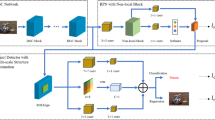
Abstract
Recently, significant improvements have been achieved for object detection algorithm by increasing the size of convolutional neural network (CNN) models, but the resulting increase of computational complexity poses an obstacle to practical applications. And some of the lightweight methods fail to consider the characteristics of object detection into and suffer a huge loss of accuracy. In this paper, we design a multi-scale feature lightweight network structure and specific convolution module for object detection based on depthwise separable convolution, which not only reduces the computational complexity but also improves the accuracy by using the specific position information in object detection. Furthermore, in order to improve the detection accuracy for small objects, we construct a multi-channel position-aware map and propose training based on knowledge distillation for object detection to train the lightweight model effectively. Last, we propose a training strategy based on a key-layer guiding structure to balance performance with training time. The experimental results show that on the COCO dataset that takes the state-of-the-art object detection algorithm, YOLOv3, as the baseline, our model size is compressed to 1/11 while accuracy drops by 7.4 mmAP, and the computational latency on the GPU and ARM platforms are reduced to 43.7% and 0.29%, respectively. Compared with the state-of-the-art lightweight object detection model, MNet V2 + SSDLite, the accuracy of our model increases by 3.5 mmAP while the inferencing time stays nearly the same. On the PASCAL VOC2007 dataset, the accuracy of our model increases by 5.2 mAP compared to the state-of-the-art lightweight algorithm based on knowledge distillation. Therefore, in terms of accuracy, parameter count, and real-time performance, our algorithm has better performance than lightweight algorithms based on knowledge distillation or depthwise separable convolution.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szegedy, C., Alexander, T., Dumitru, E.: Deep neural networks for object detection. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1, 2553–2561 (2013)
Lecun, Y., Yoshua, B., Geoffrey, E.: Hinton.: deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1, 91–99 (2015)
Redmon, J., Farhadi,A.: YOLOv3: an incremental improvement. arXiv: Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit (2018)
Smolyanskiy, N., Kamenev,A., Smith. J.M.: Toward low-flying autonomous MAV trail navigation using deep neural networks for environmental awareness. Robotics (2017)
Kim, Y.M., Park, E., Yoo, S.: Compression of deep convolutional neural networks for fast and low power mobile applications. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2015)
Guo, Y.: A survey on methods and theories of quantized neural networks. Learning (2018).
Han, S., Mao, H., Dally, W, J.: Deep compression: compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and Huffman coding. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2015)
Golub, G.H., Reinsch, C.: Singular value decomposition and least squares solutions. Num. Math. 14(5), 403–420 (1970)
Howard, A., Zhu, M., Chen, B.: MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2017)
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M.: ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2017)
Iandola, F., Han, S., Moskewicz, M.W.: SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2017)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1, 6517–6525 (2017)
Hinton, G.E., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. Mach. Learn. (2015).
Romero, A., Ballas, N., Kahou, S.E.: FitNets: hints for thin deep nets. Learning (2014)
Chen, G., Choi, W., Yu, X.: Learning efficient object detection models with knowledge distillation. Neural Inf. Process. Systems 1, 742–751 (2017)
Mehta, R., Ozturk, C.: Object detection at 200 frames per second. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2018)
Wang, T., Yuan, L., Zhang, X.: Distilling object detectors with fine-grained feature imitation. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1, 4933–4942 (2019)
Chen, C., Liu, M., Tuzel, O., Xiao, J.: R-CNN for small object detection. Asian Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 214–230 (2016)
Guo, Z., Zhang, W., Liang, Z., Shi, Y., Huang, Q.: Multi-scale object detection using feature fusion recalibration network. IEEE Access 8, 51664–51673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980737
Huval, B., Coates, A., Ng, A, Y.: Deep learning for class-generic object detection. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit (2013)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollar, A.: Mask R-CNN. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 2980–2988 (2017)
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 1440–1448 (2015)
Li, Z., Peng, C., Yu, G.: Light-head R-CNN: in defense of two-stage object detector. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit (2017).
Sermanet, P., Eigen, D., Zhang, X.: OverFeat: integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2013).
Redmon, J., Divvala, S.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1, 779–788 (2016)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D.: SSD: single shot multibox detector. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 21–37 (2016)
Denil, M., Shakibi, B., Dinh, L.: Predicting parameters in deep learning. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1, 2148–2156 (2013)
Cheng, Y., Wang, D., Zhou, P.: A survey of model compression and acceleration for deep neural networks. Learning (2017)
Srinivas, S., Subramanya, A., Babu, R.V.: Training sparse neural networks. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1, 455–462 (2017)
Jia, H., Xiang, X., Fan, D.: DropPruning for model compression. Learning (2018)
Li, H., Kadav, A., Durdanovic, I.: Pruning filters for efficient convnets. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2016)
He, Y., Zhang, X., Sun, J.: Channel pruning for accelerating very deep neural networks. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 1398–1406 (2017)
Zhuang, Z., Tan, M., Zhuang, B.: Discrimination-aware channel pruning for deep neural networks. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1, 883–894 (2018)
He, Y., Lin, J., Liu, Z.: AMC: AutoML for model compression and acceleration on mobile devices. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 815–832 (2018)
Gupta, S., Agrawal, A., Gopalakrishnan, K.: Deep learning with limited numerical precision. Learning (2015)
Xu, Y., Zhang, S., Qi, Y.: DNQ: dynamic network quantization. Learning (2018)
Jaderberg, M., Vedaldi, A., Zisserman, A.: Speeding up Convolutional neural networks with low rank expansions. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2014)
Lin, M., Chen, Q., Yan, S.: Network in network. Neural Evolut. Comput. (2013)
Ma, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, H.: ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1, 122–138 (2018)
Wong, A., Famouri, M., Shafiee, M.J.: YOLO nano: a highly compact you only look once convolutional neural network for object detection. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2019)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M.: MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 4510–4520 (2018)
Tan, M., Pang, R. Le, Q.V.: EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection[C]. In 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 2020, pp. 10778–10787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01079.
Ba, L.J., Caruana, R.: Do deep nets really need to be deep. Learning (2013)
Zeiler, M.D., Krishnan, D., Taylor, G.W.: Deconvolutional networks. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit (2010)
Everingham, M., Eslami, S.M., Van Gool, L.: The pascal visual object classes challenge: a retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 111(1), 98–136 (2015)
Lin, T., Maire, M., Belongie, S.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. european conference on computer vision, 2014: 740–755.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 115(3), 211–252 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Zhang, S., Du, H. et al. Position-aware lightweight object detectors with depthwise separable convolutions. J Real-Time Image Proc 18, 857–871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-01027-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-01027-1