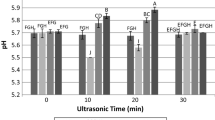
Abstract
Washing is a key process in surimi processing, whereby lipids, water-soluble proteins, pigments, and other factors that impede gel formation are separated from the fish. However, this process significantly reduces the meat yield of raw fish and destroys its nutrients, generating more organic wastewater. To enhance the process efficiency, ultrasound is used to assist washing process. This study aims to investigate the effects of ultrasound-assisted washing at different power levels (0 W, 150 W, 250 W, 350 W, and 450 W) on the quality, biochemical characteristics, protein conformation and gel-forming ability of surimi from silver carp. The results showed that ultrasound-assisted washing could increase yield by over 4% and reduce crude fat content by approximately 0.5% than control group. Protein secondary structure indicated that ultrasonic treatment of 250 W didn’t cause significant loss of α-helix. Moreover, the gel strength of 450 W group was roughly 17% more than that in control group. 250 W ultrasound-assisted washing was the most effective and significantly improved the productivity and quality of surimi.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. If any raw data files is needed in another format, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
M. Yingchutrakul, N. Wasinnitiwong, S. Benjakul, A. Singh, Y. Zheng, E. Mubango, Y. Luo, Y. Tan, H. Hong, Asian Carp, an Alternative Material for Surimi Production: Progress and Future. Foods 11(9), 1318 (2022)
N. Walayat, J. Liu, A. Nawaz, R.M. Aadil, M. López-Pedrouso, J.M. Lorenzo, Role of Food Hydrocolloids as Antioxidants along with Modern Processing Techniques on the Surimi Protein Gel Textural Properties, Developments, Limitation and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants 11(3), 486 (2022)
A.M. Martín-Sánchez, C. Navarro, J.A. Pérez-Álvarez, V. Kuri, Alternatives for Efficient and Sustainable Production of Surimi: A Review. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safe. 8(4), 359–374 (2009)
J.M.D.A. Kim, C.H. Liu, J.B. Eun, J.W. Park, R. Oshimi, K. Hayashi, B. Ott, T. Aramaki, M. Sekine, Surimi from fillet frames of channel catfish. J. Food Sci. 61(2), 428–432 (1996)
E.C.J.H. Hui-Huang Chen, Color and Gel-forming Properties of Horse Mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) as Related to Washing Conditions. J. Food Sci. 62(5), 985–991 (1997)
N. Badfar, M. Abdollahi, P.R. Stubbe, A. Jafarpour, Texture and viscoelastic characteristics of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi affected by combination of washing regimes and hydrogen peroxide. J. Texture Stud. 53(4), 490–502 (2022)
C. Liu, W. Li, B. Lin, S. Yi, B. Ye, H. Mi, J. Li, J. Wang, X. Li, Effects of ozone water rinsing on protein oxidation, color, and aroma characteristics of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi. J. Food Process. Preserv. 45(10), 15811 (2021)
L. Zhang, Q. Li, J. Shi, B. Zhu, Y. Luo, Changes in chemical interactions and gel properties of heat-induced surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during setting and heating: Effects of different washing solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 75, 116–124 (2018)
X. Gao, J. You, T. Yin, S. Xiong, R. Liu, Simultaneous effect of high intensity ultrasound power, time, and salt contents on gelling properties of silver carp surimi. Food Chem. 403, 134478 (2023)
C.P. O Donnell, B.K. Tiwari, P. Bourke, P.J. Cullen, Effect of ultrasonic processing on food enzymes of industrial importance. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 21(7), 358–367 (2010)
P. Cintas, Ultrasound and green chemistry − Further comments. UltrasonicsSonochem. 28, 257–258 (2016)
P. Somjid, W. Panpipat, T. Petcharat, M. Chaijan, Biochemical property and gel-forming ability of mackerel (Auxis thazard) surimi prepared by ultrasonic assisted washing. RSC Adv. 11(57), 36199–43627 (2021)
T. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Feng, Y. Liu, R. Suo, J. Jin, W. Wang, Ultrasonic pretreatment improves the gelation properties of low-salt Penaeus vannamei (Litopenaeus vannamei) surimi. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 86, 106031 (2022)
R. Saleem, R. Ahmad, Effect of low frequency ultrasonication on biochemical and structural properties of chicken actomyosin. Food Chem. 205, 43–51 (2016)
