Abstract
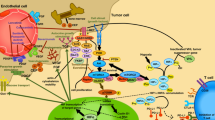
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway is a very well-known pathway implicated in proliferation, growth and metastatic development of various tumor types. Consequently, EGFR pathway inhibitors have provided clinical benefits in many tumor types. EGFR expression is reported in up to 95% of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and is considered high (3+) in up to 60%. In preclinical models, the EGFR pathway appears implicated in tumor development. Its mode of action includes the common EGFR signal transduction cascades, but it also interacts with the angiogenic pathway, especially the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) pathway. Monotherapy with EGFR pathway inhibitors does not appear to modify the history of metastatic RCC (MRCC) and does not justify further experiments in this setting. The issues now requiring attention are the degree to which the EGFR pathway is involved in RCC tumors expressing high EGFR levels—a phase III study suggests that it influences outcome in these patients—and the clinical benefit of associating antiangiogenic therapy and EGFR pathway inhibitors in the light of successive phases II trials. In conclusion, the EGFR pathway is probably not a major pathway in RCC development compared to the antiangiogenic pathways, but could play a role in association with antiangiogenics or in the event of progression after antiangiogenic therapy. Additional preclinical data is needed to support these hypotheses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravaud A, Debled M (1999) Present achievements in the medical treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 31:77–87
Fyfe G, Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA et al (1995) Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol 13:688–696
Negrier S, Escudier B, Lasset C et al (1998) Recombinant human interleukin-2, recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, or both in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 338:1272–1278
Medical Research Council Renal Cancer Collaborators (1999) Interferon-alpha and survival in metastatic renal carcinoma: early results of a randomised controlled trial.Lancet 353:14–17
Bui MH, Seligson D, Han KR et al (2003) Carbonic anhydrase IX as an independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res 9:802–811
Negrier S, Perol D, Ravaud A et al (2006) Is intravenous IL2 superior to subcutaneous IL2 in good prognosis patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving a combination of IL2 and alpha interferon? Results of the prospective randomized PERCY Duo trial. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:225s, (Abstract 4536)
Negrier S, Perol D, Ravaud A et al (2005) Do cytokines improve survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of intermediate prognosis? Results of the prospective randomized PERCY Quattro trial. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:380s, (Abstract 4511)
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM et al (2003) A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:427–4349
Escudier B, Szczylik C, Eisen T et al (2005) Randomized phase III trial of the Raf kinase and VEGFR inhibitor sorafenib (BAY-439006) in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:380s, (Abstract 4510)
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczk P et al (2006) Phase III randomized trial of sunitinib malate (SU 11248) as first-line systemic therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:2s, (Abstract 3)
Schlessinger J (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211–225
Slichenmyer WJ, Fry DW (2001) Anticancer therapy targeting ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Semin Oncol 28 (Suppl 16):67–79
Herbst RS, Shin DM (2002) Monoclonal antibodies to target epidermal growth factor receptor-positive tumors: a new paradigm for cancer therapy. Cancer 94:1593–1611
Olayioye M, Neve R, Lane H, et al (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167
Alroy I, Yarden Y (1997) The ErbB signaling network in embryogenesis and oncogenesis: signal diversification through combinatorial ligand-receptor interactions. FEBS Lett 410: 83–86
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG (1998) Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res 74:49–139
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Okamura K, Morimoto A, Hamanaka R et al (1992) A model system of tumour angiogenesis: involvement of transforming growth factor-a in tube formation of human microvascular endothelial cells induced by oesophageal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186:1471–1479
Hirata A, Ogawa S, Kometani T et al (2002) ZD1839 (Iressa) induces antiangiogenic effects through inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res 62:2554–2560
Baker CH, Solorzano CC, Fidler IJ (2002) Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling for therapy of metastatic human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 62:1996–2003
Goldman CK, Kim J, Wong WL et al (1993) Epidermal growth factor stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor production by human glioma cells: a model of glioblastoma multiforme pathophysiology. Mol Biol Cell 4:121–133
Akagi M, Kawaguchi M, Liu W et al (2003) Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer 88:796–802
Perrotte P, Matsumoto T, Inoue K et al (1999) Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor anti-body C225 inhibits angiogenesis in human transitional cell carcinoma growing orthotopically in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 5:257–265
Kumar R, Yarmand-Bagheri R (2001) The role of HER2 in angiogenesis. Semin Oncol 28:27–32
Bruns CJ, Solorzano CC, Harbison MT et al (2000) Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor leads to apoptosis of endothelial cells and therapy of human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 60:2926–2935
Oh HY, Kwon SM, Kim SI et al (2005) Antiangiogenic effect of ZD 1839 against murine renal cell carcinoma (RENCA) in an orthotopic mouse model. Urol Int 75:159–165
Kedar D, Baker CH, Killion JJ et al (2002) Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling inhibits angiogenesis leading to regression of human renal cell carcinoma growing orthotopically in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 8:592–600
Gomella LG, Anglard P, Sargent ER et al (1990) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene analysis in renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 143:191–193
Ishikawa J, Maeda S, Umezu K et al (1990) Amplification and overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human renal-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 45:1018–1021
Moch H, Sauter G, Buchholz N et al (1997) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is associated with rapid tumor cell proliferation in renal cell carcinoma. Human Pathol 28:1255–1259
