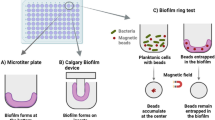
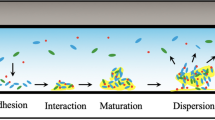
Abstract
This article highlights the role of biophysical principles in biofilm growth and propagation in food environments, an area that is of increasing concern to food processors due to the high resistance of biofilms to conventional remediation methodologies. First, the general characteristics of biofilms are discussed including their structure and physiological characteristics. Transfer and propagation mechanisms consisting of attachment followed by growth and subsequent detachment are reviewed. General growth models that are currently used in laboratories focusing on biofilm research are compared and emerging characterization techniques are discussed. An overview over current practices and techniques to remediate biofilms in a variety of environments is given. Remediation techniques that are reviewed include application of sanitizers and detergents. Finally, future research needs are briefly summarized.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Moretro and S. Langsrud, Listeria monocytogenes: biofilm formation and persistence in food-processing environments. Biofilms 1, 107 (2004).
R.M. Donlan, Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8, 881 (2002).
C.A. Fux, J.W. Costerton and P.S. Stewart et al., Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13, 34 (2005).
P. Stoodley, S. Wilson and L. Hall-Stoodley et al., Growth and detachment of cell clusters from mature mixed-species biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 67, 5608 (2001).
K. Kierek-Pearson and E. Karatan, Biofilm development in bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol 57, 79 (2005).
R. Van Houdt and C.W. Michiels, Role of bacterial cell surface structures in Escherichia coli biofilm formation. Res Microbiol 156, 626 (2005).
J.F. Frank, Microbial attachment to food and food contact surfaces. Adv Food Nutr Res 43, 319 (2001).
C. Ganesh Kumar and S.K. Anand, Significance of microbial biofilms in food industry: a review. Intl J Food Microbiol 42, 9 (1998).
S.K. Hood and E.A. Zottola, Adherence to stainless steel by foodborne microorganisms during growth in model food systems. Intl J Food Microbiol 37, 145 (1997).
S. Wong, D. Street and S.I. Delgado et al., Recalls of foods and cosmetics due to microbial contamination reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. J Food Prot 63, 1113 (2000).
H.F. Jenkinson and H.M. Lappin-Scott, Biofilms adhere to stay. Trends Microbiol 9, 9 (2001).
Y.H. An and R.J. Friedman, Laboratory methods for studies of bacterial adhesion. J Microbiol Methods 30, 141 (1997).
R.J. Doyle, Microbial Growth in Biofilms—Part A: Developmental and Molecular Biological Aspects (Academic Press, San Diego, CA 2001).
G.A. O'Toole, H.B. Kaplan and R. Kolter, Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol 54, 49 (2002).
L.V. Poulsen, Microbial biofilm in food processing. Lebensm-Wiss Technol 32, 321 (1999).
I.W. Sutherland, The biofilm matrix—an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol 9, 222 (2001).
K.Y. Kim and J.F. Frank, Effect of nutrients on biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes on stainless steel. J Food Prot 58, 24 (1995).
N.G. Marriott, Principles of Food Sanitation (Aspen Publishers, Gaithersburg, MD, 1999).
P. Sommer, C. Martin-Rouas and E. Mettler, Influence of the adherent population level on biofilm population, structure and resistance to chlorination. Food Microbiol 16, 503 (1999).
A.E. Hodgson, S.M. Nelson and M.R.W. Brown et al., A simple in vitro model for growth control of bacterial biofilms. J Appl Bacteriol 79, 87 (1995).
S.L. Kuchma and G.A. O'Toole, Surface-induced and biofilm-induced changes in gene expression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11, 429 (2000).
G.A. O'Toole and R. Kolter, Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28, 449 (1998).
S. Sauer, A.K. Camper, G.D. Ehrlich, et al., Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J Bacteriol 184, 1140 (2002).
