Abstract
Purpose
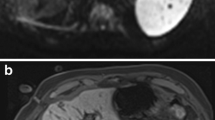
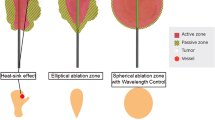
Microwave thermal ablation (MWA) opens up a new scenario in the field of image-guided tumour ablation thanks to its potential advantages over validated radiofrequency ablation (RFA). In this pilot study, we assessed the technical success, safety and efficacy of MWA in treating hepatic malignancies.
Materials and methods
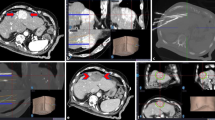
After obtaining informed consent, we enrolled 15 inoperable patients, for a total of 19 lesions (ten metastases, nine hepatocellular carcinoma) with a mean diameter of 47 mm (range 14–78 mm). Mean follow-up was 8 (range 1–14) months.
Results
Technical success reached 100%. Complications (one major and one minor) occurred in two cases. Complete ablation, obtained in 68.4% of cases, showed no significant correlation with either cancer histological type or with lesion diameter. At follow-up, treatment failures occurred in 60% of cases; lesion diameter was the only prognostic factor for maintaining complete ablation.
Conclusions
Our preliminary results should encourage further trials of this technique. MWA proved to be feasible and safe in treating advanced-stage liver tumours and represented an additional therapeutic attempt to be validated in further and larger efficacy studies.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
La termoablazione con microonde (MWA) prospetta un nuovo scenario nel campo delle ablazioni tumorali imaging-guidate per i potenziali vantaggi rispetto all’ormai validata termoablazione con radiofrequenze (RFA). Con questo studio pilota ne abbiamo valutato successo tecnico, sicurezza ed efficacia nel trattamento dei tumori epatici maligni.
Materiali e metodi
Previo consenso informato, abbiamo arruolato 15 pazienti non operabili, portatori di 19 lesioni (10 metastasi [MTS], 9 carcinomi epatici [HCC]) con diametro medio di 47 mm (range 14–78 mm). Il follow-up medio è stato di 8 mesi (range 1–14 mesi).
Risultati
Il successo tecnico è stato del 100%. In due casi sono state registrate complicanze (1 maggiore e 1 minore). L’ablazione completa (AC), ottenuta nel 68,4% dei casi, non ha dimostrato correlazioni statisticamente significativa né con l’istotipo, né con il diametro delle lesioni. Nel follow-up, il fallimento del trattamento (FT) si è verificato complessivamente nel 60% dei casi; il diametro delle lesioni è stato l’unico fattore prognostico per l’AC mantenuta nel tempo.
Conclusioni
I risultati preliminari del nostro studio incoraggiano la sperimentazione di questa tecnica. La MWA è stata fattibile e sicura nel trattamento di neoplasie epatiche avanzate, e ha costituito un tentativo terapeutico oltre i protocolli oncologici standard da sottoporre al vaglio di più ampi studi di efficacia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Tsim NC, Frampton AE, Habib NA, Jiao LR (2010) Surgical treatment for liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol 16:927–933
Wong SL, Mangu PB, Choti MA et al (2010) Clinical evidence review on radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases. Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:493–508
Veltri A, Sacchetto P, Tosetti I et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: small size favorably predicts technique effectiveness and survival. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:948–956
Tabuse K, Katsumi M, Kobayashi Y et al (1985) Microwave surgery: hepatectomy using a microwave tissue coagulator. World J Surg 9:136–143
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2009) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. JVIR 20(S):S377–S390
Ahmed M, Brace CL, Lee FT et al (2011) Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 258:351–369
Martin RCG, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM et al (2010) Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation of hepatic tumors: a prospective review of a 5-year experience. Ann Surg Oncol 17:171–178
Boutros C, Somasundar P, Garrean S et al (2010) Microwave coagulation therapy for hepatic tumors: Review of the literature and critical analysis. Surgical Oncology 19:e22–e32
Brace CL (2010) Microwave tissue ablation: biophysics, technology, and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 38:5–78
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF et al (2003) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. JVIR 14(9 Pt 2):S199–S202
Lencioni R, Llovet JM (2010) Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 30:52–60
Garrean S, Hering J, Saied A et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of primary and metastatic liver tumors: a critical review of the literature. Am J Surg 195:508–520
Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J et al (2005) Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation: Multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg 242:158–171
Ng KK, Poon RT, Lo CM et al (2008) Analysis of recurrence pattern and its influence on survival outcome after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 12:183–191
Viglietti D, Guarnieri T, Sacchetto P et al (2010) Risultati a lungo termine della termoablation con radiofrequenze (RFA) di metastasi epatiche (MTS) da carcinoma colo-rettale (CRC): le dimensioni si confermano il primo fattore prognostico. Riassunti 44° Congresso Nazionale SIRM. Radiol Med 115(Supplement):295
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL et al (2011) Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. JVIR 21:S192–S203
Ong SL, Gravante G, Metcalfe MS et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation for primary and secondary liver malignancies: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:599–605
Parfitt JR, Marotta P, Alghamdi M et al (2007) Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transplantation: use of a pathological score on explanted livers to predict recurrence. Liver Transpl 13:543–551
Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y et al (2002) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223:331–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veltri, A., Gazzera, C., Rotondella, C. et al. Image-guided microwave ablation of hepatic tumours: preliminary experience. Radiol med 117, 378–392 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0745-y