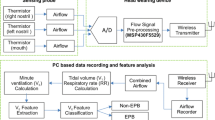
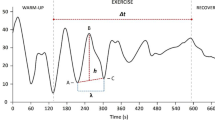
Abstract
Breathing pattern as periodic breathing (PB) in chronic heart failure (CHF) is associated with poor prognosis and high mortality risk. This work investigates the significance of a number of time domain parameters for characterizing respiratory flow cycle morphology in patients with CHF. Thus, our primary goal is to detect PB pattern and identify patients at higher risk. In addition, differences in respiratory flow cycle morphology between CHF patients (with and without PB) and healthy subjects are studied. Differences between these parameters are assessed by investigating the following three classification issues: CHF patients with PB versus with non-periodic breathing (nPB), CHF patients (both PB and nPB) versus healthy subjects, and nPB patients versus healthy subjects. Twenty-six CHF patients (8/18 with PB/nPB) and 35 healthy subjects are studied. The results show that the maximal expiratory flow interval is shorter and with lower dispersion in CHF patients than in healthy subjects. The flow slopes are much steeper in CHF patients, especially for PB. Both inspiration and expiration durations are reduced in CHF patients, mostly for PB. Using the classification and regression tree technique, the most discriminant parameters are selected. For signals shorter than 1 min, the time domain parameters produce better results than the spectral parameters, with accuracies for each classification of 82/78, 89/85, and 91/89 %, respectively. It is concluded that morphologic analysis in the time domain is useful, especially when short signals are analyzed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardi L, Porta C, Spicuzza L, Bellwon J, Spadacini G, Frey A, Yeung L, Sanderson JE, Pedretti R, Tramarin R (2002) Slow breathing increases arterial baroreflex sensitivity in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 105:143–145
Bhardwaj A, Rehman S, Mohammed A, Gaggin H, Barajas L, Barajas J, Moore S, Sullivan D, Januzzi J (2012) Quality of life and chronic heart failure therapy guided by natriuretic peptides: results from the proBNP outpatient tailored chronic heart failure therapy (protect) study. Am Heart J 164(793):799e1
Bouvy M, Heerdink E, Leufkens H, Hoes A (2003) Predicting mortality in patients with heart failure: a pragmatic approach. Heart 89(6):605–609
Corra U, Pistono M, Mezzani A, Braghiroli A, Giordano A, Lanfranchi P, Bosimini E, Gnemmi M, Giannuzzi P (2006) Sleep and exertional periodic breathing in chronic heart failure: prognostic importance and interdependence. Circulation 113(1):44–50
Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson P, Stromberg A, van Veldhuisen D, Atar D, Hoes A, Keren A, Mebazaa A, Nieminen M, Priori S, Swedberg K (2008) Esc guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the european society of cardiology. Eur Heart J 29(19):2388–2442
Fernandez H, Pattyn N, Mairesse O, Meeusen R, Mcdonald-Nethercott E, Neyt X (2013) One year monitoring of nocturnal periodic breathing at the antarctic pole. Sleep Med 14(Supplement 1):e119
Francis DP, Willson K, Davies LC, Coats AJ, Piepoli M (2000) Quantitative general theory for periodic breathing in chronic heart failure and its clinical implications. Circulation 102(18):2214–2221
Garde A, Laguna P, Giraldo B, Jané R, Sörnmo L (2012) Ensemble-based time alignment of biomedical signals. In: 7th international workshop on biosignal interpretation BSI2012, Como, Italy, pp 1–4
Garde A, Sörnmo L, Jané R, Giraldo B (2010) Breathing pattern characterization in chronic heart failure patients using respiratory flow signal. Ann Biomed Eng 38(12):3572–3580
Garde A, Sörnmo L, Jané R, Giraldo B (2010) Correntropy-based spectral characterization of respiratory patterns in patients with chronic heart failure. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(8):1964–1972
Guazzi M, Raimondo R, Vicenzi M, Arena R, Proserpio C, Braga SS, Pedretti R (2007) Exercise oscillatory ventilation may predict sudden cardiac death in heart failure patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(4):299–308
Hanly PJ, Zuberi-Khokhar NS (1996) Increased mortality associated with Cheyne–Stokes respiration in patients with congestive heart failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153(1):272–276
Javaheri S, Parker TJ, Liming JD, Corbett WS, Nishiyama H, Wexler L, Roselle GA (1998) Sleep apnea in 81 ambulatory male patients with stable heart failure. Types and their prevalences, consequences, and presentations. Circulation 97(21):2154–2159
Kaneko Y, Floras JS, Usui K, Plante J, Tkacova R, Kubo T, Ando S, Bradley TD (2003) Cardiovascular effects of continuous positive airway pressure in patients with heart failure and obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 348(13):1233–1241
Kesper K, Canisius S, Penzel T, Ploch T, Cassel W (2012) Ecg signal analysis for the assessment of sleep-disordered breathing and sleep pattern. Med Biol Eng Comput 50:135–144
