Abstract
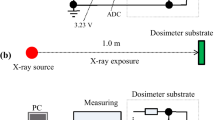
In this study, a newly developed capacitor dosimeter was evaluated using electron beams commonly utilized in radiotherapy. The capacitor dosimeter comprised a silicon photodiode, 0.47-μF capacitor, and dedicated terminal (dock). Before electron beam irradiation, the dosimeter was charged using the dock. The doses were measured without using a cable by reducing the charging voltages using the currents from the photodiode during irradiation. A commercially available parallel-plane-type ionization chamber and solid–water phantom were used for dose calibration with an electron energy of 6 MeV. In addition, the depth doses were measured using a solid–water phantom at electron energies of 6, 9, and 12 MeV. The doses were proportional to the discharging voltages, and the maximum dose difference in the calibrated doses measured using a two-point calibration was approximately 5% in the range of 0.25–1.98 Gy. The depth dependencies at energies of 6, 9, and 12 MeV corresponded to those measured using the ionization chamber.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hensley FW, Major G, Edel C, Hauswald H, Bischof M (2014) Technical and dosimetric aspects of the total skin electron beam technique implemented at Heidelberg University Hospital. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 19:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2013.07.002
Desai KR, Pezner RD, Lipsett JA et al (1988) Total skin electron irradiation for mycosis fungoides: relationship between acute toxicities and measured dose at different anatomic sites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 15:641–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(88)90306-9
Bourgouin A, Hackel T, Marinelli M, Kranzer R, Schüller A, Kapsch RP (2022) Absorbed-dose-to-water measurement using alanine in ultra-high-pulse-dose-rate electron beams. Phy Med Biol 67:205011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ac950b
Chand S, Mehra R, Chopra V (2021) Recent developments in phosphate materials for their thermoluminescence dosimeter (TLD) applications. Luminescence 36:1808–1817. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3960
Ciarmatori A, Nocetti L, Mistretta G, Zambelli G, Costi T (2016) Reducing absorbed dose to eye lenses in head CT examinations: the effect of bismuth shielding. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 39:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0445-y
Lopez-Rendon X, Stratis A, Zhang G et al (2020) Peak skin and eye lens radiation dose from brain perfusion CT: CTDIvol and Monte Carlo based estimations. Eur J Radiol 126:108950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108950
Anam C, Dewi WK, Masdi M, Haryanto F, Fujibuchi T, Dougherty G (2021) Investigation of eye lens dose estimate based on AAPM Report 293 in Head Computed Tomography. J Biomed Phys Eng 11:563–572. https://doi.org/10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2104-1304
Marsh RM, Silosky M (2015) Characterization and implementation of OSL dosimeters for use in evaluating the efficacy of organ-based tube current modulation for CT scans of the face and orbits. Med Phys 42:1730–1738. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4915076
Zhang D, Li X, Gao Y, Xu XG, Liu B (2013) A method to acquire CT organ dose map using OSL dosimeters and ATOM anthropomorphic phantoms. Med Phys 40:081918. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4816299
Christensen JB, Togno M, Nesteruk KP et al (2021) Al2O3: C optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters (OSLDs) for ultra-high dose rate proton dosimetry. Phys Med Biol 66:085003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/abe554
Han MJ, Yang SW, Bae SI et al (2021) Evaluation of monoxide film-based dosimeters for surface dose detection in electron therapy. PLoS ONE 16:0251441. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0251441
Wang X, Li G, Zhao J, Song Y, Xiao J, Bai S (2019) Verification of eye lens dose in IMRT by MOSFET measurement. Med Dosim 44:107–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2018.02.015
Hsing CH, Oanh LDH, Chao TC et al (2021) MOSFET dose measurements for proton SOBP beam. Phys Med 81:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.12.007
Buzurovic I, Showalter TN, Studenski MT et al (2013) Commissioning and implementation of an implantable dosimeter for radiation therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 14:234–252. https://doi.org/10.1120/jacmp.v14i2.3989
Su Z, Zhang L, Ramakrishnan V, Hagan M, Anscher M (2011) Investigations of interference between electromagnetic transponders and wireless MOSFET dosimeters: a phantom study. Med Phys 38:2450–2454. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3578602
Tendler I, Brůža P, Andreozzi J (2019) Rapid multisite remote surface dosimetry for total skin electron therapy: scintillator target imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103:767–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.030
Tendler II, Bruza P, Jermyn M (2020) Technical note: a novel dosimeter improves total skin electron therapy surface dosimetry workflow. J Appl Clin Med Phys 21:158–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12880
Yamaguchi S, Sato E (2019) Product development of a condenser dosimeter using a skin-insulated USB-A-substrate with a silicon X-ray diode. Radiol Phys Technol 12:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-018-00493-4
Yamaguchi S, Sato E, Ieko Y, Ariga H, Yoshioka K (2020) A capacitor dosimeter with disposable silicon-diode substrates for 4-MV X-ray beam detection in radiation therapy. Physics Open 4:100026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physo.2020.100026
Yamaguchi S, Ieko Y, Ariga H, Yoshioka K (2021) Characterization of an under-development capacitor dosimeter equipped with a silicon X-ray diode. Rev Sci Instrum 92:123101. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0061061
Alabdoaburas MM, Mege JP, Chavaudra J et al (2015) Experimental assessment of out-of-field dose components in high energy electron beams used in external beam radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 16:435–448. https://doi.org/10.1120/jacmp.v16i6.5616
Jeong S, An S, Kwon YC et al (2023) Development of a real-time in vivo dosimetry tool for electron beam therapy using a flexible thin film solar cell coated with scintillator powder. Med Phys 50:557–569. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.15947
Elsayad K, Moustakis C, Simonsen M et al (2018) In-vivo dosimetric analysis in total skin electron beam therapy. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol 6:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phro.2018.05.002
Baba MH, Singh BK, Wani SQ (2022) In vivo dosimetry for dose verification of total skin electron beam therapy using Gafchromic® EBT3 film dosimetry. J Med Phys 47:362–366. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmp.jmp_72_22
Dische S, Saunders MI, Williams C, Hopkins A, Aird E (1993) Precision in reporting the dose given in a course of radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 29:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8140(93)90146-y
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our deepest appreciation to Honorary Professor Eiichi Sato. He made a significant contribution to the design principle of the capacitor dosimeter discussed in this study. Without his support, this study would not have materialized. We also thank Nobuaki Mega for his help with the experiments. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for the English language editing service.
Funding
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 17K09068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Satoshi Yamaguchi: writing—original draft and editing, Yoshiro Ieko: visualization and investigation, Hisanori Ariga: supervision, and Kunihiro Yoshioka: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, S., Ieko, Y., Ariga, H. et al. Electron beam detection in radiotherapy using a capacitor dosimeter equipped with a silicon photodiode. Med Biol Eng Comput 61, 2197–2205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02870-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02870-7