Abstract
Purpose
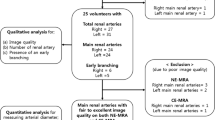
This study was performed to assess the feasibility, interobserver variability, sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy of raw data and postprocessed images from a low-field (0.5-T) magnetic resonance (MR) unit in evaluating vascular complications of kidney grafts.
Materials and methods
We enrolled 49 patients undergoing MR angiography (MRA) for a clinical suspicion of renal artery stenosis. The raw data, maximum intensity projections (MIP) and multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) image sets were evaluated independently. We calculated the number and degree of stenosis, and sensitivity, specificity and accuracy for MIP, MPR and raw data image sets, together with interobserver variability.
Results
Interobserver agreement was substantial. There were no differences among the MIP and MPR algorithms and raw data images for the detection of stenosis. Raw data images were more accurate in quantifying the severity of stenosis, with higher sensitivity (75% vs. 62.5%), equal specificity and higher diagnostic accuracy (75% vs. 71.43%).
Conclusions
Contrast-enhanced MRA, even with a low-field (0.5-T) unit, is a feasible, sensitive and accurate technique for the study of the renal arteries of the transplanted kidney.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Valutare la fattibilità tecnica, la variabilità tra gli esaminatori, la specificità, la sensibilità e l’accuratezza diagnostica delle immagini partizionali e delle ricostruzioni, acquisite con un tomografo RM a basso campo (0,5 T) nelle complicanze vascolari del rene trapiantato.
Materiali e metodi
Abbiamo selezionato 49 pazienti sottoposti a tomografia RM per sospetta stenosi dell’arteria renale. Sono state valutate indipendentemente, le immagini partizionali, le proiezioni di massima intensità (MIP) e le ricostruzioni multiplanari (MPR). Abbiamo calcolato il numero e l’entità delle stenosi, la sensibilità, la specificità e l’accuratezza sia delle immagini partizionali che delle ricostruzioni, ed abbiamo valutato la concordanza tra i due radiologi che hanno esaminato ciascun caso.
Risultati
La concordanza inter-osservatore è risultata elevata. Non abbiamo riscontrato differenze nel riconoscimento della stenosi tra le ricostruzioni MIP e MPR e le immagini partizionali. Le immagini partizionali hanno dimostrato maggior affidabilità nel quantificare la severità della stenosi, con elevata sensibilità (75% vs. 62,5%), uguale specificità e maggior accuratezza diagnostica (75% vs 71,43%).
Conclusioni
L’angio-RM con contrasto iniettato con tecnica «a bolo di contrasto», per lo studio delle arterie renali dei reni trapiantati, è una metodica fattibile dal punto di vista pratico, sensibile e con un’ottima accuratezza diagnostica, anche con apparecchiatura RM a basso campo (0,5 T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
AIRT (2005) AIRT Report, Editrice Compositroi, Bologna
Kahan BD, Ponticelli C (2000) Principles and practice of renal transplantation, Martin Dunitz Ltd, London
Samhan M, Sinam T, Al Mousowi M (1999) Vascular complications in renal recipients, Transplant Proc 31:3227–3228
Beyga ZT and Kahan BD (1998) Surgical complications of kidney transplantation. J Nephrol 11:137–145
Vidne BA, Leapman SB, Butt KM, Kountz SL (1976) Vascular complications in human transplantation. Surgery 79:77–81
Vegeto A, Berardinelli L (1999) Il trapianto di rene. UTET, Torino
Danovitch GM (2001) Handbook of kidney transplantation. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Bruno S, Remuzzi G, Ruggenti P (2004) Transplant renal artery stenosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:134–141
Fervenza FC, Lafayette RA, Alfrey EJ, Petersen J (1998) Renal artery stenosis in kidney transplants. Am J Kidney Dis 31:142–148
Hohenwalter M, Skowlund C, Erickson S et al (2001) Renal transplant evaluation with MR angiography and MR imaging. RadioGraphics 21:1505–1517
Thornton MJ, Thornton F, O’Callaghan J et al (1999) Evaluation of dynamic gadolinium-enhanced breath-hold MR angiography in the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:1279–1283
Mittal T K, Evans C, Perkins T et al (2001) Renal arteriography using gadolinium enhanced 3D MRA angiography — clinical experience with the technique, its limitations and pitfalls. Brit J Radiol 74:495–502
Hillman BJ (1989) Imaging advances in the diagnosis of renovascular hypertension. AJR Am J Roentgenol 153:5–14
Wong W, Fynn PS, Higgins RM, Walters H et al (1996) Transplant renal artery stenosis in 77 patients-does it have an immunologic cause?. Transplantations 61:215–219
Ferreiros J, Mendez R, Jorquera M et al (1999) Using gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography to assess arterial inflow stenosis after kidney transplantation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:751–757
Johnson DBS, Lerner CA, Prince MR et al (1997) Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of renal transplants. Magn Reson Imaging 15:13–20
Omary RA, Baden JG, Becker BN et al (2000) Impact of MR angiography on the diagnosis and management of renal transplant dysfunction. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 11:991–996
North American Symptomatic Carotic Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patiens with high-grade carotid stenosis. N. Engl J Med 325:445–453
Volk M, Strotzer M, Lenhart M et al (2000) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiography of renal artery stenosis: diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:1583–1588
Baskaran V, Pereles FS., Nemcek AA et al (2002) Gadolinium-enhanced 3D MR angiography of renal artery stenosis: a pilot comparison of maximum intensity projection, multiplanar reformatting, and 3D volume-rendering postprocessing algorithms. Acad Radiol 9:50–59
Landis RJ, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Dong Q, Schoenberg SO, Carlos RC et al (1999) Diagnosis of renal vascular disease with MR angiography. RadioGraphics 19:1535–1554
Glockner JF (2001) Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography: applications for abdominal imaging. RadioGraphics 21:357–370
Mittal TK, Eans C, Perkins T et al (2001) Renal arteriography using gadolinium enhanced 3D MR angiography-clinical experience with the technique, its limitations and pitfalls. Brit J Radiol 74:495–502
Petersen MJ, Cambria RP, Kaufman JA et al (1995) Magnetic resonance angiography in the preoperative evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 21:891–899
Sun Y, Parker DL (1999) Performance analysis of maximum intensity projection algorithm for display of MRA images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18:1154–1169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stecco, A., Oronzo, P., Armienti, F. et al. Contrast-bolus MR angiography of the transplanted kidney with a low-field (0.5-T) scanner: diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of images and reconstructions in the evaluation of vascular complications. Radiol med 112, 1026–1035 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-007-0203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-007-0203-z