Abstract
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) have shown great potential in providing communication and control for individuals with severe motor disabilities. However, traditional BCIs that rely on electroencephalography (EEG) signals suffer from low information transfer rates and high variability across users. Recently, eye movement signals have emerged as a promising alternative due to their high accuracy and robustness. Eye movement signals are the electrical or mechanical signals generated by the movements and behaviors of the eyes, serving to denote the diverse forms of eye movements, such as fixations, smooth pursuit, and other oculomotor activities like blinking. This article presents a review of recent studies on the development of BCI typing systems that incorporate eye movement signals. We first discuss the basic principles of BCI and the recent advancements in text entry. Then, we provide a comprehensive summary of the latest advancements in BCI typing systems that leverage eye movement signals. This includes an in-depth analysis of hybrid BCIs that are built upon the integration of electrooculography (EOG) and eye tracking technology, aiming to enhance the performance and functionality of the system. Moreover, we highlight the advantages and limitations of different approaches, as well as potential future directions. Overall, eye movement signals hold great potential for enhancing the usability and accessibility of BCI typing systems, and further research in this area could lead to more effective communication and control for individuals with motor disabilities.
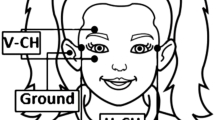
Graphical Abstract
This article delves into three pivotal components of the BCI typing system: data, algorithms, and interaction. The system leverages eye movement and EEG data as inputs, which are processed through algorithms for data fusion, feature extraction, and classification to yield output results. Furthermore, it facilitates real-time interaction by providing visual feedback via an efficient user interface.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolpaw JR, Birbaumer N, Heetderks WJ et al (2000) Brain-Computer Interface Technology: A Review of the First International Meeting. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 8(2):164–173. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRE.2000.847807
Hosni SM, Shedeed HA, Mabrouk MS, Tolba MF (2019) EEG-EOG based Virtual Keyboard: Toward Hybrid Brain Computer Interface. Neuroinformatics 17(3):323–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9402-0
Maslova O, Komarova Y, Shusharina N, Kolsanov A, Zakharov A, Garina E, Pyatin V (2023) Non-invasive EEG-based BCI spellers from the beginning to today: a mini-review. Front Hum Neurosci 23(17):1216648. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2023.1216648
Welton T, Brown DJ, Evett L, Sherkat N (2016) A brain–computer interface for the Dasher alternative text entry system. Univers Access Inf Soc 15(1):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-014-0375-y
Cao L, Xia B, Maysam O, Li J, Xie H, Birbaumer N (2017) A synchronous motor imagery based neural physiological paradigm for brain computer interface speller. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00274
Farwell L, Donchin E (1988) Talking off the top of your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 70:510–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(88)90149-6
Zhang D, Li J (2017) Exploring the power of mind: Status and prospect of brain-computer interfaces Multi-modal emotion recognition and its application in user experiencehttps://doi.org/10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.09.008
Ramirez-Quintana JA, Madrid-Herrera L, Chacon-Murguia MI, Corral-Martinez LF (2021) Brain-Computer Interface System Based on P300 Processing with Convolutional Neural Network, Novel Speller, and Low Number of Electrodes. Cognit Comput 13(1):108–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09744-2
Mussabayeva A, Jamwal PK, Akhtar MT (2021) Ensemble voting-based multichannel eeg classification in a subject-independent p300 speller. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 11(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311252
Chen X, Wang Y, Nakanishi M, Jung TP, Gao X (2014) Hybrid frequency and phase coding for a high-speed SSVEP-based BCI speller. In: 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC 2014. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. 3993–3996. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944499
Chen Y, Yang C, Ye X, Chen X, Wang Y, Gao X (2021) Implementing a calibration-free SSVEP-based BCI system with 160 targets. J Neural Eng 18(4). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac0bfa
Chen J, Wang Y, Maye A et al (2021) A spatially-coded visual brain-computer interface for flexible visual spatial information decoding. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:926–933. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3080045
Guney OB, Oblokulov M, Ozkan H (2022) A Deep Neural Network for SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 69(2):932–944. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2021.3110440
Katyal EA, Singla R (2021) EEG-based hybrid QWERTY mental speller with high information transfer rate. Med Biol Eng Comput 633–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02310-w/Published
Uma M, Prabhu S, Subramaniyam M, Min SN (2021) Analysis of Effect of RSVP Speller BCI Paradigm Along with CNN to Analysis P300 Signals. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Vol 12776 LNAI. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH 2021:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78114-9_7