J.F. Frank and R.A.N. Chmielewski, Effectiveness of sanitation with quaternary ammonium compoind or chlorine on stainless steel and other domestic food-preparation surfaces. J Food Prot 60, 43 (1997).
S. Vatanyoopaisarn, A. Nazli and C.E.R. Dodd et al., Effect of flagella on initial attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel. Appl Environ Microbiol 66, 860 (2000).
K.J. Bolton, C.E.R. Dodd and G.C. Mead et al., Chlorine resistance of strains fo Staphylococcus aureus isolated from poultry processing plants. Lett Appl Microbiol 6, 31 (1988).
C.K. Bower and M.A. Daeschel, Resistance reponses of microorganisms in food environments. Int J Food Microbiol 50, 33 (1999).
R.M. Donlan and J.W. Costerton, Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 15, 167 (2002).
W.M. Dunne, Bacterial Adhesion: Seen any good biofilms lately? Clin Microbiol Rev 15, 155 (2002).
J.F. Frank, R.A.N. Gillett and G.O. Ware, Association of Listeria spp. contamination in the dairy processing plant environment with the presence of staphylococci. J Food Prot 53, 928 (1990).
J.F. Frank and R.A. Koffi, Surface-adherent growth of Listeria monocytogenes is associated with increased resistance to surfactant sanitizers and heat. J Food Prot 53, 550 (1990).
M.W. LeChevallier, C.D. Cawthon and R.G. Lee, Inactivation of biofilm bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 54, 2492 (1988).
J.C. Nickel and J.W. Costerton, Bacterial biofilms and catheters: A key to understanding bacterial straegies in catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Can J Infect Dis 3, 619 (1992).
G. Reid, C. Tieszer and R. Foerch et al., Adsoption of ciprofloxacin to urinary catheters and effect on subsequent bacterial adheion and survival. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces 1, 9 (1993).
E. Werner, F. Roe and A. Bugnicourt et al., Stratified growth in Pseudomonas areuginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 6188 (2004).
S.E. Crampton, C. Gerke and F. Gotz, In: Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 336 Microbial Growth in Biofilms Part A. Developmental and Molecular Biological Aspects, edited by R.J. Doyle (San Diego, CA 2001), p. 239.
G.M. Dunny and S.C. Winans, Cell–cell Signaling in Bacteria (ASM Press, Washington, DC 1999).
S. Moller, C. Sternberg and J.B. Andersen et al., In situ gene expression in mixed-cultures biofilms: evidence of metabolic interactions between community members. Appl Environ Microbiol 64, 721 (1998).
A.N. Hassan, D.M. Birt and J.F. Frank, Behavior of Listeria monocytogenes in a Pseudomona putida biofilm on a condensate-forming surface. J Food Prot 67, 322 (2004).
K.C. Sasahara and E.A. Zottola, Biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes utilizes a primary colonizing microorganism in flowing systems. J Food Prot 56, 1022 (1993).
V. Leriche and B. Carpentier, Limitation of adhesion and growth of Listeria monocytogenes on stainless steel surfaces by Staphylococcus sciuri biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 88, 594 (2000).
D.E. Norwood and A. Gilmour, The differential adherence capabilities of two Listeria monocytogenes strains in monoculture and multispecies biofilms as function of temperature. Lett Appl Microbiol 33, 320 (2001).
M.S. Chae and H. Schraft, Cell viability of Listeria monocytogenes biofilms. Food Microbiol 18, 103 (2001).
M.S. Chae and H. Schraft, Comparative evaluation of adhesion and biofilm formation of different Listeria monocytogenes strains. Int J Food Microbiol 62, 103 (2000).
R.B. Tompkin, V.N. Scott and D.T. Bernard et al., Guidelines to prevent post-processing contamination from Listeria monocytogenes. Dairy Food Environ Sanit 19, 551 (1999).
