Abstract
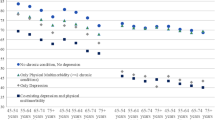
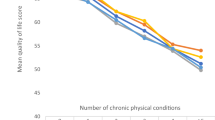
Comorbidity is found to be more prevalent among older people and increases the need for health care. This study examined the effects of chronic comorbidity on psychological well-being of elderly people. A cross-sectional, descriptive study among Northern Malaysians was conducted, involving 385 older people aged 60 years and above randomly selected through multistage random sampling. All respondents completed a questionnaire booklet containing sociodemographic characteristics, self reported chronic morbidity, and WHO-5 Well-Being Index. Findings of this study demonstrated the prevalence and the mean morbidity were 77.7% and 1.62 (SD = 1.48), respectively. The mean score for the psychological well-being was 57.96 (SD = 22.97). Results of multiple regression analysis indicated psychological well-being is negatively affected by the number of concurrent chronic conditions. The results also showed that chronic comorbidity has the most negative effect on psychological well-being. Therefore, it is important to identify mediating factors and coping strategies that might improve psychological well-being of elderly people with coexisting morbid conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abla Mehio, S., Monique, C., Rania, A. T., Ziyad, M., & Hassen, A.-A. (2009). Validation of the Arabic version of the 5-item WHO well being index in elderly population. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 24(1), 106–107. doi:10.1002/gps.2079.
Awata, S., Bech, P., Koizumi, Y., Seki, T., Kuriyama, S., Hozawa, A., et al. (2006). Validity and utility of the Japanese version of the WHO-Five Well-Being Index in the context of detecting suicidal ideation in elderly community residents. International Psychogeriatrics, 19(01), 77–88.
Bayliss, E. A., Bayliss, M. S., Ware, J. E., & Steiner, J. F. (2004). Predicting declines in physical function in persons with multiple chronic medical conditions: what we can learn from the medical problem list. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 2(1), 47–55.
Behera, C., Rautji, R., & Sharma, R. K. (2007). Suicide in elderly: a study in South Delhi (1996–2005). Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine &Toxicology, 1(1), 13–18.
Bonsignore, M., Barkow, K., Jessen, F., & Heun, R. (2001). Validity of the five-item WHO Well-Being Index (WHO-5) in an elderly population. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 251, 27–31.
Farezadi, Z., Normah, C. D., Zubaidah, J., & Maria, C. (2008). Chronic pain and psychological well-being. Paper presented at the Simposium Sains Kesihatan Kebangsaan 18–19 Jun, Hotel Legend, Kuala Lumpur.
Field, A. (2009). Discovering statistics using SPSS. London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Fuchs, Z., Blumstein, T., Novikov, I., Walter-Ginzburg, A., Lyanders, M., Gindin, J., et al. (1998). Morbidity, comorbidity, and their association with disability among community-dwelling oldest-old in Israel. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological and Medical Sciences, 53(6), 447–455.
Gaskell, H., Derry, S., Moore, A., & McQuay, H. J. (2008). Prevalence of anaemia in older persons: systematic review. BioMed Central Geriatrics, 8(1), 1.
Gijsen, R., Hoeymans, N., Schellevis, F. G., Ruwaard, D., Satariano, W. A., & van den Bos, G. A. M. (2001). Causes and consequences of comorbidity a review. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 54(7), 661–674.
Guralnik, J. M. (1996). Assessing the impact of comorbidity in the older population. Annals of Epidemiology, 6(5), 376–380.
Hootman, J. M., & Helmick, C. G. (2006). Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 54(1), 226–229.
Hootman, J., Bolen, J., Helmick, C., & Langmaid, G. (2006). Prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation-United States, 2003–2005. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 55, 1089–1092.
Jelicic, M., Kempen, G., & Passchier, J. (1998). Psychological well-being in older adults suffering from chronic headache. Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain, 38(4), 292–294.
Joshi, K., Kumar, R., & Avasthi, A. (2003). Morbidity profile and its relationship with disability and psychological distress among elderly people in Northern India. International Journal of Epidemiology, 32(6), 978–987.
Jui, Y. (2001). The aging male in Malaysia. The Aging Male, 4(2), 106–108.
Kalache, A. (1999). Active ageing makes the difference. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 12(4), 449.
Kant, S., Mishra, P., & Goswami, A. (2004). Morbidity among elderly persons residing in a resettlement colony of Delhi. Indian Journal of Preventive and Social Medicine, 35(1 & 2), 1–9.
Karlsen, B., Bru, E., & Hanestad, B. R. (2002). Self-reported psychological well-being and disease-related strains among adults with diabetes. Psychology and Health, 17, 459–473.
