Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to verify the usefulness of preoperative breast magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer.
Materials and methods
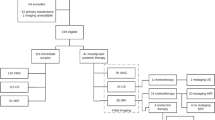
A retrospective analysis of 291 patients with invasive breast cancer newly diagnosed with conventional breast imaging (mammography and ultrasound) was performed. All patients underwent MR imaging prior to surgery. The MR imaging detection rate of additional malignant cancers occult to mammography and ultrasound was calculated. Data were analysed with Fisher’s exact test (p<0.05) according to the following parameters: histopathological features of the index tumour (histological type and size) and mammographic density [according to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classification from 1 fatty to 4 dense). The gold standard was the histological examination on the surgical specimen.
Results
MR imaging identified 40 mammographically and sonographically occult malignant lesions other than the index cancer in 27/291 patients (9%). These additional cancers were located in the same quadrant as the index cancer in 13 women (4%), in a different quadrant in 12 (4%) and in the contralateral breast in the remaining two (1%). The cancer detection rate in the subgroup of index cancers with lobular histological type was 25%, significantly higher (p=0.03) than the detection rate of 11% recorded in the subgroup of ductal cancers. The cancer detection rate in the subgroup of index cancers >2 cm was 27%, significantly higher (p=0.001) than the rate of 8% found in the subgroup of index cancers <2 cm. Mammographic density was not correlated (p=0.48) with MR detection of additional cancer, with 14% of additional malignancies being detected in both dense and fatty breasts.
Conclusions
In patients with newly diagnosed invasive breast cancer, preoperative MR imaging is useful for detecting additional synchronous malignancies that are not detected on conventional breast imaging. The cancer detection rate is 9%. The use of preoperative MR imaging as an adjunct to conventional breast imaging in women with an infiltrating lobular index cancer and an index cancer >2 cm is especially beneficial.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Verificare l’utilità dell’esecuzione della risonanza magnetica (RM) mammaria preoperatoria in pazienti con carcinoma invasivo della mammella.
Materiali e metodi
Sono state analizzate retrospettivamente 291 pazienti con carcinoma invasivo della mammella sottoposte a mammografia, ecografia e RM prima di intervento chirurgico. È stato calcolato il tasso diagnostico aggiuntivo di lesioni maligne sincrone rispetto al tumore principale identificate dalla sola RM, occulte alla mammografia e all’ecografia. I dati sono stati analizzati con il test esatto di Fisher (p<0,05) secondo i seguenti parametri: caratteri istologici della lesione principale (istotipo tumorale e dimensione), densità mammografica (classificazione Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System [BI-RADS] in categorie da 1=adiposa a 4=densa). Il gold standard è stato l’esame istologico del pezzo operatorio.
Risultati
L’indagine RM ha diagnosticato 40 lesioni maligne sincrone in 27/291 Pazienti (tasso diagnostico: 9%). Le lesioni maligne identificate dalla RM erano nello stesso quadrante rispetto alla lesione principale in 13 pazienti (4%), interessavano un altro quadrante in 12 pazienti (4%) e la mammella controlaterale nei rimanenti 2 pazienti (1%). Una correlazione significativa positiva (p=0,03) è emersa tra il tasso di identificazione RM di lesione maligna e istotipo lobulare del carcinoma principale (lesioni maligne sincrone sono state rilevate nel 25% dei tumori lobulari vs 11% dei tumori duttali). Una correlazione significativa (p=0,001) è stata osservata tra identificazione RM di lesione maligne e dimensione della lesione principale superiore a 2 cm (lesioni maligne sincrone sono state diagnosticate dalla RM nel 27% dei tumori superiori a 2 cm vs 8% dei tumori inferiori a 2 cm). L’aspetto radiologico della densità mammaria non è risultato correlato (p=0,48) con l’incidenza di malignità, in quanto lesioni maligne sincrone sono state trovate nel 14% dei casi sia con seno denso che adiposo.
