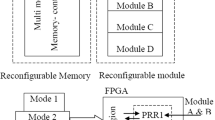
Abstract
Fine grained reconfigurable architectures, like Xilinx field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) provide a high flexibility through runtime re-programming, called dynamic and partial reconfiguration. This feature allows for runtime adaptation of the system architecture and behavior configured on the FPGA. The exploitation of this feature enables to load video image processing algorithms on-demand in order to adapt the configuration in correspondence to the changing requirements of the application depending on the image content. For high resolution sensor images, this novel computing paradigm can provide a huge benefit in power reduction and performance gain for actual and future embedded electronic systems. This paper presents a two dimensional system approach exploiting dynamic and partial reconfiguration in order to adapt the system architecture to the actual requirements of image processing applications. The methodology of runtime reconfiguration can be exploited beneficially for highly adaptive multiprocessor systems. Such systems, different from the traditional static approach for multi- and many-core architectures have the advantage, for providing computational performance directly linked to the requirements of the application. The architecture presented in this paper allows for adapting the processing elements as well as the communication infrastructure which is a novel 2D switch-based Network-on-Chip. The presented approach follows and extends the actual trend in computer science of using many- and multi-core processors for bridging the gap between required computation performance for future application in the field of image processing.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpha-Data.: http://www.alpha-data.com
Batcher, K.: Sorting networks and their applications. In: AFIPS spring joint computing conference, pp. 307–314 (1968)
Benini, L., De Micheli, G.: Networks on chip: a new paradigm for systems on chip design. In: Proc. design, automation and test in Europe conference and exhibition, pp. 418–419 (2002)
Becker, J., Huebner, M., Paulsson, K., Thomas, A.: Dynamic reconfiguration on-demand: real-time adaptivity in next generation microelectronics. In: ReCoSoC, pp. 35–42. University of Montpellier II (2005)
Becker, J., Thomas, A. Scalable processor instruction set extension. IEEE. Des. Test. Comput. 22(2),136–148 (2005)
Cray Inc. USA: Cray xd1, datasheet. http://www.cray.com
Fujitsu Limited.: Sparc t1000. http://www.fujitsu.com/downloads/SPARCE/brochures/sparc-enterprise- t1000.pdf
Gaisler, J.: The leon processor user’s manual. http://www.gaisler.com
Goehringer, D., Huebner, M., Schatz, V., Becker, J.: Runtime adaptive multi-processor system-on-chip: Rampsoc. In: Proceedings of IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium IPDPS 2008, Miami, FL, USA, 14–18 April 2008
Goehringer, D., Majer, M., Teich, J.: Bridging the gap between relocatability and available technology: the erlangen slot machine. In: Dynamically reconfigurable architectures, number 06141 in Dagstuhl seminar proceedings, Dagstuhl, Germany, 02–07 April 2006
Hartenstein, R. Why we need reconfigurable computing education. RC-Education Workshop, Karlsruhe, Germany (2006)
Huebner, M., Becker, T., Becker, J.: Real-time lut-based network topologies for dynamic and partial fpga self-reconfiguration. In: Proceedings of 17th symposium on integrated circuits and systems design SBCCI 2004, pp. 28–32, 7–11 September 2004
Huebner, M., Braun, L., Becker, J., Claus, C., Stechele, W.: Physical configuration on-line visualization of xilinx virtex-ii fpgas. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society annual symposium on VLSI ISVLSI 2007, pp. 41–46, 9–11 March (2007)
Huerta, P., Castillo, J., Martfnez, J.I., Lopez, V.: A microblaze based multiprocessor soc. In: WSEAS transactions on circuits and systems (2005)
Huebner, M., Schuck, C., Becker, J.: Elementary block based 2-dimensional dynamic and partial reconfiguration for virtex-ii fpgas. In: Proceedings of 20th international parallel and distributed processing symposium IPDPS 2006, p. 8, 25–29 April (2006)
