Abstract
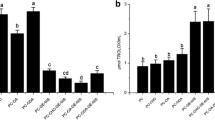
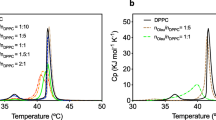
Liposome entrapment may improve activity of protein or polypeptide antimicrobials against a variety of microorganisms. In this study, ability of liposomes to withstand exposure to environmental and chemical stresses typically encountered in foods and food processing operations were tested. Liposomes consisting of distearoylphosphatidylcholine (PC) and distearoylphosphatidylglycerol (PG), with 0, 5, or 10 μg/ml of the antimicrobial peptide nisin entrapped, were exposed to elevated temperatures (25–75 °C) and a range of pH (5.5–11.0). Ability of liposomes to maintain integrity was assessed by measuring the encapsulation efficiency (EE), ζ-potential, and particle size distribution of liposomes. Distearoylphosphatidylcholine, PC/PG 8:2, and PC/PG 6:4 (mole fraction) liposomes retained between ~70–90% EE despite exposure to elevated temperature and alkaline or acidic pH. Particle size of liposomes averaged between 100 and 240 nm depending on liposome preparation. Liposomal surface charge depended primarily on phospholipid composition and changed little with inclusion of nisin. Surface charge was not affected by temperature for PC and PC/PG 8:2 but decreased for PC/PG 6:4 liposomes. Our results suggest that liposomes containing nisin may be suitable for use as antimicrobial-active ingredients in low- or high-pH foods subjected to moderate heat treatments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.S. Chrai, R. Murari and I. Ahmad, Biopharm-Appl T Bio 15, 40 (2002).
R.L. Juliano, Trends Pharmacol Sci 2, 39 (1981).
T.M. Allen and L.G. Cleland, Biochim Biophys Acta 597, 418 (1980).
M.C. Taira, N.S. Chiaramoni, K.M. Pecuch and S. Alonso-Romanowski, Drug Deliv 11, 123 (2004).
K. Makino, T. Yamada, M. Kimura, T. Oka, H. Ohshima and T. Kondo, Biophys Chemist 41, 175 (1991).
R.R.C. New, In: Liposomes: A Practical Approach, edited by R.R.C. New (Oxford University Press, New York, NY 1990), p. 33.
J.C. Shah, Y. Sadhale and D.M. Chilukuri, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47, 229 (2001).
J. Lasch, V. Weissig and M. Brandl, In: Liposomes: A Practical Approach, edited by V.P. Torchilin and V. Weissig (Oxford University Press, New York, NY 2003), p. 3.
T.M. Taylor, P.M. Davidson, B.D. Bruce and J. Weiss, J Agric Food Chem 53, 8722 (2005).
B.F. Gibbs, S. Kermasha, I. Alli and C.N. Mulligan, Int J Food Sci Nutr 50, 213 (1999).
R.-O. Benech, E.E. Kheadr, R. Laridi, C. Lacroix and I. Fliss, Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 3683 (2002).
R.-O. Benech, E.E. Kheadr, C. Lacroix and I. Fliss, Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 5607 (2002).
L.M. Were, B. Bruce, P.M. Davidson and J. Weiss, J Food Prot 67, 922 (2004).
L.M. Were, B.D. Bruce, P.M. Davidson and J. Weiss, J Agric Food Chem 51, 8073 (2003).
J.M. Jay, M.J. Loessner and D.A. Golden, Modern Food Microbiology (Springer, New York, NY 2005), p. 301.
E.A. Johnson and A.E. Larson, In: Antimicrobials in Foods, edited by P.M. Davidson, J.N. Sofos and A.L. Branen (CRC Press, New York, NY 2005), p. 361.
J.S. Boland, P.M. Davidson, B. Bruce and J. Weiss, J Food Prot 67, 285 (2004).
J.K. Branen and P.M. Davidson, Int J Food Microbiol 90, 63 (2004).
D.-S. Jung, F.W. Bodyfelt and M.A. Daeschel, J Dairy Sci 75, 387 (1992).