X. Zhang, Q. Guo, W. Shi, Ultrasound-assisted processing: Changes in gel properties, water-holding capacity, and protein aggregation of low-salt Hypophthalmichthys molitrix surimi by soy protein isolate. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 92, 106258 (2023)
P. Somjid, W. Panpipat, L.Z. Cheong, M. Chaijan, Reduced Washing Cycle for Sustainable Mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) Surimi Production: Evaluation of Bio-Physico-Chemical, Rheological, and Gel-Forming Properties. Foods 10(11), 2717 (2021)
Y. Shi, H. Wang, Y. Zheng, Z. Qiu, X. Wang, Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Vacuum Impregnation Antifreeze Protein on the Water-Holding Capacity and Texture Properties of the Yesso Scallop Adductor Muscle during Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Foods 11(3), 320 (2022)
B. Sun, Y. Zhao, J. Yu, J. Ling, H. Shang, Z. Liu, The combined efficacy of superchilling and high CO2 modified atmosphere packaging on shelf life and quality of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 26(6), 655–664 (2017)
J.J. Matsumoto, T. Kanamitsu, A Biuret Method for Determining Fish Muscle Proteins. Nihon-suisan-gakkai-shi 21(4), 284–288 (1955)
P.D. Simplicio, K. H. Cheeseman, T. F. Slater, The Reactivity of the Sh Group of Bovine Serum Albumin with Free Radicals. Free Radical Res. 14(4), 253–262 (1991)
L. Chen, G. Zhou, W. Zhang, Effects of High Oxygen Packaging on Tenderness and Water Holding Capacity of Pork Through Protein Oxidation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 8(11), 2287–2297 (2015)
C. H. Fiske, Y. Subbarow, The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. Biological Chem. 66(2), 375–400 (1925)
U.K. Laemmli, Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature (London) 227(5259), 680–685 (1970)
M. Zhang, F. Li, X. Diao, B. Kong, X. Xia, Moisture migration, microstructure damage and protein structure changes in porcine longissimus muscle as influenced by multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Meat Sci. 133, 10–18 (2017)
N. Buamard, S. Benjakul, Improvement of gel properties of sardine (Sardinella albella) surimi using coconut husk extracts. Food Hydrocoll. 51, 146–155 (2015)
X. Xia, B. Kong, J. Liu, X. Diao, Q. Liu, Influence of different thawing methods on physicochemical changes and protein oxidation of porcine longissimus muscle. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 46(1), 280–286 (2012)
J.W. Park, Surimi and Surimi Seafood, 3rd edn. (CRC Press, Taylor and Francis, 2013)
G. Velazquez, P. Miranda-Luna, G. López-Echevarría, M. Vázquez, J.A. Torres, J.A. Ramírez, Effect of Pacific whiting wash water proteins on Alaska pollack surimi gels. J. Texture Stud. 39(3), 296–308 (2008)
D. Kang, Y. Zou, Y. Cheng, L. Xing, G. Zhou, W. Zhang, Effects of power ultrasound on oxidation and structure of beef proteins during curing processing. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 33, 47–53 (2016)
R. Zhang, S. Xiong, J. You, Y. Hu, R. Liu, T. Yin, Effects of Ozone Treatments on the Physicochemical Changes of Myofibrillar Proteins from Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) during Frozen Storage. J. Food Quality 2017, 9506596 (2017)
H.C. Bertram, H.J. Andersen, NMR and the water-holding issue of pork. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 124(s1), 35–42 (2015)
M. Tan, J. Xie, Exploring the Effect of Dehydration on Water Migrating Property and Protein Changes of Large Yellow Croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during Frozen Storage. Foods 10(4), 784 (2021)
K.L. Pearce, K. Rosenvold, H.J. Andersen, D.L. Hopkins, Water distribution and mobility in meat during the conversion of muscle to meat and ageing and the impacts on fresh meat quality attributes - A review. Meat Sci. 89(2), 111–124 (2011)
Z. Gao, Effects of curing process on myofibrillar protein characteristics and water distribution of beef (in chinese). Food Fermentation Ind. 47(24), 179–186 (2021)
C. Arzeni, K. Martínez, P. Zema, A. Arias, O.E. Pérez, A. M. R. Pilosof, Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. J. Food Eng. 108(3), 463–472 (2012)
Y. An, J. You, S. Xiong, T. Yin, Short-term frozen storage enhances cross-linking that was induced by transglutaminase in surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chem. 257, 216–222 (2018)
G. Cao, X. Chen, B. Hu, Z. Yang, M. Wang, S. Song, L. Wang, C. Wen, Effect of ultrasound-assisted resting on the quality of surimi-wheat dough and noodles. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 94, 106322 (2023)