M.C.M. van Loosdrecht, D. Eikelbook and A. Gjaltema et al., Biofilm structures. Water Sci Technol 32, 35 (1995).
J. Wimpenny, W. Manz and U. Szewzyk, Heterogeneity in Biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24, 661 (2000).
M.C.M. van Loosdrecht, C. Picioreanu and J.J. Heijnen, A more unifying hypthesis for biofilm structures. FEMS Microbiol Lett 24, 181 (1997).
L.B. Purevdorj-Gage and P. Stoodley, Biofilm structure, behaviour, and hydrodynamics. In: Microbial biofilms, edited by M. Ghannoum and G.A. O'Toole (ASM Press, Washington, DC 2004), p. 160.
K.W. Millsap, G. Reid and H.C. van der Mei et al., Adhesion of Lactobacillus species in urine and phosphate buffer to silicone rubber and glass under flow. Biomaterials 18, 87 (1996).
M.A. Pereira, M. Kuehn and S. Wuertz et al., Effect of flow regime on the architecture of a Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilm. Biotechnol Bioeng 78, 164 (2002).
H.H.M. Rijnaarts, W. Norde and E.J. Bouwer et al., Bacterial adhesion under static and dynamic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 59, 3255 (1993).
M. Fletcher, Bacterial attachement in aquatic environments: a diversity of surfaces and adhesion strategies. In: Bacterial Adhesion: Molecular and Ecological Diversity, edited by M. Fletcher (Wiley-Liss, New York 1996), p. 1.
J.N. Israelachvili, Intermolecular and Surface Forces (Academic Press, San Diego, CA 1992).
A.M. James, Charge properties of microbial cell surfaces. In: Microbial Cell Surface Analysis—Structural and Physicochemical Methods, edited by N. Mozes, P.S. Handley, H.J. Busscher and P.G. Rouxhet (VCH Publishers, New York 1991), p. 221.
D.J. McClements, Food Emulsions: Principles, Practice and Techniques (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 1999).
D.R. Olivera, Physio-Chemical Aspects of Adhesion. In: Biofilms-Science and Technology, edited by L.F. Melo, T.R. Bott, M. Fletcher and B. Capdeville (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordecht, the Netherlands 1992).
H.J. Busscher, J. Sjollema and H.C. v.d. Mei, Relatie importance of surface free energy as a measure of hydrophobicity in bacterial adhesion to solid surfaces. In: Microbial Cell Surface Hydrophobicity, edited by R.J. Doyle and M. Rosenberg (ASM, Washington, DC 1990).
G. Reid, C. Tieszer and R. Foerch et al., Adsoption of ciprofloxacin to urinary catheters and effect on subsequent bacterial adheion and survival. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces 1, 9 (1993).
M.A. Assanta, D. Roy and D. Montpetit, Adhesion of Aeromonas hydrophila to water distribution systems pipes after different contact times. J Food Prot 61, 1321 (1998).
J.B. Kaplan, M.F. Meyenhofer and D.H. Fine, Biofilm growth and detachment of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomintans. J Bacteriol 185, 1399 (2003).
E. Scott and S.F. Bloomfield, The survival and transfer of microbiological contamination via cloths, hands and utensils. J Appl Bacteriol 68, 271 (1990).
L.M. Smoot and M.D. Pierson, Influence of environmnetal stress on the kinetics and strength of attachement of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A to Buna-N rubber and stainless steel. J Food Prot 61, 1286 (1998).
J. Josephsen and F.K. Vogensen, Identificaiton of three different plasmid-encoded restriciton/modification systems in Streptococcus lactis subsp. cremoris W56. FEMS Microbiol Lett 59, 161 (1989).
R. Braindet, V. Leriche and B. Carpentier et al., Effects of the growth procedure on the surface hydrophbicity and Listeria monocytogenes cells and their adhesion to stainless steel. J Food Prot 62, 994 (1999).