Conclusioni
In pazienti con neoplasia mammaria infiltrante, l’indagine RM preoperatoria è utile nella ricerca di lesioni occulte e identifica foci multipli sincroni alla lesione principale nel 9% delle Pazienti. Il tasso diagnostico è superiore quando la neoplasia principale ha istotipo lobulare e dimensioni >2 cm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Jatoi I, Proschan MA (2005) Randomized trials of breast-conserving therapy versus mastectomy for primary breast cancer: a pooled analysis of updated results. Am J Clin Oncol 28:289–294
Veronesi U, Banfi A, Salvadori B et al (1990) Breast conservation is the treatment of choice in small breast cancer: long-term results of a randomized trial. Eur J Cancer 26:668–670
Morrow M, Schmidt R, Hassett C (1995) Patient selection for breast conservation therapy with magnification mammography. Surgery 118:621–626
Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH (1998) Occult cancer in women with dense breasts: detection with screening US—diagnostic yield and tumor characteristics. Radiology 207:191–199
Berg WA (2003) Rationale for a trial of screening breast ultrasound: American College of Radiology Imaging Network (ACRIN) 6666. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1225–1228
Corsetti V, Ferrari A, Ghirardi M et al (2006) Role of ultrasonography in detecting mammographically occult breast carcinoma in women with dense breasts. Radiol Med 111:440–448
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 220:13–30
Mann RM, Hoogeveen YL, Blickman JG, Boetes C (2008) MRI compared to conventional diagnostic work-up in the detection and evaluation of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: a review of existing literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat 107:1–14
Bartella L, Liberman L, Morris EA et al (2006) Nonpalpable mammographically occult invasive breast cancers detected by MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:865–870
Liberman L (2004) Breast cancer screening with MRI — what are the data for patients at high risk? New Engl J Med 351:497–500
Sardanelli F, Giuseppetti GM, Canavese G et al (2008) Indications for breast magnetic resonance imaging. Consensus document “Attualità in senologia”, Florence 2007. Radiol Med 113:1085–1095
Sardanelli F (2010) Overview of the role of preoperative breast MRI in the absence of evidence on patient outcome. Breast 19:3–6
Solin LJ (2010) Counterview: pre-operative breast MRI is not recommended for all patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Breast 19:7–9
Kuhl C (2007) The current status of breast MR imaging. Part I. Choice of technique, image interpretation, diagnostic accuracy, and transfer to clinical practice. Radiology 244:356–378
Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS et al (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology 233:830–849
Boetes C, Mus RD, Holland R et al (1995) Breast tumors: comparative accuracy of MR imaging relative to mammography and US for demonstrating extent. Radiology 197:743–747
Mumtaz H, Hall-Craggs MA, Davidson T et al (1997) Staging of symptomatic primary breast cancer with MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:417–424
Ikeda O, Nishimura R, Miyayama H et al (2004) Magnetic resonance evaluation of the presence of an extensive intraductal component in breast cancer. Acta Radiol 45:721–725
Satake H, Shimamoto K, Sawaki A et al (2000) Role of ultrasonography in the detection of intraductal spread of breast cancer: correlation with pathologic findings, mammography and MR imaging. Eur Radiol 10:1726–1732
Liberman L, Morris EA, Dershaw DD et al (2003) MR imaging of the ipsilateral breast in women with percutaneously proven breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:901–910
Lehman CD, Gatsonis C, Kuhl CK et al (2007) MRI evaluation of the contralateral breast in women with recently diagnosed breast cancer. N Engl J Med 356:1295–1303
Houssami N, Ciatto S, Macaskill P et al (2008) Accuracy and surgical impact of magnetic resonance imaging in breast cancer staging: systematic review and meta-analysis in detection of multifocal and multicentric cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:3248–3258
Brennan ME, Houssami N, Lord S et al (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging screening of the contralateral breast in women with newly diagnosed breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis of incremental cancer detection and impact on surgical management. J Clin Oncol 27:5640–5649
Solin LJ, Orel SG, Hwang WT et al (2008) Relationship of breast magnetic resonance imaging to outcome after breast-conservation treatment with radiation for women with early-stage invasive breast carcinoma or ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 26:386–391
Turnbull L, Brown S, Harvey I et al (2010) Comparative effectiveness of MRI in breast cancer (COMICE) trial: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 375:563–571
Bedrosian I, Mick R, Orel SG et al (2003) Changes in the surgical management of patients with breast carcinoma based on preoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer 98:468–473
Mann RM (2010) The effectiveness of MR imaging in the assessment of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 18:259–276
Mann RM, Loo CE, Wobbes T (2010) The impact of preoperative breast MRI on the re-excision rate in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119:415–422
Cubuk R, Tasali N, Narin B et al (2010) Correlation between breast density in mammography and background enhancement in MR mammography. Radiol Med 115:434–441
Arpino G, Bardou VJ, Clark GM, Elledge RM (2004) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: tumor characteristics and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res 6:R149–R156
Yeatman TJ, Cantor AB, Smith TJ et al (1995) Tumor biology of infiltrating lobular carcinoma. Implications for management. Ann Surg 222:549–559
Li CI, Uribe DJ, Daling JR (2005) Clinical characteristics of different histologic types of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 93:1046–1052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girardi, V., Carbognin, G., Camera, L. et al. Multifocal, multicentric and contralateral breast cancers: breast MR imaging in the preoperative evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Radiol med 116, 1226–1238 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0704-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0704-7