C. Yuanming, T. Mingtang, B. Chuhan, X. Jing, Effect of ultrasonic thawing on the physicochemical properties, freshness, and protein-related properties of frozen large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). J. Food Sci. 87(1), 52–67 (2021)
C. Wen, J. Zhang, J. Zhou, Y. Duan, H. Zhang, H. Ma, Effects of slit divergent ultrasound and enzymatic treatment on the structure and antioxidant activity of arrowhead protein. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 49, 294–302 (2018)
A. Amir, S. Parisa, M. Naghmeh, M. Alireza, M. Maryamalsaddat, N. Azadeh, G. Yi-gong, P. Anubhav, Modification of functional, rheological and structural characteristics of myofibrillar proteins by high-intensity ultrasonic and papain treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 72, 102748 (2021)
L. Zhang, Q. Li, H. Hong, Y. Luo, Prevention of protein oxidation and enhancement of gel properties of silver carp ( Hypophthalmichthys molitrix ) surimi by addition of protein hydrolysates derived from surimi processing by-products. Food Chem. 316(C), 126343 (2020)
R. Liu, Q. Liu, S. Xiong, Y. Fu, L. Chen, Effects of high intensity unltrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of myosin from silver carp. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 37, 150–157 (2017)
X. Gao, J. Yongsawatdigul, R. Wu, J. You, S. Xiong, H. Du, R. Liu, Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment modes on gelation properties of silver carp surimi. Food Sci. Technol. 150, 111945(2021)
L. Tang, J. Yongsawatdigul, Physicochemical properties of tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus ) actomyosin subjected to high intensity ultrasound in low NaCl concentrations. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 63(C), 104922 (2020)
L. De-Yang, T. Zhi-Feng, L. Zi-Qiang, W. Chao, L. Hui-Lin, G. Chao, Z. Da-Yong, Effect of hydroxyl radical induced oxidation on the physicochemical and gelling properties of shrimp myofibrillar protein and its mechanism. Food Chem. 351, 129344 (2021)
Z. Zhang, Y. Yang, P. Zhou, X. Zhang, J. Wang, Effects of high pressure modification on conformation and gelation properties of myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 217, 678–686 (2017)
M. Tan, J. Ye, Y. Chu, J. Xie, The effects of ice crystal on water properties and protein stability of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Int. J. Refrig. 130, 242–252 (2021)
D.E. Igartúa, M.C. Dichano, S.B. Ferrari, G.G. Palazolo, D.M. Cabezas, Combination of pH-shifting, ultrasound, and heat treatments to enhance solubility and emulsifying stability of rice protein isolate. Food Chem. 433, 137319 (2024)
G. Xiong, M. Han, Z. Kang, Y. Zhao, X. Xu, Y. Zhu, Evaluation of protein structural changes and water mobility in chicken liver paste batters prepared with plant oil substituting pork back-fat combined with pre-emulsification. Food Chem. 196, 388–395 (2016)
M. Tan, Z. Ding, J. Mei, J. Xie, Effect of cellobiose on the myofibrillar protein denaturation induced by pH changes during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 373, 131511 (2022)
S. Yi, M. Liang, F. Yu, D. Hongjie, Z. Yuhao, The improvement of gel and physicochemical properties of porcine myosin under low salt concentrations by pulsed ultrasound treatment and its mechanism. Food Res. Int. 141, 110056 (2021)
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Shanghai Ocean University Education Foundation (grant number X-0008–21-0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zeyu Song: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Funding acquisition; Investigation; Project administration; Writing-original draft; Writing-review and editing. Songxing Zhang: Data curation; Formal analysis; Investigation. Xinjuan Qi: Formal analysis; Funding acquisition; Validation. Mingyu Yin: Formal analysis; Funding acquisition; Validation; Writing-review and editing. Xichang Wang: Conceptualization; Funding acquisition; Investigation; Writing-review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Zhang, S., Qi, X. et al. Application of ultrasound technology in the washing process of surimi: improvement of meat yield and gel quality. Food Biophysics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-024-09843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-024-09843-9