A.A. Mafu, D. Roy and J. Goulet et al., Characterization of physiochemical forces involved in adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 57, 1969 (1991).
P. Chavant, B. Martinie and T. Meylheuc et al., Listeria monocytogenes L028: Surface physiochemical properties and ability to form biofilms at different temperatures and growth phases. Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 728 (2002).
G. Wirtanen and T. Mattila-Sandholm, Epifluorescence image analysis and cultivation of foodborn biofilm bacteria grown on stainless steel surfaces. J Food Prot 56, 678 (1993).
J. Azaredo and R. Oliveira, The role of exopolymers in the attachment of Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Biofouling 16, 59 (2000).
H. Al-Makhlafi, J. McGuire and M. Daeschel, Influence of preabsorbed milk proteins on adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to hydrophobic and hydrophilic silica surfases. Appl Environ Microbiol 60, 3560 (1994).
H. Al-Makhlafi, A. Nasir and J. McGuire et al., Adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to silica surfaces after suqential and competitive adsoption of bovine serum albumin and B-lactoglobulin Appl Environ Microbiol 61, 2013 (1995).
L.-M. Barnes, M.F. Lo and M.R. Adams et al., Effect of milk proteins on adhesion of bacteria to stainless steel surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 4543 (1999).
D. Cunliffe, C.A. Smart and C. Alexander et al., Bacterial adesion at synthetic surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 4995 (1999).
J.W. Costerton, Overview of microbial biofilms. J Ind Microbiol 15, 137 (1995).
J.W. Costerton, K.J. Cheng and G.G. Geesey et al., Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41, 435 (1987).
I. Kapper, C.J. Rupp and R. Cargo et al., Viscoelastic fluid description of bacterial biofilm material properties. Biotechnol Bioeng 80, 289 (2002).
B. Purevdorj, J.W. Costerton and P. Stoodley, Influence of hydrodynamics and cell signaling on the structure and behavior of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 4457 (2002).
P.J. Herald and E.A. Zottola, Attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel surfaces at various temperature and pH values. J Food Sci 53, 1549 (1988).
K.Y. Kim and J.F. Frank, Effect of growth nutrients on attachement of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel. J Food Prot 57, 720 (1994).
L.M. Smoot and M.D. Pierson, Effect of environmental stress on the ability of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A to attach to food contact surfaces. J Food Prot 61, 1293 (1998).
A.G. Moltz and S.E. Martin, Formation of biofilms by Listeria monocytogenes under various growth conditions. J Food Prot 68, 92 (2005).
S. Stepanovic, I. Cirkovic and L. Ranin et al., Biofilm formation by Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes on plastic surface. Lett Appl Microbiol 38, 428 (2004).
A.A. Mafu, D. Roy and J. Goulet et al., Attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel, glass, polypropylene, and rubber surfaces after short contact times. J Food Prot 53, 742 (1990).
S. Wilson, M.A. Hamilton and G.C. Hamilton et al., Statistical quantification of detachment rates and size distributions of cell clumps form wild-type (PAO1) and cell signaling mutant (JP1) Pseudomonas aeuginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 5847 (2004).
C. Fux, S. Wilson and P. Stoodley, Detachment characteristics and oxacillin resitance of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm emboli in an in vitro catheter infection model. J Bacteriol 186, 4486 (2004).
B. Purevdorj-Gage, W.J. Costerton and P. Stoodley, Phenotypic differentiation and seeding dispersal in non-mucoid and mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbiology 151, 1569 (2005).
C.J. Rupp, C.A. Fux and P. Stoodley, Viscoelasticity of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in responce to fluid shear allows resistance to detachment and facilitates rolling microation. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 2175 (2005).
C. Rupp, S. Wilson and P. Stoodley, Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Rolling Along the Lumen of a Glass Tube. (ASM MicrobeLibrary.org, 2002).
S.M. Hunt, E.M. Werner and B. Huang et al., Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 7418 (2004).