L.V. Thomas and J. Delves-Broughton, In: Antimicrobials in Food, edited by P.M. Davidson, J.N. Sofos and A.L. Branen (CRC Press, New York, NY 2005), p. 237.
J. Delves-Broughton, Food Technol 44, 110 (1990).
P. Pinnaduwage and B.D. Bruce, J Biol Chem 271, 32907 (1996).
J. Tramer and G.G. Fowler, J Sci Food Agric 15, 522–528 (1964).
Y.-F. Hsieh, T.-L. Chen, Y.-T. Wang, J.-H. Chang and H.-M. Chang, J Food Sci 67, 2808 (2002).
H. Kitano, Y. Akatsuka and N. Ise, Macromolecules 24, 42 (1991).
Y.P. Zhang, R.N. Lewis and R.N. McElhaney, Biophys J 72, 779 (1997).
E.J. Findlay and P.G. Barton, Biochemistry 17, 2400 (1978).
T. Taylor, P.M. Davidson, B. Bruce and J. Weiss, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45, 587 (2005).
D.J. McClements, Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 2005).
R. Willumeit, M. Kumpugdee, S.S. Funari, K. Lohner, B.P. Navas, K. Brandenburg, S. Linser and J. Andra, Biochim Biophys Acta 1669, 125 (2005).
Y.-Z. Huang, J.-Q. Gao, W.-Q. Liang and S. Nakagawa, Biol Pharm Bull 28, 387 (2005).
R.M. Straubinger, N. Duzgunes and D. Papahadjopoulos, FEBS Lett 179, 148 (1985).
S.-C. Lee, H.-G. Yuk, D.-H. Lee, K.-E. Lee, Y.-I. Ludescher and R.D. Ludescher, J Biochem Mol Biol 35, 358 (2002).
R. El-Jastimi, K. Edwards and M. Lafleur, Biophys J 77, 842 (1999).
F.H. Gao, T. Abee and W.N. Konings, Appl Environ Microbiol 57, 2164 (1991).
C. Van Kraau, E. Breukink, H.S. Rollema, R. Siezen, R.A. Demel, B. De Kruijkk and O.P. Kuipers, Eur J Biochem 247, 114 (1997).
A.J.M. Driessen, H.W. van den Hooven, W. Kuiper, M. van de Kamp, H.-G. Sahl, R.N.H. Konings and W.N. Konings, Biochemistry 34, 1606 (1995).
E. Breukink and B. de Kruijff, Biochim Biophys Acta 1462, 223 (1999).
W. Liu and J.N. Hansen, Appl Environ Microbiol 56, 2551 (1990).
E. Breukink, P. Ganz, B. De Kruijff and J. Seelig, Biochemistry 39, 10247 (2000).
J.R. Wiener, R.R. Wagner and E. Freire, Biochemistry 22, 6117 (1983).
G. Yohannes, K.-H. Pystynen, M.-L. Riekkola and S.K. Wiedmer, Anal Chim Acta 560, 50–56 (2006).
R. Laridi, E.E. Kheadr, R.-O. Benech, J.C. Vuillemard, C. Lacroix and I. Fliss, Int Dairy J 13, 325 (2003).
T.M. Bayerl and M. Bloom, Biophys J 58, 357 (1990).
D.B. Fenske and P.R. Cullis, Biophys J 64, 1482 (1993).
B.B. Bonev, W.C. Chan, B.W. Bycroft, G.C.K. Roberts and A. Watts, Biochemistry 39, 11425 (2000).
R. El-Jastimi and M. Lafleur, Biochim Biophys Acta 1324, 151 (1997).
R. El-Jastimi and M. Lafleur, Biochim Biophys Acta 1418, 97 (1999).
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by a USDA NRI grant (USDA NRI 2004-35201-15358) and the Massachusetts and Tennessee Experiment Station (Hatch MAS 00911 and TEN 00263).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, T.M., Gaysinsky, S., Davidson, P.M. et al. Characterization of Antimicrobial-bearing Liposomes by ζ-Potential, Vesicle Size, and Encapsulation Efficiency. Food Biophysics 2, 1–9 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-007-9023-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-007-9023-x