Abstract
Background
Tendon without paratenon presents the reconstructive surgeon with a tissue coverage challenge. Integra® dermal regenerative template has been shown to initiate a stable, vascularized bed for skin grafting over tendon. However, histological processes that occur during incorporation have not been described. The purpose of this study is to characterize the pattern of changes that occur when Integra® is applied to an avascular tendon. We hypothesize that vascular incorporation will originate from the wound periphery and proceed toward the tendon center.
Methods
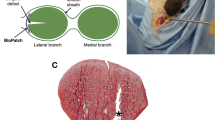
A full-thickness defect was created over a denuded Achilles tendon in a single hind limb in eight New Zealand white rabbits. Integra was placed over the avascular tendon, and the limb was dressed and splinted. Two animals were euthanized at each timepoint (weeks 1, 2, 3, and 4), and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained tissue specimens were microscopically evaluated.
Results
Week 1 specimens demonstrated limited adherence between Integra and the tendon, while myofibroblasts were found encircling the tendon. No cellularity was noted centrally. At week 2, the dermis–Integra junction had increasing vascularity and the central portion developed increasing cellularity. By week 3, Integra was completely revascularized. At week 4, Integra had the histological appearance of normal dermis.
Conclusion
Neovascularization of Integra® over exposed tendon occurs from the peripheral tissue. Ingrowth proceeds from the dermis–Integra interface toward the center of the graft. Four weeks after application to the denuded tendon, Integra has the histological appearance of native dermis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke JF, Yannas IV, Quinby WC, Bondoc CC, Jung WK. Successful use of physiologically acceptable artificial skin in the treatment of extensive burn injury. Ann Surg. 1981;194:413–28.
Chan ES, Lam PK, Liew CT, Lau HC, Yen RS, King WW. A new technique to resurface wounds with composite biocompatible epidermal graft and artificial skin. J Trauma. 2001;50:358–62.
Gottlieb ME. Management of complex and pathological wounds with Integra. In: Lee BY, editor. The wound management manual. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2004. p. 226–89.
Graham PG, Helmer SD, Haan JM, et al. The use of Integra dermal regeneration template in the reconstruction of traumatic degloving injuries. J Burn Care Res. 2013;34:261–6.
Heimbach D, Luterman A, Burke J, et al. Artificial dermis for major burns. A multicenter randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 1988;208:313–20.
Helgeson MD, Potter BK, Evans KN, et al. Bioartificial dermal substitute: a preliminary report on its use for the management of complex combat-related soft tissue wounds. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21:394–9.
Hunt JA, Moisidis E, Haertsch P. Initial experience of Integra in the treatment of post-burn anterior cervical neck contracture. Br J Plast Surg. 2000;53:652–8.
Jeng JC, Fidler PE, Sokolich JC, et al. Seven years’ experience with Integra as a reconstructive tool. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:120–6.
Lee LF, Porch JV, Spenler W, Garner WL. Integra in lower extremity reconstruction after burn injury. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121:1256–62.
Lorenz C, Petracic A, Hohl HP, Wessel L, Waag KL. Early wound closure and early reconstruction. Experience with a dermal substitute in a child with 60 percent surface area burn. Burns. 1997;23:505–8.
Loss M, Wedler V, Kunzi W, Meuli-Simmen C, Meyer VE. Artificial skin, split-thickness autograft and cultured autologous keratinocytes combined to treat a severe burn injury of 93% of TBSA. Burns. 2000;26:644–52.
Moiemen NS, Staiano JJ, Ojeh NO, Thway Y, Frame JD. Reconstructive surgery with a dermal regeneration template: clinical and histologic study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;108:93–103.
Repta R, Ford R, Hoberman L, Rechner B. The use of negative-pressure therapy and skin grafting in the treatment of soft-tissue defects over the Achilles tendon. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;55:367–70.
Shores JT, Hiersche M, Gabriel A, et al. Tendon coverage using artificial skin substitute. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1544–50.
Stern R, McPherson M, Longaker MT. Histologic study of artificial skin used in the treatment of full-thickness thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1990;11:7–13.
Tompkins RG, Hilton JF, Burke JF, et al. Increased survival after massive thermal injuries in adults: preliminary report using artificial skin. Crit Care Med. 1989;17:734–40.
Weigert R, Choughri H, Casoli V. Management of severe hand wounds with Integra dermal regeneration template. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011;36:185–93.
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided by the Memorial Medical Center Foundation, Springfield, IL.
Conflict of Interest
John Hulsen declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ryan Diederich declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Michael W. Neumeister declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Reuben A. Bueno, Jr. declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Statement of Animal Rights
The authors, JH, RD, MN, RB, Jr., certify that all institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hulsen, J., Diederich, R., Neumeister, M.W. et al. Integra® dermal regenerative template application on exposed tendon. HAND 9, 539–542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-014-9630-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-014-9630-1