Abstract
Objective
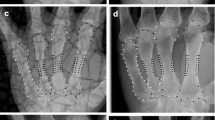
Digital X-ray radiogrammetry (DXR) is a computer-assisted technique used to quantify cortical bone density of the metacarpals. The influence of metacarpal bone rotation and type of cast material on bone mineral density (BMD) measurements using the DXR technique was tested.
Methods
The bone mineral density of the hand was measured by DXR, and rotation error (DXR–RE) as coefficients of variation were calculated, to verify reliability and reproducibility of this radiogeometric technique to assess in particular minor disease-related changes in the metacarpal bone mass. The reproducibility of the DXR measurements was also investigated using different cast materials (mull, elastic, and plastic).
Results
There were no significant changes in absolute values of DXR–BMD observed between 0 to \(19^\circ \) angulation. The relative DXR–RE ranged between 0 % (degree 1) and 0.70 % (degrees 15 and 19) for DXR–BMD. Regarding the different cast materials, DXR–BMD revealed a coefficient of variation with 0.41 % (mull cast) and 0.21 % (elastic cast). For the plastic cast, the DXR technique was not able to perform an analysis of DXR–BMD.
Conclusion
The study revealed no significant influence of metacarpal rotation on the measurements of metacarpal bone mineral density as estimated by DXR. DXR measurements are not optimal when cast material is used. DXR can accurately quantify periarticular cortical bone mass. This is significant especially for rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions where X-ray imaging of arthritic hands with varying degrees of deformity is performed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density (g/cm\(^{2}\))
- CAD:
-
Computer-assisted detection
- CT:
-
Cortical thickness (cm)
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation in %
- DXR:
-
Digital X-ray radiogrammetry
- MCI:
-
Metacarpal index
- RE:
-
Rotation error
- W:
-
Metacarpal bone width (cm)
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
References
Haugeberg G, Green MJ, Quinn MA, Marzo-Ortega H, Proudman S, Karim Z, Wakefield RJ, Conaghan PG, Stewart S, Emery P (2006) Hand bone loss in early undifferentiated arthritis: evaluating bone mineral density loss before the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:736–740
Hoff M, Haugeberg G, Ødegård S, Syversen S, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Kvien TK (2009) Cortical hand bone loss after 1 year in early rheumatoid arthritis predicts radiographic hand joint damage at 5-year and 10-year follow-up. Ann Rheum Dis 68:324–329
Hoff M, Bøyesen P, Haugeberg G, Vis M, Woolf AD, Havaardsholm EA, Dijkmans BA, Kvien TK, Uhlig T, Lems WF (2010) High disease activity is a predictor of cortical hand bone loss in post-menopausal patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: a 5-year multicentre longitudinal study. Rheumatology 49:1676–1682
Pfeil A, Haugeberg G, Hansch A, Renz DM, Lehmann G, Malich A, Wolf G, Böttcher J (2011) The value of digital X-ray radiogrammetry in the assessment of inflammatory bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:666–6674
Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Mentzel HJ, Kramer A, Schäfer ML, Lehmann G, Eidner T, Petrovitch A, Malich A, Hein G, Kaiser WA (2006) Peripheral bone status in rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by digital X-ray radiogrammetry (DXR) and compared with multi-site quantitative ultrasound (QUS). Calcif Tissu Int 78:25–34
Böttcher J, Malich A, Pfeil A, Petrovitch A, Lehmann G, Heyne JP, Hein G, Kaiser WA (2004) Potential clinical relevance of digital radiogrammetry for quantification of periarticular bone demineralization in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis depending on severity and compared with DXA. Eur Radiol 14:631–637
Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Rosholm A, Petrovitch A, Seidl BE, Malich A, Kramer A, Lehmann G, Hein G, Kaiser WA (2005) Digital X-ray radiogrammetry combined with semi-automated analysis of joint space distances as a new diagnostic approach in rheumatoid arthritis—a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheum 52:3850–3859
Forslind K, Kälvesten J, Hafström I, Svensson B, for the BARFOT Study Group (2012) Does digital X-ray radiogrammetry have a role in identifying patients at increased risk for joint destruction in early rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res Ther 14(5):R219
Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Rosholm A, Malich A, Petrovitch A, Heinrich B, Lehmann G, Mentzel HJ, Hein G, Linß W, Kaiser WA (2005) Influence of image-capturing parameters on digital X-ray radiogrammetry. J Clin Densitom 8:87–94
Hoff M, Dhainaut A, Kvien TK, Forslind K, Kälvesten J, Haugeberg G (2009) Short-time in vitro and in vivo precision of direct digital X-ray radiogrammetry. J Clin Densitom 12:17–21
Dhainaut A, Hoff M, Kälvesten J, Lydersen S, Forslind K, Haugeberg G (2011) Long-term in-vitro precision of direct digital X-ray radiogrammetry. Skeletal Radiol 40:1575–1579
Schäfer ML, Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Hansch A, Malich A, Maurer MH, Streitparth F, Röttgen R, Renz DM (2012) Comparison between amputation-induced demineralization and age-related bone loss using digital X-ray radiogrammetry. J Clin Densitom 15:135–145
Hyldstrup L, Nielsen SP (2001) Metacarpal index by digital X-ray radiogrammetry: normative reference values and comparison with dual X-ray absorptiometry. J Clin Densitom 4:299–306
Jorgensen JT, Andersen PB, Rosholm A, Bjarnason NH (2000) Digital X-ray radiogrammetry: a new appendicular bone densitometric method with high precision. Clin Physiol 20:330–335
Rosholm A, Hyldstrup L, Baeksgaard L, Grunkin M, Thodberg HH (2001) Estimation of bone mineral density by digital X-ray radiogrammetry: theoretical background and clinical testing. Osteoporos Int 12:961–969
Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Rosholm A et al (2006) Computerized digital imaging techniques provided by digital X-ray radiogrammetry as new diagnostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. J Digit Imaging 19:279–288
Kälvesten J, Brismar TB, Persson A (2014) Potential sources of quantification error when retrospectively assessing metacarpal bone loss from historical radiographs by using digital X-ray radiogrammetry: an experimental study. J Clin Densitom 17(1):104–108
Aeberli D, Eser P, Bonel H, Widmer J, Caliezi G, Varisco PA, Möller B, Villiger PM (2010) Reduced trabecular bone mineral density and cortical thickness accompanied by increased outer bone circumference in metacarpal bone of rheumatoid arthritis patients: a cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R119
Jawaid WB, Crosbie D, Shotton J, Reid DM, Stewart A (2006) Use of digital x-ray radiogrammetry in the assessment of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:459–464
Haugeberg G, Lodder MC, Lems WF, Uhlig T, Ørstavik RE, Dijkmans BAC, Kvien T, Woolf AD (2004) Hand cortical bone mass and its associations with radiographic joint damage and fractures in 50–70 year old female patients with rheumatoid arthritis: cross sectional Oslo-Truro-Amsterdam (OSTRA) collaborative study. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1331–1334
Rau R, Lingg G, Wassenberg S, Schorn C, Scherer A (2005) Imaging techniques in rheumatology: conventional radiography in rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol 64:473–487
Pfeil A, Oelzner P, Renz DM, Lehmann G, Wolf G, Boettcher J (2014) Visualisation of structural damage as a surrogate marker of radiographic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(4):e24
Colt E, Kälvesten J, Cook K, Khramov N, Javed F (2010) The effect of fat on the measurement of bone mineral density by digital X-ray radiogrammetry (DXR-BMD). Int J Body Compos Res 8:41–44
Ono S, Entezami P, Chung KC (2011) Reconstruction of the rheumatoid hand. Clin Plast Surg 38:713–727
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Monika Arens (managing director, Arewus GmbH) and Jacob Algulin (managing director, Sectra, Sweden) for use of the digital X-ray radiogrammetry equipment. Also, many thanks to Günter Ditze (Forschungswerkstatt Friedrich—Schiller—University Jena) for the planning and construction of the phantom equipment and to Rüdiger Vollandt (PhD) for the statistical advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfeil, A., Renz, D.M., Fröber, R. et al. Influence of angulation on metacarpal bone mineral density measurements using digital X-ray radiogrammetry. Int J CARS 10, 587–592 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1076-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1076-y