Rathi N, Singla R, Tiwari S (2021) A novel approach for designing authentication system using a picture based P300 speller. Cogn Neurodyn 15(5):805–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09664-3
Li M, He D, Li C, Qi S (2021) Brain–computer interface speller based on steady-state visual evoked potential: A review focusing on the stimulus paradigm and performance. Brain Sci 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040450
Mahanama B, Jayawardana Y, Rengarajan S et al (2022) Eye movement and pupil measures: A review. Frontiers in Computer Science 3:733531. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2021.733531
Majaranta P, Räihä KJ (2002) Twenty Years of Eye Typing: Systems and Design Issues. In: Proceedings of the 2002 symposium on Eye tracking research & applications. pp 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1145/507072.507076
Kalaganis FP, Chatzilari E, Nikolopoulos S, Kompatsiaris I, Laskaris NA (2018) An error-aware gaze-based keyboard by means of a hybrid BCI system. Sci Rep 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31425-2
Chang Z, Di Martino JM, Aiello R et al (2021) Computational Methods to Measure Patterns of Gaze in Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA Pediatr 175(8):827–836. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.0530
Kim M, Kim BH, Jo S (2015) Quantitative Evaluation of a Low-Cost Noninvasive Hybrid Interface Based on EEG and Eye Movement. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 23(2):159–168. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2365834
Wolpaw JR, Ramoser H, Mcfarland DJ, Pfurtscheller G (1998) EEG-Based Communication: Improved Accuracy by Response Verification. Vol 6. https://doi.org/10.1109/86.712231
Bai X, Li M, Qi S, Ng ACM, Ng T, Qian W (2023) A hybrid P300-SSVEP brain-computer interface speller with a frequency enhanced row and column paradigm. Front Neurosci 17:1133933. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1133933
Han J, Xu M, Xiao X, Yi W, Jung T-P, Ming D (2023) A high-speed hybrid brain-computer interface with more than 200 targets. J Neural Eng 20(1):016025. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/acb105
Raheel A, Anwar SM, Majid M, Khan B, Ehatisham H (2016) Real time text speller based on eye movement classification using wearable EEG sensors. In: Proceedings of 2016 SAI Computing Conference, SAI 2016. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. 2016:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1109/SAI.2016.7555977
Nguyen TH, Yang DL, Chung WY (2018) A high-rate BCI speller based on eye-closed EEG Signal. IEEE Access 6:33995–34003. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2849358
Chugh N, Aggarwal S (2023) Hybrid Brain-Computer Interface Spellers: A Walkthrough Recent Advances in Signal Processing Methods and Challenges. Int J Human-Comput Interact 39(15):3096–3113. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2093445
Yildiz M, Ülkütaş HÖ (2018) A New PC-Based Text Entry System Based on EOG Coding. Adv Human-Comput Interact. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8528176
Duraisamy S, Reddy MR (2020) A high performance asynchronous EOG speller system. Biomed Signal Process Control 59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101898
Jia Y, Tyler CW (2019) Measurement of saccadic eye movements by electrooculography for simultaneous EEG recording. Behav Res Methods 51(5):2139–2151. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-019-01280-8
Duraisamy S, Reddy MR (2020) A virtual speller system using SSVEP and electrooculogram. Adv Eng Inf 44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2020.101059
Duraisamy S, Reddy MR (2021) Stimulus Paradigm for an Asynchronous Concurrent SSVEP and EOG Based BCI Speller System. IEEE Access 9:127484–127495. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3112257
Lee MH, Williamson J, Won DO, Fazli S, Lee SW (2018) A High Performance Spelling System based on EEG-EOG Signals with Visual Feedback. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 26(7):1443–1459. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2839116
Yu Y, Liu Y, Yin E, Jiang J, Zhou Z, Hu D (2019) An Asynchronous Hybrid Spelling Approach Based on EEG-EOG Signals for Chinese Character Input. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(6):1292–1302. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2914916
Zhang J, Zhou K, Mao S, Chen Y (2022) A novel hybrid BCI system based on SSVEP and EOG. In Proceedings of SPIE 12500, Fifth International Conference on Mechatronics and Computer Technology Engineering (MCTE 2022), 125002J. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2660968
Zhang J, Gao S, Zhou K, Cheng Y, Mao S (2023) An online hybrid BCI combining SSVEP and EOG-based eye movements. Front Hum Neurosci 17:1103935. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2023.1103935
Ha J, Park S, Im CH (2022) Novel hybrid brain-computer interface for virtual reality applications using steady-state visual-evoked potential-based brain–computer interface and electrooculogram-based eye tracking for increased information transfer rate. Front Neuroinform 16:758537. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2022.758537
Duchowski TA (2017) Eye tracking: methodology theory and practice. Springer International Publishing AG. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57883-5
Naeem Mannan MM, Kamran MA, Kang S, Choi HS, Jeong MY (2020) A hybrid speller design using eye tracking and SSVEP brain–computer interface. Sensors (Switzerland) 20(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030891
Stawicki P, Gembler F, Rezeika A, Volosyak I (2017) A novel hybrid mental spelling application based on eye tracking and SSVEP-based BCI. Brain Sci 7(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7040035
