Abstract
Background
Several experiences in the literature report SBRT as an effective treatment option for medically inoperable early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and oligometastatic disease. The optimal fractionation schedules and total dose remain controversial. In this study, we evaluated the safety in terms of toxicity and efficacy of using of 8–10 fractions schedules with Helical Tomotherapy (HT) for primary and metastatic lung lesions.
Methods
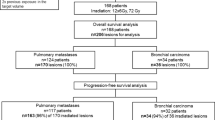
Between March 2014 and May 2016, a total of 39 patients (median age 72 years, range 26–91) were treated with HT-SBRT for malignant lung lesions: 22 patients with early stage NSCLC, 17 with oligometastases. Patients received 8–10 fractions with lower daily dose for central and ultracentral lesions. Treatment-related toxicity was evaluated using CTCAE v 4.0 scale. Local control (LC), overall survival (OS) and toxicity rates were prospectively collected.
Results
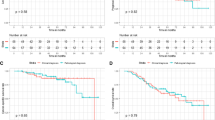
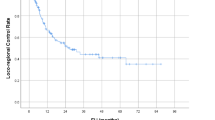
Median duration of RT was 15 days (range 10–26 days) and no interruption occurred. With a median follow-up of 13 months (range 3–29), we reported one G2 pneumonitis (2.6%) and one G2 chest pain (2.6%); no ≥ G2 esophagitis was registered. Actuarial local control rate was 95.5% both at 12 and 24 months for early stage NSCLC and 92.9% both at 12 and 24 months for metastatic patients. OS rate was 94.4 and 92.3% at 1 year, and 94.4 and 83.9% at 2 years in primary and metastatic group, respectively.
Conclusions
The use of 8–10 fractions schedule HT-SBRT for lung malignancies results in high LC and OS rates with minimal toxicities reported.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novello S, Barlesi F, Califano R, Cufer T, Ekman S, Levra MG, Kerr K, Popat S, Reck M, Senan S, Simo GV, Vansteenkiste J, Peters S, ESMO Guidelines Committee (2016) Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 27(suppl 5):v1–v27
Ricardi U, Frezza G, Filippi AR, Badellino S, Levis M, Navarria P, Salvi F, Marcenaro M, Trovò M, Guarneri A, Corvò R, Scorsetti M (2014) Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for stage I histologically proven non-small cell lung cancer: an Italian multicenter observational study. Lung Cancer 84(3):248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.02.015 (Epub 2014 Mar 13)
Palma D, Visser O, Lagerwaard FJ, Belderbos J, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2010) Impact of introducing stereotactic lung radiotherapy for elderly patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a population-based time-trend analysis. J Clin Oncol 28(35):5153–5159. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.0731 (Epub 2010 Nov 1)
Chang JY, Balter PA, Dong L, Yang Q, Liao Z, Jeter M, Bucci MK, McAleer MF, Mehran RJ, Roth JA, Komaki R (2008) Stereotactic body radiation therapy in centrally and superiorly located stage I or isolated recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72(4):967–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.001
Verstegen NE, Oosterhuis JWA, Palma DA, Rodrigues G, Lagerwaard FJ, van der Elst A, Mollema R, van Tets WF, Warner A, Joosten JJA, Amir MI, Haasbeek CJA, Smit EF, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2013) Stage I-II non-small-cell lung cancer treated using either stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) or lobectomy by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS): outcomes of a propensity score-matched analysis. Ann Oncol 24(6):1543–1548. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt026 (first published online February 20, 2013)
Palma DA, Senan S (2012) Early-stage non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients: should stereotactic radiation therapy be the standard of care? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84(5):1058–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.07.2353
Alongi F, Arcangeli S, Filippi AR, Ricardi U, Scorsetti M (2012) Review and uses of stereotactic body radiation therapy for oligometastases. Oncologist 17(8):1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0092 (Epub 2012 Jun 20; Review)
Guckenberger M, Andratschke N, Alheit H et al (2014) Definition of stereotactic body radiotherapy: Principles and practice for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 190(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-013-0450-y
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C, Papiez L, Tudor K, DeLuca J, Ewing M, Abdulrahman R, DesRosiers C, Williams M, Fletcher J (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(30):4833–4839
Li Q, Swanick CW, Allen PK, Gomez DR, Welsh JW, Liao Z, Balter PA, Chang JY (2014) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) using 70 Gy in 10 fractions for non-small cell lung cancer: exploration of clinical indications. Radiother Oncol 112(2):256–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2014.07.010
Bral S, Gevaert T, Linthout N, Versmessen H, Collen C, Engels B, Storme G (2011) Prospective, risk-adapted strategy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: results of a Phase II trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80(5):1343–1349