Hofmockel G, Riess S, Bassukas ID et al (1997) Epidermal growth factor family and renal cell carcinoma: expression and prognostic impact. Eur Urol 31:478–484
Ravaud A, Gardner J, Hawkins R et al (2006) Efficacy of lapatinib in patients with high tumor EGFR expression: results of a phase III trial in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:217s, (Abstract 4502)
Langner C, Ratschek M, Rehak P et al (2004) Are heterogeneous results of EGFR immunoreactivity in renal cell carcinoma related to non-standardised criteria for staining evaluation? J Clin Pathol 57:773–775
Merseburger AS, Hennenlotter J, Simon P et al (2005) Membranous expression and prognostic implications of epidermal growth factor receptor protein in human renal cell cancer. Anticancer Res 25:1901–1907
Seliger B, Rongcun Y, Atkins D et al (2000) Her-2/neu is expressed in human renal cell carcinoma at heterogeneous levels independently of tumor grading and staging and can be recognized by HLA-A2.1-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int J Cancer 87:349–359
Stumm G, Eberwein S, Rostock-Wolf S et al (1996) Concomitant overexpression of the EGFR and erbB-2 genes in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is correlated with differentiation and metastasis. Int J Cancer 69:17–22
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–20132
Sakaeda T, Okumura N, Gotoh A et al (2005) EGFR mRNA is upregulated, but somatic mutations of the gene are hardly found in renal cell carcinoma in Japanese patients. Pharm Res 22:1757–1761
Hawkins RE, Ravaud A, von der Maase H et al (2006) Lapatinib extend survival in patients with high ErbB1 tumor expression: subgroup results of a phase III trial in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 17 (Suppl 9):ix 145, (Abstract 4400)
Everitt JI, Walker CL, Goldsworthy TW et al (1997) Altered expression of transforming growth factor-alpha: an early event in renal cell carcinoma development. Mol Carcinogen 19:213–219
Price JT, Wilson HM, Haites NE (1996) Epidermal growth factor increases the in vitro invasion, motility and adhesion interactions of the primary renal carcinoma cell line, A 704. Eur J Cancer 32 A:1977–1982
Asakuma J, Sumimoto M, Asano T et al (2004) Modulation of tumor growth and tumor induced angiogenesis after epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition by ZD 1839 in renal cell carcinoma. 171:897–902
Prewett M, Rothman M, Waksal H et al (1998) Mouse-human chimeric anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody C225 inhibits the growth of human renal cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 4:2957–2966
De Paulsen N, Brychzy A, Fournier MC et al (2001) Role of transforming growth factor-alpha in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)(−/−) clear cell renal carcinoma cell proliferation: a possible mechanism coupling VHL tumor suppressor inactivation and tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1387–1392
Gunaratnam L, Morley M, Franovic A et al (2003) Hypoxia inducible factor activates the transforming growth factor-alpha/epidermal growth factor receptor growth stimulatory pathway in VHL (−/−) renal cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 278:44966–44974
Smith K, Gunaratnam, Morley M et al (2005) Silencing of epidermal growth factor receptor suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-2-driven VHL −/− renal cancer. Cancer Res 65:5221–5230
Perera AD, Kleymenova EV, Walker CL et al (2000) Requirement for the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene for functional epidermal growth factor receptor blockade by monoclonal antibody C225 in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6:1518–1523
Lager DJ, Slagel DD, Palechek PL (1994) The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor alpha in renal cell carcinoma. Modern Pathol 7:544–548
Ljungberg B, Grafvels M, Damber JE (1994) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression and binding capacity in renal cell carcinoma, in relation to tumor stage, grade and DNA ploidy. Uroligical Res 22:305–308
Kallio JP, Hirvikoski P, Helin H et al (2003) Membranous location of EGFR immunostaining is associated with good prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 89:1266–1269
Prewett M, Rothman M, Waksal H et al (1998) Mouse-human chimeric anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody C225 inhibits the growth of human renal cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 4:2957–2966
Motzer RJ, Amato R, Todd M et al (2003) Phase II trial of antiepidermal growth factor receptor antibody C225 in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 21:99–101
Yang X-D, Jia X-C, Corvalan JRF et al (1999) Eradication of established tumors by a fully human monoclonal antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor without concomitant chemotherapy. Cancer Res 59:1236–1243
Yang XD, Jia XC, Corvalan JRF et al (2001) Development of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 38:17–23
Rowinsky EK, Schwartz GH, Gollob JA et al (2004) Safety, pharmacokinetics, and activity of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:3003–3015
Drucker B, Bacik J, Ginsberg M et al (2003) Phase II trial of ZD 1839 (Iressa) in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 21:341–345
Dawson NA, Guo C, Zak R et al (2004) A phase II trial of gefitinib (Iressa, ZD 1839) in stage IV and recurrent renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:7812–7819
Jermann M, Stahel RA, Salzberg M et al (2006) A phase II, open-label study of gefitinib (Iressa) in patients with locally advanced, metastatic, or relapsed renal-cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57:533–539
Hidalgo M, Siu LL, Nemunaitis J et al (2001) Phase I and pharmacology study of OSI-774, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 19:3267–3279
Mekhail TM, Abou-Jawde RM, Boumerhi G et al (2005) Validation and extension of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic factors model for survival in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 23:832–841
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J et al (1999) Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 17:2530–2540
Hainsworth JD, Sosman JA, Spigel DR et al (2005) Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with a combination of bevacizumab and erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 23:7889–7896
Bukowski RM, Kabbinavar F, Figlin RA et al (2006) Bevacizumab with or without erlotinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:18S, (Abstract 4523)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravaud, A., de Clermont, H., Pasticier, G. et al. Epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway and renal cell carcinoma. Targ Oncol 2, 99–105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-007-0044-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-007-0044-7