La-Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Maestri R, Mortara A, Capomolla S, Febo O, Ferrari R, Franchini M, Gnemmi M, Opasich C, Riccardi PG, Traversi E, Cobelli F (2003) Short-term heart rate variability strongly predicts sudden cardiac death in chronic heart failure patients. Circulation 107:565–570
Lanfranchi PA, Braghiroli A, Bosimini E, Mazzuero G, Colombo R, Donner CF, Giannuzzi P (1999) Prognostic value of nocturnal Cheyne–Stokes respiration in chronic heart failure. Circulation 99(11):1435–1440
Levy W, Mozaffarian D, Linker D, Sutradhar S, Anker S, Cropp A, Anand I, Maggioni A, Burton P, Sullivan M, Pitt B, Poole-Wilson P, Mann D, Packer M (2006) The seattle heart failure model: prediction of survival in heart failure. Circulation 113(11):1424–1433
Lorenzi-Filho G, Dajani H, Leung R, Floras J, Douglas T (1999) Entrainment of blood pressure and heart rate oscillations by periodic breathing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:1147–1154
Lorenzi-Filho G, Genta PR, Figueiredo AC, Inoue D (2005) Cheyne-Stokes respiration in patients with congestive heart failure: causes and consequences. Clinics 60(4):333–344
Mansfield DR, Gollogly NC, Kaye DM, Richardson M, Bergin P, Naughton MT (2004) Controlled trial of continuous positive airway pressure in obstructive sleep apnea and heart failure. Am J Respit Crit Care Med 169(3):361–366
McFadden J, Price R, Eastwood H, Briggs R (1982) Raised respiratory rate in elderly patients: a valuable physical sign. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 284:626–627
Nussbaumer-Ochsner Y, Ursprung J, Siebenmann C, Maggiorini M, Bloch K (2012) Effect of short-term acclimatization to high altitude on sleep and nocturnal breathing. Sleep 35(3):419–423
Peduzzi P, Concato J, Feinstein A et al (1995) Importance of events per independent variable in proportional hazards regression analysis. II. accuracy and precision of regression estimates. J Clin Epidemiol 48:1503–1510
Pinna G, Maestri R, Robbi E, Rovere ML (2008) Periodic breathing and state instability during supine laboratory recordings in chronic heart failure patients. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference engineering in medicine and biology, pp 5398–5401
Pinna GD, Maestri R, Mortara A, Johnson P, Witkowski T, Ponikowski P, Andrews D, Capomolla S, La Rovere MT, Sleight P (2006) Nocturnal periodic breathing is an independent predictor of cardiac death and multiple hospital admissions in heart failure. Proc Comput Cardiol 33:837–840
Pinna GD, Maestri R, Mortara A, La Rovere MT, Fanfulla F, Sleight P (2000) Periodic breathing in heart failure patients: testing the hypothesis of instability of the chemoreflex loop. J Appl Physiol 89(6):2147–2157
Pocock S, Wang D, Pfeffer M, Yusuf S, McMurray J, Swedberg K, Ostergren J, Michelson E, Pieper K, Granger C (2006) Predictors of mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 27(1):65–75
Poletti R, Passino C, Giannoni A, Zyw L, Prontera C, Bramanti F, Clerico A, Piepoli M, Emdin M (2008) Risk factors and prognostic value of daytime cheyne-stokes respiration in chronic heart failure patients. Int J Cardiol 137(1):47–53
Ponikowski P, Anker SD, Chua TP, Francis D, Banasiak W, Poole-Wilson PA, Coats AJ, Piepoli M (1999) Oscillatory breathing patterns during wakefulness in patients with chronic heart failure: clinical implications and role of augmented peripheral chemosensitivity. Circulation 100(24):2418–2424
Ribeiro JP (2006) Periodic breathing in heart failure: bridging the gap between the sleep laboratory and the exercise laboratory. Circulation 113(1):9–10
Rodriguez-Molinero A, Narvaiza L, Ruiz J, Barron CG (2013) Normal respiratory rate and peripheral blood oxygen saturation in the elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc 61(12):2238–2240
Solin P, Roebuck T, Johns D, Walters E, Naughton M (2000) Peripheral and central ventilatory responses in central sleep apnea with and without congestive heart failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:2194–2200
Vazir A, Dayer M, Hastings PC, McIntyre HF, Henein MY, Poole-Wilson PA, Cowie MR, Morrell MJ, Simonds AK (2006) Can heart rate variation rule out sleep-disordered breathing in heart failure? Eur Respir J 27(3):571–577
Yamashiro S (2007) Non-linear dynamics of human periodic breathing and implications for sleep apnea therapy. Med Biol Eng Comput 45:345–356
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Secretaria d’Universitats i Recerca, del Departament d’Economía i Coneixement de la Generalitat de Catalunya (Consolidated research group GRC 2014 SGR 1569).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garde, A., Sörnmo, L., Laguna, P. et al. Assessment of respiratory flow cycle morphology in patients with chronic heart failure. Med Biol Eng Comput 55, 245–255 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1498-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1498-5