Abstract
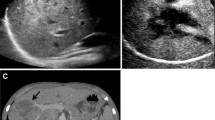
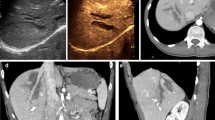
US has a relevant role in the initial assessment of non-traumatic emergencies of the abdomen, sometimes being conclusive and some other times for selecting the patients for further imaging with CT. Injection of a contrast medium may give to the radiologist additional information to that obtained at baseline US and Doppler examination, since real-time, contrast-enhanced US (CEUS) may allow observing findings in the abdomen not recognizable at baseline US or even at color Doppler imaging. Extravascular use of microbubbles may also be useful in clinical practice to rapidly solve a number of unclear aspects. CEUS has a number of distinct advantages in acute patients, including its quickness, low invasiveness, and its possible bedside use. The information based on contrast enhancement is useful for initial diagnosis, therapeutic decision making, and follow-up of the critically ill patients. The purpose of this review is to illustrate the possibilities and limitations of abdominal CEUS in the acute setting, with special emphasis on the detection and characterization of acute inflammatory processes, infarcts, and hemorrhages.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catalano O, Lobianco R, Sandomenico F, Mattace Raso M, Siani A (2004) Real-time, contrast-enhanced sonographic imaging in emergency radiology. Radiol Med 108:454–469
Cokkinos DD, Antypa E, Kalogeropoulos I, Tomais D, Ismailos E, Matsiras I, Benakis S, Piperopoulos PN (2013) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound performed under urgent conditions. Indications, review of the technique, clinical examples and limitations. Insights Imaging 4:185–198
Farina A, Catalano O (2014) Ecografia con mezzi di contrasto “CEUS”. E.L.I. Medica, Napoli
Piscaglia F, Nolsøe C, Dietrich CF et al (2012) The EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical practice of contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS): update 2011 on non-hepatic applications. Ultraschall Med 33:33–59
Thorelius L (2004) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: beyond the liver. Eur Radiol 13(suppl 3):91–108
Thorelius L (2004) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for extrahepatic lesions: preliminary experience. Eur J Radiol 51(suppl):31–38
Calabrese E, Catalano O, Nunziata A, D’Errico A, Petrillo A (2014) Bedside contrast-enhanced sonography (CEUS) of the critically-ill patient. J Ultrasound Med 33:1685–1693
Adamietz B, Wenkel E, Uder M, Meyer T, Schneider I, Dimmler A, Bautz W, Janka R (2007) Contrast enhanced sonography of the gallbladder: a tool in the diagnosis of cholecystitis? Eur J Radiol 61:262–266
Xie XH, Xu HX, Xie XY et al (2010) Differential diagnosis between benign and malignant gallbladder diseases with real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur Radiol 20:239–248
Zechner PM, Rienmüller S, Dorr K, Genger C, Wurzer H (2012) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound detects gallbladder perforation in a patient with acute abdominal pain. Am J Emerg Med 30:516.e5–516.e6
Incesu L, Yazicioglu AK, Selcuk MB, Ozen N (2004) Contrast-enhanced power Doppler US in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Eur J Radiol 50:201–209
Esteban JM, Aleixandre A, Hurtado MJ, Maldonado L, Mora FJ, Nogués E (2003) Contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of inflammatory abdominal masses in Crohn’s disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:253–259
Ripollés T, Martinez-Pérez MJ, Paredes JM, Vizuete J, Garcìa-Martìnez E, Jimènez-Restrepo DH (2013) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differentiation between phlegmon and abscess in Crohn’s disease and other abdominal conditions. Eur J Radiol 82:e525–e531