L.K. Sawyer and S.W. Hermanowicz, Detachment of Aeromonas hydrophila and Pseudomonas aeruginosa due to variations in nutrient supply. Water Sci Technol 41, 139 (2000).
D.G. Allison, B. Ruiz and C. SanJose et al., Extracellular products as mediators of the formation and detachment of Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 167, 179 (1998).
A. Boyd and A.M. Chakrabarty, Role of alginate lyase in cell detachment of Pseudomona aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 60, 2355 (1994).
K.M. Thormann, R.M. Savilee and S. Shukla et al., Induction of rapid detachment in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms. J Bacteriol 187, 1014 (2005).
A.C. Lee Wong, Biofilms in food processing environments. J Dairy Sci 81, 2765 (1998).
A.F. Merry, T.E. Miller and G. Findon et al., Touch contamination levels during anaesthetic procedures and their relationship to hand hygiene procedures: a clinical audit. Br J Anaesth 87, 291 (2001).
D.R. Patrick, G. Findon and T.E. Miller, Residual moisture determines the level of touch-contact-associated bacterial transfer following hand washing. Epidemiol Infect 119, 319 (1997).
S.A. Sattar, S. Springthorpe and S. Mani et al., Transfer of bacteria from fabrics to hands and other fabrics: development and application of a quantitative method using Staphylococcus aureus as a model. J Appl Bacteriol 90, 962 (2001).
G. Midelet and B. Carpentier, Transfer of microorganisms, including Listeria monocytogenes from various materials to beef. Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 4015 (2001).
K. Dastorri and B. Makin, Adhesion measurements for electrostatic powder coating using drop test rig and virtual oscilloscope. J Electrost 51, 509 (2001).
P. Stoodley, R. Cargo and C.J. Rupp et al., Biofilm material properties as related to shear induced deformation and detachment phenomena. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 361 (2002).
P. Stoodley, D. deBeer and Z. Lewandowski, Liquid flow in biofilm systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 60, 2711 (1994).
C. Picioreanu, M.C.M. van Loodstrecht and J.J. Heijnen, Two-dimensional model of biofilm detachment caused by internal stress from liquid flow. Biotechnol Bioeng 72, 205 (2001).
S.P. Cole, J. Harwood and R. Lee et al., Characterization of monospecies biofilm formation by Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol 186, 3124 (2004).
D. Djordjevic, M. Wiedmann and L.A. McLandsborough, Microtiter plate assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 2950 (2002).
G. Ramage, K. VandeWalle and B.L. Wickes, et al., Characteristics of biofilm formation by Candida albicans. Rev Iber Micol 18, 163 (2001).
M. Augustin and T. Ali-Vehmas, Assessment of enzymatic cleaning agents and disinfectants against bacterial biofilms. J Pharmacol Pharm Sci 7, 55 (2004).
R.J.C. McLean, C.L. Bates and M.B. Barnes et al., Methods of studying biofilms. In: Microbial Biofilms, edited by M. Ghannoum and G.A. O'Toole (ASM Press, Washington, DC 2004), p. 379.
H. Ceri, M.E. Olson and C. Stremick et al., The Calgary Biofilm Device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J Clin Microbiol 37, 1771 (1999).
N. Cerca, G.B. Pier and M. Vilanova et al., Influence of batch or fed-batch growth on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. Lett Appl Microbiol 39, 420 (2004).
J.N. Anderl, M.J. Franklin and P.S. Stewart, Role of antibiotic penetration limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm resistance to ampicilin and ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44, 1818 (2000).
G. Borrielo, E. Werner and F. Roe et al., Oxygen limitation contributes to antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48, 2659 (2004).
E.J. Wentland, P.S. Stewart C.-T. Huang et al., Spatial variations in growth rate within Klebsiella pneumoniae colonies and biofilm. Biotechnol Prog 12, 316 (1996).