Mazzola R, Fiorentino A, Ricchetti F, Giaj Levra N, Fersino S, Di Paola G, Lo Casto A, Ruggieri R, Alongi F (2016) Cone-beam computed tomography in lung stereotactic ablative radiation therapy: predictive parameters of early response. Br J Radiol 20:20160146
Mazzola R, Fiorentino A, Di Paola G, Giaj Levra N, Ricchetti F, Fersino S, Tebano U, Pasetto S, Ruggieri R, Salgarello M, Alongi F (2017) Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for lung oligometastases: predictive Parameters of early response by (18)FDG-PET/CT. J Thorac Oncol 12(3):547–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2234
Louie AV, Senan S, Patel P, Ferket BS, Lagerwaard FJ, Rodrigues GB, Salama JK, Kelsey C, Palma DA, Hunink MG (2014) When is a biopsy-proven diagnosis necessary before stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for lung cancer? A decision analysis. Chest 146(4):1021–1028. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.13-2924
Marcenaro M, Vagge S, Belgioia L, Agnese D, Lamanna G, Mantero E, Gusinu M, Garelli S, Cavagnetto F, Agostinelli S, Corvò R (2013) Ablative or palliative stereotactic body radiotherapy with helical tomotherapy for primary or metastatic lung tumor. Anticancer Res 33(2):655–660
Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, Emery RS, Forster KM, Jiang SB, Kapatoes JM, Low DA, Murphy MJ, Murray BR, Ramsey CR, Van Herk MB, Vedam SS, Wong JW, Yorke E (2006) The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76a). Med Phys 33:3874–3900. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2349696
Chang HJ, Ko HL, Lee CY, Wu RH, Yeh YW, Jiang JS, Kao SJ, Chi K (2012) Hypofractionated radiotherapy for primary or secondary oligometastatic lung cancer using Tomotherapy. Radiat Oncol 27(7):222. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-7-222
Arcangeli S, Agolli L, Portalone L, Migliorino MR, Lopergolo MG, Monaco A et al (2015) Patterns of CT lung injury and toxicity after stereotactic radiotherapy delivered with helical tomotherapy in early stage medically inoperable NSCLC. Br J Radiol 88:20140728
Franks KN, Jain P, Snee MP (2015) Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 27(5):280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2015.01.006 (Epub 2015 Mar 4)
Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Tomatis S, Cozzi L, De Rose F, Mancosu P, Alongi F, Clerici E, Lobefalo F, Tozzi A, Reggiori G, Fogliata A, Scorsetti M (2014) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (sbrt) in lung oligometastatic patients: role of local treatments. Radiat Oncol 9(1):91. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-9-91
Moustakis C, Blanck O, Ebrahimi Tazehmahalleh F, Ka Heng Chan M, Ernst I, Krieger T, Duma MN, Oechsner M, Ganswindt U, Heinz C, Alheit H, Blank H, Nestle U, Wiehle R, Kornhuber C, Ostheimer C, Petersen C, Pollul G, Baus W, Altenstein G, Beckers E, Jurianz K, Sterzing F, Kretschmer M, Seegenschmiedt H, Maass T, Droege S, Wolf U, Schoeffler J, Haverkamp U, Eich HT, Guckenberger M (2017) Planning benchmark study for SBRT of early stage NSCLC : results of the DEGRO Working Group Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 193(10):780–790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-017-1151-8
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Wahl RL, Jacene H, Kasamon Y, Lodge MA (2009) From RECIST to PERCIST: evolving considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J Nucl Med 50(Suppl 1):122S–150S. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.108.057307 (Review)
Scorsetti M, Alongi F, Castiglioni S, Clivio A, Fogliata A, Lobefalo F, Mancosu P, Navarria P, Palumbo V, Pellegrini C, Pentimalli S (2011) Feasibility and early clinical assessment of flattening filter free (FFF) based stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) treatments. Radiation oncology 6(1):113
Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Mancosu P, Alongi F, Clerici E, Tozzi A, Iftode C, Reggiori G, Tomatis S, Infante M, Alloisio M (2013) Volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free (FFF) beams for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with medically inoperable early stage non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Radiother Oncol 107(3):414–418
Lischalk JW, Woo SM, Kataria S, Aghdam N, Paydar I, Repka MC, Anderson ED, Collins BT (2016) Long-term outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) with fiducial tracking for inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Radiat Oncol 5:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-016-0273-4
De Bari B, Filippi AR, Mazzola R, Bonomo P, Trovò M, Livi L, Alongi F (2015) Available evidence on re-irradiation with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy following high-dose previous thoracic radiotherapy for lung malignancies. Cancer Treat Rev 41(6):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.04.002 (Epub 2015 Apr 16. Review)
Sterpin E, Janssens G, Orban de Xivry J, Goossens S, Wanet M, Lee JA, Delor A, Bol V, Vynckier S, Gregoire V, Geets X (2012) Helical tomotherapy for SIB and hypo-fractionated treatments in lung carcinomas: a 4D Monte Carlo treatment planning study. Radiother Oncol 104(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2012.06.005