Catalano O, Cusati B, Nunziata A, Siani A (2004) Real-time, contrast-specific sonography imaging of acute splenic disorders: a pictorial review. Emerg Radiol 11:15–21
Catalano O, Sandomenico F, Mattace Raso M, Siani A (2004) Low mechanical index contrast-enhanced sonographic findings of pyogenic hepatic abscesses. AJR 182:447–450
Kim KW, Choi BI, Park SH et al (2004) Pyogenic hepatic abscesses: distinctive features for hypovascular hepatic malignancy on contrast-enhanced ultrasound with SH U 508A; early experience. Ultrasound Med Biol 30:725–733
Kim B, Lim HK, Choi MH et al (2011) Detection of parenchymal abnormalities in acute pyelonephritis by pulse inversion harmonic imaging with and without microbubble ultrasonographic contrast agent. Correlation with computed tomography. J Ultrasound Med 20:5–14
Fontanilla T, Minaya J, Cortés C, Hernando CG, Arangüena RP, Arriaga J, Carmona MS, Alcolado A (2012) Acute complicated pyelonephritis: contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Abdom Imaging 37:639–646
Mitterberger M, Pinggera GM, Colleselli D et al (2008) Acute pyelonephritis: comparison of diagnosis with computed tomography and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. BJU Int 101:341–344
Setola SV, Catalano O, Sandomenico F, Siani A (2007) Contrast-enhanced sonography of the kidney. Abdom Imaging 32:21–28
Kim JH, Eun HW, Lee HK et al (2003) Renal perfusion abnormality. Coded harmonic angio US with contrast agent. Acta Radiol 44:166–171
Görg C, Egbring J, Bert T (2009) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of epiploic appendagitis. Ultraschall Med 30:163–167
Brocchi E, Piscaglia F, Bonora M, Celli N, Venturi A, Fantini L, Tomassetti P, Corinaldesi R, Pezzilli R (2005) Echo-enhanced ultrasonography: is it the future gold standard of imaging in acute pancreatitis? JOP 6:464–466
Golea A, Badea R, Socaciu M, Diaconu B, Iacob D (2010) Quantitative analysis of tissue perfusion using contrast-enhanced transabdominal ultrasound (CEUS) in the evaluation of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Med Ultrason 12:198–204
Schreyer AG, Landfried K, Jung EM, da Silva NP, Poschenrieder F, Dornia C, Wiggermann P, Dendl LM, Holler E, Stroszczynski C, Friedrich C (2011) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for differential diagnosis of suspected GvHD in patients after allogeneic transplantation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 49:129–136
Bertolotto M, Martegani A, Aiani L, Zappetti R, Cernic S, Cova MA (2008) Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for detecting renal infarcts proven by contrast enhanced CT. A feasibility study. Eur Radiol 18:376–383
Bertolotto M, Catalano O (2009) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: past, present, and future. Ultrasound Clin 4:339–367
Catalano O, Farina R (2012) Ecografia con mezzo di contrasto–CEUS. Edizioni Librarie Internazionali, Napoli
von Herbay A, Schick D, Horger M, Gregor M (2006) Low-MI-sonography with the contrast-agent SonoVue in the diagnosis of infarction of the spleen, kidney, liver and pancreas. Ultraschall Med 27:445–450
Görg C, Graef C, Bert T (2006) Contrast-enhanced sonography for differential diagnosis of an inhomogeneous spleen of unknown cause in patients with pain in the left upper quadrant. J Ultrasound Med 25:729–734
Le Dorze M, Bouglé A, Deruddre S, Duranteau J (2012) Renal Doppler ultrasound: a new tool to assess renal perfusion in critical illness. Shock 37:360–365
Schneider A, Johnson L, Goodwin M, Schelleman A, Bellomo R (2011) Bench-to-bedside review: contrast enhanced ultrasonography-a promising technique to assess renal perfusion in the ICU. Crit Care 15:157
Giannetti A, Biscontri M, Randisi P, Cortese B, Minacci C, Stumpo M (2010) Contrast-enhanced sonography in the diagnosis of acute mesenteric ischemia: case report. J Clin Ultrasound 38:156–160