Jaehne, B.: Digitale Bildverarbeitung. Springer, Berlin [u.a.] (1989)
Jantsch, A., Tenhunen, H.: Networks on chip. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Hingham, MA (2003)
Kumar, S., Jantsch, A., Soininen, J.-P., Forsell, M., Millberg, M., Oberg J., Tiensyrja K., Hemani A.: A network on chip architecture and design methodology. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society annual symposium on VLSI, pp. 105–112, 25–26 April (2002)
Knuth, D., E.: The Art of Computer Programming, Sorting and Searching, vol 3, 2nd edn, Addison Wesley Longman Publishing Co. Inc., Redwood City, CA (1998)
Lysaght, P., Blodget, B., Mason, J., Young, J., Bridgford, B.: Invited paper: enhanced architectures, design methodologies and cad tools for dynamic reconfiguration of xilinx fpgas. In: Proceedings of international conference on field programmable logic and application FPL 2006, pp. 1–6, Madrid, Spain, 28–30 August (2006)
Layer, C., Pfleiderer, H.-J.: A reconfigurable recurrent bitonic sorting network for concurrently accessible data. In: FPL, pp. 648–657 (2004)
Michaelsen, E., Middelmann, W., Soergel, U.: Cognitive vision and perceptual grouping by production systems with blackboard control, an example for high-resolution sar-images. In: VISAPP 2006 (2006)
Michaelsen, E., Stilla, U.: Estimating urban activity on high-resolution thermal image sequences aided by large scale vector maps. In: Proceedings of remote sensing and data fusion over urban areas IEEE/ISPRS joint workshop 2001, pp. 25–29, 8–9 Novomber (2001)
Pham, D., Asano, S., Bolliger, M., Day, M.N., Hofstee, H.P., Johns, C., Kahle, J., Kameyama, A., Keaty, J., Masubuchi, Y., Riley, M., Shippy, D., Stasiak, D., Suzuoki, M., Wang, M., Warnock, J., Weitzel, S., Wendel, D., Yamazaki, T., Yazawa, K.: The design and implementation of a first-generation cell processor. In: Proceedings digest of technical papers solid-state circuits conference ISSCC 2005 IEEE International , pp. 184–592, 10–10 February (2005)
Paulsson, K., Huebner, M., Zou, J., H.and Becker.: Realization of real-time control flow oriented automotive applications on a soft-core multiprocessor system based on xilinx virtex ii fpgas. In: ARC05, Portugal (2005)
Stechele, W.: Dynamically reconfigurable systems-on-chip for video-based driver assistance. In: Dagstuhl seminar proceedings 06141 on dynamically reconfigurable architectures. (2006)
Inc. The MathWorks. Matlab compiler. http://www.mathworks.com
The MathWorks Inc.: Matlab/simulink hdl coder userguide. http://www.mathworks.com
Ullmann, M., Huebner, M., Grimm, B., and Becker, J.: An fpga run-time system for dynamical on-demand reconfiguration. In: Proceedings of 18th international parallel and distributed processing symposium, pp. 135– (2004)
Worm, F., Ienne, P., Thiran, P., de Micheli G.: An adaptive low-power transmission scheme for on-chip networks. In: Proceedings of 15th international symposium on system synthesis, pp. 92–100 (2002)
Wolf, W.: The future of multiprocessor systems-on-chips. In: Proceedings of 41st design automation conference, pp. 681–685 (2004)
Xilinx:. Difference-based partial reconfiguration (xapp290). http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Xilinx microblaze reference guide. http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Xilinx picoblaze userguide (ug129). http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Xilinx systemgenerator userguide. http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Xilinx virtex-4 configuration guide. http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Xilinx virtex-5 configuration guide (ug191). http://www.xilinx.com
Xilinx:. Acceldsp synthesis tool user guide (release 9.2.00). http://www.xilinx.com (2007). Accessed August 2007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, L., Göhringer, D., Perschke, T. et al. Adaptive real-time image processing exploiting two dimensional reconfigurable architecture. J Real-Time Image Proc 4, 109–125 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-008-0095-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-008-0095-8