Abstract
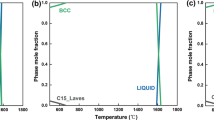
The structure and changes in the electrical resistivity of hafnium in the process of its electrolytic saturation with hydrogen have been studied at room temperatures. It has been established by X-ray diffraction that the surface layer in this case is enriched with a nonstoichiometric HfH2−x hydride (δ phase) whose concentration decreases fast with depth. A solid solution of hydrogen in hafnium has been found. The realization of a uniform distribution of the concentration of hydrogen and the hydride over the sample volume is retarded by a low mobility of hydrogen in the hafnium hydride and a weak solubility of hydrogen in hafnium. At the attained values of x, the resistivity of the hydride is higher than the resistivity of the initial hafnium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. J. Goldschmidt, Interstitial Alloys (Butterworths, London, 1967; Mir, Moscow, 1971).
O. M. Barabash and Yu. N. Koval', Crystal Structure of Metals and Alloys (Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 1986) [in Russian].
A. M. Shalaev, Properties of Irradiated Metals and Alloys (Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 1985) [in Russian].
Powder Diffraction File, (JCPDS, Swarthmore, Pa, 1977-1988).
E. Fromm and E. Gebhardt, Gase and Kohlestoff in Metallen (Springer, Berlin, 1976; Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1980).
V. I. Mikheeva, Transition Metal Hydrides (Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow, 1960) [in Russian].
S. D. Gertsriken and I. Ya. Dekhtyar', Diffusion of Metals and Alloys in Solids (Fizmatgiz, Moscow, 1960) [in Russian].
P W. Bickel and T. G. Berlincourt, “Electrical Properties of Hydrides and Deuterides of Zirconium,” Phys. Rev. B: Solid State 2 (12), 4807–4813 (1970).
B. Tsuchiya, M. Teshigawara, K. Konashi, et al., “Isotope Effects in Thermal Diffusivity and Electrical Resistivity of Zirconium Hydride and Deuteride,” J. Nucl. Sci. Techn. 39 (4), 402–406 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.V. Azhazha, K.V. Kovtun, S.V. Malykhin, B.A. Merisov, A.T. Pugachev, E.N. Reshetnyak, G.Ya. Khadzhai, 2008, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2008, Vol. 105, No. 2, pp. 201–205.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azhazha, R.V., Kovtun, K.V., Malykhin, S.V. et al. Accumulation of hydrogen in hafnium: Structure and electrical resistivity. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 105, 188–192 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11508-008-2011-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11508-008-2011-7