungus is referable to L. taurica. The ITS sequence for this fungus was identical with those reported for L. taurica hosted by Capsicum annuum in Australia and Elaeagnus angustifolia in Iran. This is the third host species and second monocot, in addition to Allium cepa and Solanum tuberosum, reported for L. taurica from Washington State, where the fungus was unreported before 2004.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Kipmann DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. — Journal of Molecular Biology 219: 403–410.
Braun U (1987) A monograph of the Erysiphales (powdery mildews). — Beihefte zur Nova Hedgwigia 89: 1–700.
Braun U (1995) The Powdery Mildews (Erysiphales) of Europe. Gustav Fischer, Jena. 337 pp.
Braun U, Cook RTA, Inman AJ, Shin H-D (2002) The taxonomy of powdery mildew fungi. In Bélanger RR, Bushnell WR, Dik AJ, and Carver TLW (eds) The Powdery Mildews: A Comprehensive Treatise, pp. 13–55. APS Press, St. Paul, MN.
Cerkauskas RF, Buonassisi A (2003) First report of powdery mildew of greenhouse pepper caused by Leveillula taurica in British Columbia, Canada. — Plant Disease 87: 1151.
Cook RTA, Inman AJ, Billings C (1997) Identification and classification of powdery mildew anamorphs using light and scanning electron microscopy and host range data. — Mycological Research 101: 975–1002.
Cunningham JH, Takamatsu SA, Lawrie C, Pascoe IG (2003) Molecular identification of anamorphic powdery mildews (Erysiphales). — Australasian Plant Pathology 32: 421–428.
Davy AJ, Bishop GF (1991) Triglochin maritima L. (Triglochin maritimum L.). — Journal of Ecology 79: 531–555.
Farr DF, Billis GF, Chamuris GP, Rossman AY (1989) Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. APS Press. St. Paul, Minnesota, USA.
Farr DF, Rossman AY, Palm ME, & Mccray EB (2004) Fungal Databases, Systematic Botany & Mycology Laboratory, ARS, USDA. (http://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/)
Fogel BN, Crain CM, Bertness MD (2004) Community level engineering effects of Triglochin maritima (seaside arrowgrass) in a salt marsh in northern New England, USA. — Journal of Ecology 92: 589–597.
Forster RL (1989) Powdery mildew of greenhouse cucumbers and tomatoes caused by Leveillula taurica in Idaho. — Plant Disease 73: 1020
Glawe DA, Du Toit LJ, Pelter GQ (2004) First report of powdery mildew on potato caused by Leveillula taurica in North America. Online. Plant Health Progress doi:10.1094/PHP-2004-1214-01-HN.
Khodaparast SA, Takamatsu S, Hedjaroude G-A (2001) Phylogenetic structure of the genus Leveillula (Erysiphales: Erysiphaceae) inferred from the nucleotide sequences of the rDNA ITS region with special reference to the L. taurica species complex. — Mycological Research 105: 909–918.
Looman J (1976) Biological flora of the Canadian prairie provinces. Part 4. Triglochin, the genus. — Canadian Journal of Plant Science 56: 725–732.
Du Toit LJ, Glawe DA, Pelter GQ (2004) First report of powdery mildew of onion (Allium cepa) caused by Leveillula taurica in the Pacific Northwest. Online. Plant Health Progress doi: 10.1094/PHP-2004-1129-01-HN.
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, and White TJ (eds) PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. pp. 315–322. Academic Press, Inc., New York.
Whitson TD (ed.) (1991) Weeds of the West. Western Society of Weed Science, Western U.S. Land Grant Universities Cooperative Extension Services, and University of Wyoming, Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glawe, D.A., Dugan, F.M., Liu, Y. et al. First record and characterization of a powdery mildew on a member of the Juncaginaceae: Leveillula taurica on Triglochin maritima . Mycol Progress 4, 291–298 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0133-5
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0133-5