Kanzaki T, Hata J, Imamura H et al (2012) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with Sonazoid™ for the evaluation of bowel ischemia. J Med Ultrasonics 39:161–167
Hata J, Kamada T, Haruma K, Kusunoki H (2005) Evaluation of bowel ischemia with contrast-enhanced US: initial experience. Radiology 236:712–715
Mortele KJ, Cantisani V, Brown DL, Ros PR (2003) Spontaneous intraperitoneal hemorrhage: imaging features. Radiol Clin North Am 41:1183–1201
Goldberg BB, Merton DA, Liu J-B, Forsberg F (1998) Evaluation of bleeding sites with a tissue-specific sonographic contrast agent: preliminary experiences in an animal model. J Ultrasound Med 17:609–616
Schmiedl UP, Carter S, Martin RW, Eubank W, Winter T, Chang PP, Bauer A, Crum LA (1999) Sonographic detection of acute parenchymal injury in an experimental porcine model of renal hemorrhage: gray-scale imaging using a sonographic contrast agent. AJR 173:1289–1294
Catalano O, Sandomenico F, Mattace Raso M, Siani A (2005) Real-time, contrast-enhanced sonography: a new tool for detecting active bleeding. J Trauma 59:933–939
Catalano O, Cusati B, Nunziata A, Siani A (2006) Active abdominal bleeding: contrast-enhanced sonography. Abdom Imaging 31:9–16
Catalano O, Lobianco R, Cusati B, Siani A (2005) Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis with contrast-enhanced sonography. AJR 184:423–427
Glen P, MacQuarrie J, Imrie CW, Leen E (2004) A novel application of ultrasound contrast: demonstration of splenic arterial bleeding. Br J Radiol 77:333–334
Martegani A, Aiani L, Borghi C (2004) The use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in large vessels. Eur Radiol 14(suppl 8):P73–P86
Tarantino L, Sordelli I, Calise F, Ripa C, Perrotta M, Sperlongano P (2011) Prognosis of patients with spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Updates Surg 63:25–30
Akiyama T, Inamori M, Saito S, Takahashi H, Yoneda M, Fujita K, Fujisawa T, Abe Y, Kirikoshi H, Kubota K, Ueda M, Tanaka K, Togo S, Ueno N, Shimada H, Nakajima A (2008) Levovist ultrasonography imaging in intracystic hemorrhage of simple liver cyst. World J Gastroenterol 14:805–807
Naganuma H, Funaoka M, Fujimori S, Niwa M, Ishida H, Komatsuda T, Yamada M, Furukawa K (2006) Contrast-enhanced sonographic findings in a case of hepatobiliary cystadenoma with intracystic bleeding. J Clin Ultrasound 34:412–415
Manabe N, Hata J, Haruma K, Imamura H, Kamada T, Kusunoki H (2010) Active gastrointestinal bleeding: evaluation with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Abdom Imaging 35:637–642
Li W, Tang J, Lv F, Zhang H, Zhang S, An L (2010) Effectiveness and safety of CEUS-guided haemostatic injection for blunt splenic trauma: an animal experiment. Radiol Med 115:1080–1086
Song HP, Yu M, Zhang J, Han ZH, Su HL, Ren XL, Wei ZR, Luo W, He JG, Zhou XD (2008) Hemostasis of active bleeding from the liver with percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy under contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic guidance: an experimental study. J Ultrasound Med 27:867–874
Sparchez Z, Radu P, Sparchez M, Vasile T, Anton O, Tantau M (2013) Intracavitary applications of ultrasound contrast agents in hepatogastroenterology. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 22:349–353
Main ML (2009) Ultrasound contrast agent safety. From anecdote to evidence. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2:1057–1059
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Alessandra Trocino, Librarian at the Fondazione Pascale, for help in bibliographic research.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to mention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farina, R., Catalano, O., Stavolo, C. et al. Emergency radiology. Radiol med 120, 73–84 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0480-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0480-2