Abstract
Purpose
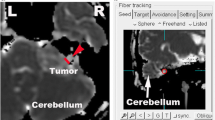
Diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) is not adequately reliable for prediction of facial and vestibulocochlear (VII–VIII) nerve locations, especially relative to a vestibular schwannoma (VS). Furthermore, it is often not possible to visualize normal VII–VIII nerves by DTT (visualization rates were 12.5–63.6 %). Therefore, DTT post-processing was optimized for normal VII–VIII nerve visualization with and without manual noise elimination.
Methods
DTT examinations of ten patients were evaluated to assess the improvement in performance by modifying seed region of interest (ROI) and fractional anisotropy (FA) threshold. Seed ROI was placed at the porus of the internal auditory meatus, and FA threshold values were either fixed or variable for each patient. DTT visualization of cranial nerves VII–VIII was evaluated and the noise effect was measured.
Results
Cranial nerves VII–VIII were visualized in 90 % of patients without using manual noise elimination by modifying the seed ROI and FA threshold. The visualization rate with FA threshold of the upper limit in each patient (100 %) was significantly higher than that with FA threshold of 0.1 (75 %) (\(p=0.02\)). The incidence rate of noise with FA threshold of the upper limit (10 %) was not significantly different than the FA threshold of 0.1 (20 %) (\(p=0.66\)).
Conclusion
Seed ROI modification and FA thresholding can improve the visualization of cranial nerve VII–VIII locations in DTT. This technique is promising for its potential to determine the relationship of cranial nerves VII–VIII to VS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC (1999) Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45(2):265–269
Mori S, van Zijl PC (2002) Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):468–480. doi:10.1002/nbm.781
Masutani Y, Aoki S, Abe O, Hayashi N, Otomo K (2003) MR diffusion tensor imaging: recent advance and new techniques for diffusion tensor visualization. Eur J Radiol 46(1):53–66
Kunimatsu A, Aoki S, Masutani Y, Abe O, Hayashi N, Mori H, Masumoto T, Ohtomo K (2004) The optimal trackability threshold of fractional anisotropy for diffusion tensor tractography of the corticospinal tract. Magn Reson Med Sci 3(1):11–17
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81(2):106–116. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.08.004
Mukherjee P, Chung SW, Berman JI, Hess CP, Henry RG (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: technical considerations. Am J Neuroradiol 29(5):843–852. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1052
Akazawa K, Yamada K, Matsushima S, Goto M, Yuen S, Nishimura T (2010) Optimum b value for resolving crossing fibers: a study with standard clinical b value using 1.5-T MR. Neuroradiology 52(8):723–728. doi:10.1007/s00234-010-0670-0
Byrnes TJ, Barrick TR, Bell BA, Clark CA (2009) Semiautomatic tractography: motor pathway segmentation in patients with intracranial vascular malformations. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 111(1):132–140. doi:10.3171/2009.2.JNS08930
Lori NF, Akbudak E, Shimony JS, Cull TS, Snyder AZ, Guillory RK, Conturo TE (2002) Diffusion tensor fiber tracking of human brain connectivity: acquisition methods, reliability analysis and biological results. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):494–515. doi:10.1002/nbm.779
Tournier JD, Calamante F, King MD, Gadian DG, Connelly A (2002) Limitations and requirements of diffusion tensor fiber tracking: an assessment using simulations. Magn Reson Med 47(4):701–708
Clark CA, Barrick TR, Murphy MM, Bell BA (2003) White matter fiber tracking in patients with space-occupying lesions of the brain: a new technique for neurosurgical planning? Neuroimage 20(3):1601–1608
Jones DK (2004) The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn Reson Med 51(4):807–815. doi:10.1002/mrm.20033
Kamada K, Todo T, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Ino K, Takano T, Kirino T, Kawahara N, Morita A (2005) Combined use of tractography-integrated functional neuronavigation and direct fiber stimulation. J Neurosurg 102(4):664–672
Kamada K, Todo T, Morita A, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Ino K, Kawai K, Kirino T (2005) Functional monitoring for visual pathway using real-time visual evoked potentials and optic-radiation tractography. Neurosurgery 57(1):121
Okada T, Miki Y, Fushimi Y, Hanakawa T, Kanagaki M, Yamamoto A, Urayama S, Fukuyama H, Hiraoka M, Togashi K (2006) Diffusion-tensor fiber tractography: intraindividual comparison of 3.0-T and 1.5-T MR imaging1. Radiology 238(2):668–678
Nucifora PGP, Verma R, Lee SK, Melhem ER (2007) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and tractography: exploring brain microstructure and connectivity1. Radiology 245(2):367–384
