Abstract
Background
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced hypothyroidism is associated with favorable survival in patients with various cancers.
Objective
We aimed to investigate the incidence of regorafenib-induced hypothyroidism and assess its prognostic value in patients with metastatic or unresectable colorectal cancer (CRC) receiving regorafenib.
Patients and Methods
This study included 68 patients treated at Asan Medical Center (Seoul, Republic of Korea) between 2014 and 2016 with metastatic or unresectable CRC refractory to standard therapies. Regorafenib (160 mg/day on days 1–21 followed by a 7-day break) was administered.
Results
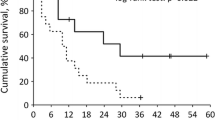
The median patient age was 58 (range 26–72) years; 61.8% of patients were male. Among the 68 patients, 50 (73.5%) showed hypothyroidism; 39 (57.4%) had subclinical and 11 (16.2%) had symptomatic hypothyroidism. Overall, the objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 7.4% and 70.6%, respectively; both were significantly higher in patients with symptomatic or subclinical hypothyroidism than in euthyroid patients (ORR 27.3% vs. 5.1% vs. 0.0%, P = 0.001; DCR 100% vs. 76.9% vs. 38.9%, P = 0.001). Median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were longer in patients with symptomatic hypothyroidism than in those with subclinical hypothyroidism (median PFS 9.1 vs. 3.8 months, P = 0.018; median OS: 19.2 vs. 9.4 months, P = 0.012) or with euthyroid status (median PFS 9.1 vs. 1.8 months, P < 0.001; median OS 19.2 vs. 4.7 months, P = 0.001). Symptomatic hypothyroidism was a significant protective factor for PFS (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.37, P = 0.006) and OS (HR = 0.35, P = 0.007); no other adverse events were associated with survival.
Conclusions
Regorafenib-induced hypothyroidism frequently occurs in patients with metastatic CRC receiving regorafenib and is associated with improved survival. Thyroid function status should be actively monitored in CRC patients receiving regorafenib.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilhelm SM, Dumas J, Adnane L, Lynch M, Carter CA, Schutz G, et al. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): a new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:245–55.
Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, Siena S, Falcone A, Ychou M, et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:303–12.
Li J, Qin S, Xu R, Yau TC, Ma B, Pan H, et al. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:619–29.
Adenis A, de la Fouchardiere C, Paule B, Burtin P, Tougeron D, Wallet J, et al. Survival, safety, and prognostic factors for outcome with Regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard therapies: results from a multicenter study (REBECCA) nested within a compassionate use program. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:412.
Garcia-Alfonso P, Feliu J, Garcia-Carbonero R, Gravalos C, Guillen-Ponce C, Sastre J, et al. Is regorafenib providing clinically meaningful benefits to pretreated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer? Clin Transl Oncol. 2016;18:1072–81.
Fukuoka S, Hara H, Takahashi N, Kojima T, Kawazoe A, Asayama M, et al. Regorafenib plus nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric (GC) or colorectal cancer (CRC): an open-label, dose-finding, and dose-expansion phase 1b trial (REGONIVO, EPOC1603) [abstract no. 2522]. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:2522.
Wolter P, Stefan C, Decallonne B, Dumez H, Bex M, Carmeliet P, et al. The clinical implications of sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism: a prospective evaluation. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:448–54.
Rini BI, Tamaskar I, Shaheen P, Salas R, Garcia J, Wood L, et al. Hypothyroidism in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:81–3.
Wong E, Rosen LS, Mulay M, Vanvugt A, Dinolfo M, Tomoda C, et al. Sunitinib induces hypothyroidism in advanced cancer patients and may inhibit thyroid peroxidase activity. Thyroid. 2007;17:351–5.
Schmidinger M, Vogl UM, Bojic M, Lamm W, Heinzl H, Haitel A, et al. Hypothyroidism in patients with renal cell carcinoma: blessing or curse? Cancer. 2011;117:534–44.
Riesenbeck LM, Bierer S, Hoffmeister I, Kopke T, Papavassilis P, Hertle L, et al. Hypothyroidism correlates with a better prognosis in metastatic renal cancer patients treated with sorafenib or sunitinib. World J Urol. 2011;29:807–13.
Baldazzi V, Tassi R, Lapini A, Santomaggio C, Carini M, Mazzanti R. The impact of sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism on progression-free survival of metastatic renal cancer patients: a prospective single-center study. Urol Oncol. 2012;30:704–10.
Kust D, Prpic M, Murgic J, Jazvic M, Jaksic B, Krilic D, et al. Hypothyroidism as a predictive clinical marker of better treatment response to sunitinib therapy. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:3177–84.
Bozkurt O, Karaca H, Hacibekiroglu I, Kaplan MA, Duzkopru Y, Uysal M, et al. Is sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism a predictive clinical marker for better response in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients? J Chemother. 2016;28:230–4.
Pani F, Massidda M, Pusceddu V, Puzzoni M, Massa E, Madeddu C, et al. Regorafenib-induced hypothyroidism and cancer-related fatigue: is there a potential link? Eur J Endocrinol. 2017;177:85–92.
Kim JE, Chae SY, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Kim TW, Kim KP, et al. 3’-Deoxy-3’-18F-fluorothymidine and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the early prediction of response to regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to all standard therapies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46(8):1713–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04330-7.
Sabatier R, Eymard JC, Walz J, Deville JL, Narbonne H, Boher JM, et al. Could thyroid dysfunction influence outcome in sunitinib-treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma? Ann Oncol. 2012;23:714–21.
Sugita K, Kawakami K, Yokokawa T, Mae Y, Toya W, Hagino A, et al. Investigation of regorafenib-induced hypothyroidism in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:4059–62.
Giampieri R, Prete MD, Prochilo T, Puzzoni M, Pusceddu V, Pani F, et al. Off-target effects and clinical outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving regorafenib: the TRIBUTE analysis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45703.
Makita N, Iiri T. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced thyroid disorders: a review and hypothesis. Thyroid. 2013;23:151–9.
Baffert F, Le T, Sennino B, Thurston G, Kuo CJ, Hu-Lowe D, et al. Cellular changes in normal blood capillaries undergoing regression after inhibition of VEGF signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H547–59.
Kamba T, Tam BY, Hashizume H, Haskell A, Sennino B, Mancuso MR, et al. VEGF-dependent plasticity of fenestrated capillaries in the normal adult microvasculature. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H560–76.
Pani F, Atzori F, Baghino G, Boi F, Tanca L, Ionta MT, et al. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with metastatic carcinoma treated with sunitinib: is thyroid autoimmunity involved? Thyroid. 2015;25:1255–61.
Acknowledgements
Regorafenib was kindly provided by Bayer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by a Grant (2014-9079) from the Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea; a Grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant number HI18C2383); and 2017 cancer research support project of the Korea Foundation for Cancer Research (CB-2017-B-2).
Conflict of interest
Jwa Hoon Kim, Sun Young Kim, Kyu-pyo Kim, Tae Won Kim, Sun Young Chae, Hwa Jung Kim, Jae Seung Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Dae Hyuk Moon, Jeong Eun Kim, and Yong Sang Hong declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Kim, S.Y., Kim, Kp. et al. Regorafenib-Induced Hypothyroidism as a Predictive Marker for Improved Survival in Metastatic or Unresectable Colorectal Cancer Refractory to Standard Therapies: A Prospective Single-Center Study. Targ Oncol 14, 689–697 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00672-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00672-2