X. Chen and P.S. Stewart, Biofilm removal caused by chemical treatments. Water Res 34, 4229 (2000).
B.B. Christensen, C. Sternberg and J.B. Andersen et al., Molecular tools for the study of biofilm physiology. Methods Enzymol 310, 20 (1999).
W.F. McCoy, J.D. Bryers and J. Robbins et al., Observations of fouling biofilm formation. Can J Microbiol 27, 910 (1981).
J.C. Nickel, I. Ruseska and J.B. Wright et al., Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27, 619 (1985).
R.M. Donlan, R. Murga and L. Carson, Growing biofilms in intravenous fluids. In: Biofilms: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, edited by J. Wimpenny, P. Gilbert, J. Walker, M. Brading, and R. Bayston (Bioline, Cardiff, Wales, 1999), p. 23.
S. Okabe, T. Itoh and H. Satoh et al., Analyses of spatial distributions of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their activity in aerobic wastewater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 5107 (1999).
R.M. Donlan, J.A. Piede and C.D. Heyes et al., Model system for growing and quantifying Streptococcus pneumonieae biofilms in situ and in real time. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 4980 (2004).
R.M. Donlan, R. Murga and J. Carpenter et al., Monochloramine disinfection of biofilm-associated Legionella pneumophila in a potable water model system. In: Legionella, edited by R. Marre, Y.A. Kwaik, C. Bartlett, N.P. Cianciotto, B.S. Fiekds, M. Frosch, J. Hacker, and P.C. Lück (American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC 2002).
D.M. Goeres, L.R. Loetterle and M.A. Hamilton et al., Statistical assessment of a laboratory method for growing biofilms. Microbiology 151, 757 (2005).
A.K. Camper, W.L. Jones and J.T. Hayes, Effect of growth conditions and substratum composition on the persistence of coliforms in mixed-population biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 62, 4014 (1996).
L.M. Laurence and A. Gilmore, Characterization of Listeria monocytognes isolated form poultry products and from the poulty-processing envronment by random amplification of polymorphic DNA and multilocus enzyme electrophorsis. Appl Environ Microbiol 61, 2139 (1995).
J.R. Knowles, S. Roller and D.B. Murray et al., Antimicrobial action of carvacrol at different stages of dual-species biofilm development by Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhymurium. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 797 (2005).
J.L. Kadurugamuwa, L.V. Sin and J. Yu et al., Noninvasive optical imaging method to evaluate postantibiotic effects on biofilm infection in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48, 2283 (2004).
I. Raad, W. Costerton and U. Sabharwal et al., Ultrastructural analysis of indwelling vascular catheters: a quantitative relationship between luminal colonization and duration of placement. J Infect Dis 168, 400 (1993).
R.C. Hunter and T.J. Beveridge, Application of a pH-sensitive fluoroprobe (C-SNARF-4) for pH microenvironment analysis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 2501 (2005).
S.C.C. Foong and J.S. Dickson, Attachment of Listeria monocytogenes on ready-to-eat meats. J Food Prot 67, 456 (2004).
P. Chavant, B. Gaillard-Martinie and M. Hébraud, Antimicrobial effects of sanitizers against planktonic and sessile Listeria monocytogenes cells according to the growth phase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 236, 241 (2004).
B. Little and P. Wagner, An overview of microbiologically influenced corrosion of metals and alloys. Can J Microbiol 42, 367 (1996).
J.R. Lawrence and T.R. Neu, Confocal laser scanning microscopy for analysis of microbial biofilms. Methods Enzymol 310, 131 (1999).
P.A. Suci, M.W. Mittelman and F.P. Yu et al., Investigation of ciprofloxacin penetration into Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38, 2125 (1994).
D.E. Nivens, J.Q. Chambers and T.R. Anderson et al., Monitoring microbial adhesion and biolfilm formation by attenuated total reflection/Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 17, 199 (1993).