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, Karasawa K, Hayakawa K, Niibe Y, Takai Y, Kimura T, Takeda A, Ouchi A, Hareyama M, Kokubo M, Kozuka T, Arimoto T, Hara R, Itami J, Araki T (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(5):1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1751
Aoki M, Hatayama Y, Kawaguchi H, Hirose K, Sato M, Akimoto H, Fujioka I, Ono S, Tsushima E, Takai Y (2016) Clinical outcome of stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary and oligometastatic lung tumors: a single institutional study with almost uniform dose with different five treatment schedules. Radiat Oncol 20(11):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0581-2
Shibamoto Y, Hashizume C, Baba F, Ayakawa S, Miyakawa A, Murai T, Takaoka T, Hattori Y, Asai R (2015) Stereotactic body radiotherapy using a radiobiology-based regimen for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: five-year mature results. J Thorac Oncol 10(6):960–964. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000525
Hodge, Tome WA, Jaradat HA, Orton NP, Khuntia D, Traynor A, Weigel T, Mehta MP (2006) Feasibility report of image guided stereotactic body radiotherapy (IG-SBRT) with tomotherapy for early stage medically inoperable lung cancer using extreme hypofractionation. Acta Oncol 45(7):890–896 (NRO)
Kim JY, Kay CS, Kim YS, Jang JW, Bae SH, Choi JY, Yoon SK, Kim KJ (2009) Helical tomotherapy for simultaneous multitarget radiotherapy for pulmonary metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75(3):703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.11.065 (Epub 2009 May 4)
Sole CV, Lopez Guerra JL, Matute R, Jaen J, Puebla F, Rivin E, Sanchez-Reyes A, Beltran C, Bourgier C, Calvo FA, Marsiglia H (2013) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy delivered by image-guided helical tomotherapy for extracranial oligometastases. Clin Transl Oncol 15(6):484–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0956-2 (Epub 2012 Nov 10)
Aibe N, Yamazaki H, Nakamura S, Tsubokura T, Kobayashi K, Kodani N, Nishimura T, Okabe H, Yamada K (2014) Outcome and toxicity of stereotactic body radiotherapy with helical tomotherapy for inoperable lung tumor: analysis of Grade 5 radiation pneumonitis. J Radiat Res. 55(3):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrt146 (Epub 2014 Jan 23)
Nagai A, Shibamoto Y, Yoshida M, Inoda K, Kikuchi Y (2014) Safety and efficacy of intensity-modulated stereotactic body radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy for lung cancer and lung metastasis. BioMed Res Int
Rosen LR, Fischer-Valuck BW, Katz SR, Durci M, Wu HT, Syh J, Patel B (2013) Helical image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for the treatment of early-stage lung cancer: a single-institution experience at the Willis-Knighton Cancer Center. Tumori 100(1):42–48
Casutt A, Bouchaab H, Beigelman-Aubry C, Bourhis J, Lovis A, Matzinger O (2015) Stereotactic body radiotherapy with helical tomotherapy for medically inoperable early stage primary and second-primary non-small-cell lung neoplasm: 1-year outcome and toxicity analysis. Br J Radiol 88(1049):20140687. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20140687 (Epub 2015 Mar 4)
Guckenberger M, Baier K, Polat B, Richter A, Krieger T, Wilbert J, Mueller G, Flentje M (2010) Dose-response relationship for radiation-induced pneumonitis after pulmonary stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 97(1):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.04.027 (Epub 2010 Jun 3)
Ricardi U, Filippi AR, Guarneri A, Giglioli FR, Mantovani C, Fiandra C, Anglesio S, Ragona R (2009) Dosimetric predictors of radiation-induced lung injury in stereotactic body radiation therapy. Acta Oncol 48:571–577
Barriger RB, Forquer JA, Brabham JG, Andolino DL, Shapiro RH, Henderson MA, Johnstone PA, Fakiris AJ (2012) A dose-volume analysis of radiation pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:457–462
Jo IY, Kay CS, Kim JY, Son SH, Kang YN, Jung JY, Kim KJ (2014) Significance of low-dose radiation distribution in development of radiation pneumonitis after helical-tomotherapy-based hypofractionated radiotherapy for pulmonary metastases. J Radiat Res 55(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrt080 (Epub 2013 Jun 11)
Wang Z, Zhu XX, Wu XH, Li B, Shen TZ, Kong QT, Li J, Liu ZB, Jiang WR, Wang Y, Hou B (2014) Gefitinib combined with stereotactic radiosurgery in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 37(2):148–153. https://doi.org/10.1097/coc.0b013e31826e071b
Chi A, Ma P, Fu G et al (2013) Critical structure sparing in stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for central lung lesions: helical tomotherapy vs. volumetric modulated arc therapy. Chen C-T (ed) PLoS One 8(4):e59729. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059729
Acknowledgements
None of the authors involved in this study received financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figlia, V., Mazzola, R., Cuccia, F. et al. Hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for lung malignancies by means of helical tomotherapy: report of feasibility by a single-center experience. Radiol med 123, 406–414 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-0858-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-0858-7