Saboor A, Benda M, Rezeika A, et al (2018) Mesh of SSVEP-based BCI and eye-Tracker for use of higher frequency stimuli and lower number of EEG channels. In: Proceedings - 2018 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology, FIT 2018. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. 2019:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1109/FIT.2018.00025
Haddad RR, Bastos-Filho TF, Tello RJMG (2019) A novel digital speller based on a hybrid brain computer interface (hbci) ssvep with eye tracking. In: IFMBE Proceedings. Vol 70. Springer Verlag 593–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2119-1_92
Lin X, Chen Z, Xu K, Zhang S (2019) Development of a High-speed Mental Spelling System Combining Eye Tracking and SSVEP-based BCI with High Scalability. In: 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, pp 6318–6322. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2019.8857408
Kalika D, Collins L, Caves K, Throckmorton C (2017) Fusion of P300 and eye-tracker data for spelling using BCI2000. J Neural Eng 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aa776b
Li H, Fang X, Ye Z, Chu X, Lu G, Yu Y (2022) A practical hybrid BCI speller for Chinese Character Input: Integrating an Eye Tracker into a P300-Based Spelling approach. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (CSSE 22). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 237–242. https://doi.org/10.1145/3569966.3570046
Ma X, Yao Z, Wang Y, Pei W, Chen H (2018) Combining brain-computer interface and eye tracking for high-speed text entry in virtual reality. In: International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Proceedings IUI. Association for Computing Machinery. 2018:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1145/3172944.3172988
Tan Y, Lin Y, Zang B et al (2022) An autonomous hybrid brain-computer interface system combined with eye-tracking in virtual environment. J Neurosci Methods 368:109442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2021.109442
Jiang L, Li X, Pei W, Gao X, Wang Y (2022) A hybrid brain-computer interface based on visual evoked potential and pupillary response. Front Hum Neurosci 16:834959. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2022.834959
Speier W, Arnold C, Pouratian N (2016) Integrating language models into classifiers for BCI communication: A review. J Neural Eng 13(3). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/13/3/031002
He S, Li Y (2017) A single-channel EOG-based speller. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25(11):1978–1987. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2716109
Fang T, Song Z, Niu L, et al (2021) Recent Advances of P300 Speller Paradigms and Algorithms. In: 9th IEEE International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, BCI 2021. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/BCI51272.2021.9385369
Yang L, Song Y, Ma K, Xie L (2021) Motor Imagery EEG Decoding Method Based on a Discriminative Feature Learning Strategy. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:368–379. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3051958
Jeannerod M (1995) Mental imagery in the motor context. Vol 33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(95)00073-C
Blankertz B, Dornhege G, Krauledat M et al (2006) The berlin brain-computer interface presents the novel mental typewriter HEX-O-SPELL. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Brain-Computer Interface Workshop and Training Course, September 21-2. Graz, Austria, pp 108–109
Chen C, Yang J, Xia B (2013) A cursor control based Chinese-English brain-computer interface speller. Transactions of Japanese Society for Medical and Biological Engineering, Published online
Xia B, Yang J, Cheng C, Xie H (2013) A Motor Imagery Based Brain-Computer Interface Speller. In Advances in Computational Intelligence: 12th International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, IWANN 2013, vol 7903. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp 413–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38682-4_44
Nama T, Samanta D (2022) Quarter Circle Speller: EEG Motor Imagery Signal-Based Text Entry System for Motor-Impaired People. Published online, Int J Hum Comput Stud
Bevilacqua M, Perdikis S, del Millán J, R, (2020) On error-related potentials during sensorimotor-based brain-computer interface: Explorations with a pseudo-online brain-controlled speller. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol 1:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1109/OJEMB.2019.2962879
Hou Y, Zhou L, Jia S, Lun X (2020) A novel approach of decoding EEG four-class motor imagery tasks via scout ESI and CNN. In: Journal of Neural Engineering. Vol 17. Institute of Physics Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ab4af6
Deng X, Zhang B, Yu N, Liu K, Sun K (2021) Advanced TSGL-EEGNet for Motor Imagery EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. IEEE Access 9:25118–25130. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3056088
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging Technology, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (54S18-014), the Key Laboratory of Biomedical Spectroscopy of Xi’an (201805050ZD1CG34), the Outstanding Award for Talent Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (29J20-052-III), “From 0 to 1” Original Innovation Project of the Basic Frontier Scientific Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (29J20-015-III).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Idea: Quan Wang, Xi Liu; Literature search and data analysis: Xi Liu; Draft: Xi Liu; Revision: Yang Si, Bingliang Hu, Quan Wang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Hu, B., Si, Y. et al. The role of eye movement signals in non-invasive brain-computer interface typing system. Med Biol Eng Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03070-7