H.C. Flemming, J. Wingender and T. Griegbe et al., Physico-chemical properties of biofilms. In: Biofilms: Recent Advances in their Study and Control, edited by L.V. Evans (Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam 2000), p. 19.
Z. Lewandowski, Structure and function of biofilms. In: Biofilms: Recent Advances in their Study and Control, edited by L. V. Evans (Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam, 2000), Vol. 1–17.
R. Murga, J.M. Miller and R.M. Donlan, Biofilm formation by gram-negative bacteria on central venous catheter connectors: effect of conditioning films in a laboratory model. J Clin Microbiol 39, 2294 (2001).
P.S. Stewart, B.M. Peyton and W.J. Drury et al., Quantitative observations of heterogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 59, 327 (1993).
T.C. Zhang and P.L. Bishop, Density, porosity, and pore structure of Biofilms. Water Res 28 (1994).
H. Beyenal, C. Donovan and Z. Lewandowski et al., Three-dimensional biofilm structure quantification. J Microbiol Methods 59, 395 (2004).
S.W. Hermanowicz, U. Schindler and P.A. Wilderer, Fractal structure of biofilms: new tools for investigation of morphology. Water Sci Technol 32, 99 (1995).
V.J.M. Allan, L.E. Macaskie and M.E. Callow, Development of a pH gradient within a biofilm is dependent upon the limiting nutrient. Biotechnol Lett 21, 407 (1999).
J.W. Costerton, Z. Lewandowski and D. DeBeer et al., Biofilms, the customized microniche. J Bacteriol 176, 2137 (1994).
I.B. Beech, J.R. Smith and A.A. Steele et al., The use of atomic force microscopy for studying interactions of bacterial biofilms with surfaces. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces 23, 231 (2002).
P.J. Bremer, G.G. Geesey and B. Drake, Atomic force microscopy examination of the topography of hydrated bacterial biofilm on a copper surface. Curr Microbiol 24, 223 (1992).
P.G. Rouxhet, N. Mozes and P.B. Dengis et al., Application of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to microorganisms. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces 2, 347 (1994).
X. Yang, H. Beyenal and G. Harkin et al., Quantifying biofilm structure using image analysis. J Microbiol Methods 39, 109 (2000).
A. Heydorn, A.T. Nielsen and M. Hentzer et al., Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program COMSTAT. Microbiology 146, 2395 (2000).
C. Niu and E.S. Gilbert, Colorimetric method for identifying plant essential oil components that affect biofilm formation and structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 6951 (2004).
C.J. Van Oss, R.J. Good and M.K. Chaudry, The role of van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds in ‘hydrophobic interactions’ between biopolymers and low energy surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 111, 378 (1986).
K. Triandafillu, D.J. Balazs and B.O. Aronsson et al., Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains to untreated and oxygen-plasma treated poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) from endotracheal intubation devices. Biomaterials 24, 1507 (2003).
L.S. Stone and E.A. Zottala, Effect of cleaning and sanitizing on the attachment of Pseudomonas fragi to stainless steel. J Food Sci 50, 957 (1985).
S.E. Lentsch, Sanitizers for an effective cleaning program. In: Sanitation Notebook for the Seafood Industry, edited by G.J. Flick, C.L. Kassem, F. Huang, D.R. Ward, M.J. Thompson and C. Fletcher (Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg, VA 1978), p. 11.
C.K. Bower, J. McGuire and M.A. Daeschel, The adhesion and detachment of bacteria and spores on food-contact surfaces. Trends Food Sci Technol 7, 152 (1996).
R.M. Donlan and J.W. Costerton, Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 15, 167 (2002).
R.M. Donlan, Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8, 881 (2002).
J.F. Frank and R.A. Koffi, Surface-adherent growth of Listeria monocytogenes is associated with increased resistance to surfactant sanitizers and heat. J Food Prot 53, 550 (1990).