Stadlbauer A, Nimsky C, Buslei R, Salomonowitz E, Hammen T, Buchfelder M, Moser E, Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging and optimized fiber tracking in glioma patients: histopathologic evaluation of tumor-invaded white matter structures. Neuroimage 34(3):949–956. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.051
Taoka T, Hirabayashi H, Nakagawa H, Sakamoto M, Myochin K, Hirohashi S, Iwasaki S, Sakaki T, Kichikawa K (2006) Displacement of the facial nerve course by vestibular schwannoma: preoperative visualization using diffusion tensor tractography. J Magn Reson Imaging 24(5):1005–1010. doi:10.1002/jmri.20725
Kabasawa H, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Abe O, Masumoto T, Hayashi N, Ohtomo K (2007) 3T PROPELLER diffusion tensor fiber tractography: a feasibility study for cranial nerve fiber tracking. Radiat Med 25(9):462–466. doi:10.1007/s11604-007-0169-8
Andreisek G, White LM, Kassner A, Tomlinson G, Sussman MS (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography of the median nerve at 1.5T: optimization of b value. Skeletal Radiol 38(1):51–59. doi:10.1007/s00256-008-0577-6
Hodaie M, Quan J, Chen DQ (2010) In vivo visualization of cranial nerve pathways in humans using diffusion-based tractography. Neurosurgery 66(4):788–795. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000367613.09324.DA discussion 795–786
Hodaie M, Chen DQ, Quan J, Laperriere N (2012) Tractography delineates microstructural changes in the trigeminal nerve after focal radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. PLoS One 7(3):e32745. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032745
Cauley KA, Filippi CG (2013) Diffusion-tensor imaging of small nerve bundles: cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, distal spinal cord, and lumbar nerve roots-clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201(2):W326–335. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9230
Chen DQ, Quan J, Guha A, Tymianski M, Mikulis D, Hodaie M (2011) Three-dimensional in vivo modeling of vestibular schwannomas and surrounding cranial nerves with diffusion imaging tractography. Neurosurgery 68(4):1077–1083. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31820c6cbe
Gerganov VM, Giordano M, Samii M, Samii A (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging-based fiber tracking for prediction of the position of the facial nerve in relation to large vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg 115(6):1087–1093. doi:10.3171/2011.7.JNS11495
Roundy N, Delashaw JB, Cetas JS (2012) Preoperative identification of the facial nerve in patients with large cerebellopontine angle tumors using high-density diffusion tensor imaging: Clinical article. J Neurosurg 116(4):697–702
Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark C, Le Bihan D, Bloch I (2002) Distortion correction and robust tensor estimation for MR diffusion imaging. Med Image Anal 6(3):191–198
Rhoton AL Jr (2000) The cerebellopontine angle and posterior fossa cranial nerves by the retrosigmoid approach. Neurosurgery 47(3 Suppl):S93–129
Silverstein H (1984) Cochlear and vestibular gross and histologic anatomy (as seen from postauricular approach). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 92(2):207–211
Ozdogmus O, Sezen O, Kubilay U, Saka E, Duman U, San T, Cavdar S (2004) Connections between the facial, vestibular and cochlear nerve bundles within the internal auditory canal. J Anat 205(1):65–75. doi:10.1111/j.0021-8782.2004.00313.x
Yamakami I, Uchino Y, Kobayashi E, Yamaura A (2003) Computed tomography evaluation of air cells in the petrous bone-relationship with postoperative cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43(7):334–338 discussion 339
Yoshino M, Kin T, Saito T, Nakagawa D, Nakatomi H, Kunimatsu A, Oyama H, Saito N (2013) Optimal setting of image bounding box can improve registration accuracy of diffusion tensor tractography. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. doi:10.1007/s11548-013-0934-3
Fujiwara S, Sasaki M, Wada T, Kudo K, Hirooka R, Ishigaki D, Nishikawa Y, Ono A, Yamaguchi M, Ogasawara K (2011) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging for the detection of diffusion abnormalities in the trigeminal nerves of patients with trigeminal neuralgia caused by neurovascular compression. J Neuroimaging 21(2):e102–108. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00508.x
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Minoru Tanaka for suggesting this investigation. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (25670618).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study as well as the findings specified in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshino, M., Kin, T., Ito, A. et al. Diffusion tensor tractography of normal facial and vestibulocochlear nerves. Int J CARS 10, 383–392 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1129-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1129-2