Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate a handheld vacuum-assisted device for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided breast biopsy.
Materials and methods
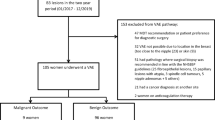
In 47 patients, a total of 47 suspicious breast lesions (mean maximum diameter 9 mm) seen with MRI (no suspicious changes on breast ultrasound or mammography) were sampled using a 10-gauge vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (VAB) device under MRI guidance. Histology of biopsy specimens was compared with final histology after surgery or with follow-up in benign lesions.
Results
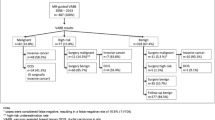
Technical success was achieved in all biopsies. Histological results from VAB revealed malignancy in 15 lesions (32%), atypical ductal hyperplasia in four lesions (8%) and benign findings in 28 lesions (60%). One of four lesions with atypical ductal hyperplasia was upgraded to ductal carcinoma in situ after surgery. One of seven lesions showing ductal carcinoma was upgraded to invasive carcinoma after surgery. Two lesions diagnosed as infiltrating carcinoma by VAB were not validated at excisional biopsy due to complete removal of the lesion during the procedure. During the follow-up (mean 18 months) of histologically benign lesions, we observed no cases of breast cancer development. Because of morphological changes on follow-up MRI scans, two lesions underwent surgical excision, which confirmed their benign nature. Besides minor complications (massive bleeding, n=1) requiring no further therapeutic intervention, no complications occurred.
Conclusions
MRI-guided biopsy of breast lesions using a handheld vacuum-assisted device is a safe and effective method for the workup of suspicious lesions seen on breast MRI alone.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Valutare l’accuratezza diagnostica dei prelievi con sistema portatile ad aspirazione retroazionata (VAB) 10 gauge sotto-guida RM nella caratterizzazione delle lesioni mammarie visibili unicamente alla RM.
Materiali e metodi
47 lesioni (diametro massimo 9 mm) visibili unicamente all’esame RM, sono state caratterizzate usando un sistema portatile ad aspirazione retroazionata (VAB) con ago da 10 Gauge, sotto guida RM. L’istologia delle biopsie VAB è stata confrontata con l’istologia definitiva dopo l’escissione chirurgica o con i reperti di follow-up.
Risultati
Il successo tecnico è stato ottenuto in tutti i casi. I risultati istologici della biopsia VAB hanno mostrato 15 lesioni maligne (32%), 4 lesioni classificabili come iperplasia duttale atipica (ADH) (8%), e 28 lesioni come benigne (60%). Alla istologia definitiva una delle quattro lesioni classificate come ADH è stata riclassificata come carcinoma duttale in situ (DCIS), mentre una delle lesioni classificate come DCIS è stata riclassificata come carcinoma invasivo. Due lesioni diagnosticate al VAB come carcinoma infiltrante non sono state riscontrate alla istologia definitiva, probabilmente a causa della totale rimozione durante la procedura VAB. Il follow-up delle lesioni benigne ha confermato la benignità delle lesioni. Due lesioni benigne che all’Imaging RM hanno mostrato una modificazione della morfologia, sono andate incontro ad intervento chirurgico che ha confermato la benignità della lesione. Ad eccezione di un massivo sanguinamento in 1 caso, non si sono osservate complicanze.
Conclusioni
I prelievi VAB sotto-guida RM sono una mammetodica sicura ed efficace per la caratterizzazione delle lesioni mammarie visibili unicamente all’RM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS et al (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology 233:830–844
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer Radiology 220:13–30
Orel SG, Schnall MD, Powell CM et al (1995) Staging of suspected breast cancer: effect of MR imaging and MR-guided biopsy. Radiology 196:115–121
Chen X, Lehman CD, Dee KE (2004) MRI-guided breast biopsy: clinical experience with 14-gauge stainless steel core biopsy needle AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:1075–1080
Liberman L, Morris EA, Dershaw DD et al (2003) Fast MRI-guided vacuumassisted breast biopsy: initial experience, AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:1283–1293
Orel SG, Rosen M, Mies C, Schnall MD (2006) MR imaging-guided 9-gauge vacuum-assisted core-needle breast biopsy: initial experience. Radiology 238:54–61
Kuhl CK, Elevelt A, Leutner CC et al (1997) Interventional breast MR imaging: clinical use of a stereotactic localization and biopsy device. Radiology 204:667–675
Helbich TH, Matzek W, Fushsjager MH (2004) Stereotactic and ultrasoundguided breast biopsy. Eur Radiol 14:383–393
Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Heinig A, Pickuth D et al (2000) Interventional MRI of the breast: lesion localisation and biopsy. Eur Radiol 10:36–45
Kuhl CK (2002) Interventional breast MRI: needle localisation and core biopsies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 21(3 Suppl):65–68
La Nette FS, Ronda HT, Mancino AT et al (2001) Magnetic Resonance imaging-guided core needle biopsy and needle localized excision of occult breast lesions. Am J Surgery 182:414–418
Jackman RJ, Burbank F, Parker SH et al (1997) Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at stereotactic breast biopsy: improved reliability with 14-Gauge, directional, vacuum assisted biopsy. Radiology 204:485–488
Kettritz U, Rotter K, Scheer I et al (2004) Stereotactic vacuum assissted breast biopsy in 2874 patients: a multicenter study. Cancer 100:245–251
Perlet C, Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Heinig A et al (2006) Resonance-guided vacuum-assisted breast biopsy results from a European Multicenter Study of 538 lesions. Cancer 106:982–990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perretta, T., Pistolese, C.A., Bolacchi, F. et al. MR imaging-guided 10-gauge vacuum-assisted breast biopsy: histological characterisation. Radiol med 113, 830–840 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0289-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0289-y