J.C. Nickel and J.W. Costerton, Bacterial biofilms and catheters: A key to understanding bacterial strategies in catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Can J Infect Dis 3, 619 (1992).
H. Anwar, J.L. Strap and J.W. Costeron, Establishment of aging biofilms: possible mechanism of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36, 1347 (1992).
T.S. Schwach and E.A. Zottola, Use of scanning eletron microscopy to demonstrate microbial attachment to beef and beef contact surfaces. J Food Sci 47, 1401 (1982).
S.H. Lee and J.F. Frank, Inactivation of surface-adherent Listeria monocytogenes hypochlorite and heat. J Food Prot 54, 4 (1991).
M.R.W. Brown and P. Gilbert, Sensitivity of biofilms to antimicrobial agents. J Appl Bacteriol 74, S87 (1993).
D.E. Jenkins, J.E. Schultz and A. Matin, Stravation-induced cross protection against heat or hydrogen peroxide challeneg of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170, 3909 (1988).
D.J. Evans, D.G. Allison and M.R.W. Brown et al., Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginos and Escherichia coli biofilms towards ciprofloxacin: Effect of specific growth rate. J Antimicrob Chemother 27, 177 (1991).
P.S. Stewart, Biofilm accumulation model that predicts antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38, 1052 (1994).
P.S. Stewart, Theoretical aspects of antibiotic diffusion into microbial biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40, 2517 (1996).
C.M. Stewart, M.B. Cole and J.D. Legan et al., Modeling the growth boundary of Staphylococcus aureus for risk assessment purposes. J Food Prot 64, 51 (2001).
P.S. Stewart, J. Rayner and F. Roe et al., Biofilm penetration and disinfection efficiancy of alkaline hypochlorite and chlorsulfamates. J Appl Microbiol 91, 525 (2001).
C.M. Stewart, M.B. Cole and J.D. Legan et al., Staphylococcus aureus growth boundries: moving towards mechanistic predictive models based on soute-specific effects. Appl Environ Microbiol 68, 1864 (2002).
P.M. Davidson, Chemical Preservatives and Natural Antimicrobial Compounds. In: Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers, edited by M.P. Doyle, L.R. Beuchat and T.J. Montville (American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC 2001), p. 593.
P.M. Davidson and A.S. Naidu, Phytochemicals. In: Natural Food Antimicrobial Systems, edited by A.S. Naidu (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 2000).
E. Drenkard, Antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbes Infect 5, 1213 (2003).
E. Le Magrex-Debar, J. Lemoine and M.-P. Gelle et al., Evaluation of biohazards in dehydrated biofilms on foodstuff packaging. Int J Food Microbiol 55, 239 (2000).
J. Knowles and S. Roller, Efficacy of Chitosan, Carvacrol, and a Hydrogen Peroxide-Based Biocide against Foodborne Microorganisms in Suspension and Adhered to Stainless Steel. J Food Prot 64, 1542 (2001).
W.M. Dunne, E.O. Mason and S.L. Kaplan, Diffusion of rifampin and vancomycin through a Staphylococcus epidermis biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37, 2522 (1993).
H. Kumon, K. Tomochika and T. Matunaga et al., A sandwich cup method for the penetration assay of antimicrobial agents through Pseudomonas exopolysaccharide. Microbiol Immunol 38, 615 (1994).
P.S. Stewart, Diffusion in Biofilms. J Bacteriol 185, 1485 (2004).
W.K. Whitekettle, Effects of surface-active chemicals on microbial adhesion. J Ind Microbiol 7, 105 (1991).
E.P. Krysinski, L.J. Brown and T.J. Marchisello, Effect of cleaners and sanitizers on Listeria monocytogenes attached to product contact surfaces. J Food Prot 55, 246 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLandsborough, L., Rodriguez, A., Pérez-Conesa, D. et al. Biofilms: At the Interface between Biophysics and Microbiology. Food Biophysics 1, 94–114 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-005-9004-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-005-9004-x