Kempen, G., Brilman, E. I., Ranchor, A. V., & Ormel, J. (1999). Morbidity and quality of life and the moderating effects of level of education in the elderly. Social Science & Medicine, 49(1), 143–149.
Latiffah, A. L., Afiah, N. M., & Shashikala, S. (2005). Psychological well-being of the elderly people in peninsular Malaysia. Inetrnational Medical Journal, 4, 38–43.
Leong, I. Y., Farrell, M. J., Helme, R. D., & Gibson, S. J. (2007). Relationship between medical comorbidity and self-rated pain, mood disturbance, and function in older people with chronic pain. Journals of Gerontology: Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 62(5), 550–555.
Lowe, B., Spitzer, R. L., Grafe, K., Kroenke, K., Quenter, A., Zipfel, S., et al. (2004). Comparative validity of three screening questionnaires for DSM-IV depressive disorders and physicians’ diagnoses. Journal of Affective Disorders, 78(2), 131–140.
Malaysian Department of Statistics. (2008). Yearbook of Statistics Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur: Department of Statistics, Malaysia.
Melnik, T. A., Hosler, A. S., Sekhobo, J. P., Duffy, T. P., Tierney, E. F., Engelgau, M. M., et al. (2004). Diabetes prevalence among Puerto Rican adults in New York City, NY, 2000. American Journal of Public Health, 94(3), 434.
Munshi, Y. I., Iqbal, M., Rafique, H., & Ahmad, Z. (2008). Geriatric morbidity pattern and depression in relation to family support in aged population of Kashmir Valley [Electronic Version]. The Internet Journal of Geriatrics and Gerontology, 4. Retrieved June 18, 2009 from http://www.ispub.com/ostia/index.php?xmlPrinter=true&xmlFilePath=journals/ijgg/vol4n1/depression.xml.
Pallant, J. F. (2007). SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using SPSS for Windows (3rd ed.). Berkshire, England: Open University Press.
Purty, A. J., Bazroy, J., Kar, M., Vasudevan, K., Veliath, A., & Panda, P. (2005). Morbidity pattern among the elderly population in the rural area of Tamil Nadu, India. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences, 35, 1–6.
Ratana, S., Manote, L., & Sutida, S. (2009). Reliability and validity of the Thai version of the WHO-Five Well-Being Index in primary care patients. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 63(2), 141–146. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2009.01933.x.
Rijken, M., van Kerkhof, M., Dekker, J., & Schellevis, F. G. (2005). Comorbidity of chronic diseases. Quality of Life Research, 14(1), 45–55.
Saipanish, R., Lotrakul, M., & Sumrithe, S. (2009). Reliability and validity of the Thai version of the WHO-Five Well-Being Index in primary care patients. Psychiatry & Clinical Neurosciences, 63(2), 141.
Schenstrom, A., Ronnberg, S., & Bodlund, O. (2006). Mindfulness-based cognitive attitude training for primary care staff: a pilot study. Complementary Health Practice Review, 11(3), 144.
Sherina, M. D., Lekhraj, R., & Mustaqim, A. (2004). Physical and mental health problems of the elderly in a rural community of Sepang, Selangor. Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, 11(1), 52–59.
Sherina, M. S., Rampal, L., Arfah Hanim, M., & Thong, P. L. (2006). The prevalence of depression among eldery warded in a territory care centre in Wilayah Persekutuan. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 61(1), 15–21.
Shuichi, A., Per, B., Sumiko, Y., Masashi, H., Susumu, S., Motoyasu, Y., et al. (2007). Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the World Health Organization-Five Well-Being Index in the context of detecting depression in diabetic patients. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 61(1), 112–119. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2007.01619.x.
Sidiah, S., Verbrugge, L., & Tengku Aizan, H. (2007). Disability and quality of life among older Malaysians. Paper presented at the PAA Annual meeting, from http://paa2008.princeton.edu/download.aspx?submissionId=80962.
Simpson, C. F., Boyd, C. M., Carlson, M. C., Griswold, M. E., Guralnik, J. M., & Fried, L. P. (2004). Agreement between self-report of disease diagnoses and medical record validation in disabled older women: factors that modify agreement. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 52(1), 123.
Streiner, D. L., & Norman, G. R. (1995). Health measurement scales: A practical guide to their development and use. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Woo, E., Han, C., Jo, S. A., Park, M. K., Kim, S., Kim, E., et al. (2007). Morbidity and related factors among elderly people in South Korea: results from the Ansan Geriatric (AGE) cohort study. BMC Public Health, 7(1), 10.
Acknowledgments
This study is a part of survey Patterns of social relationships and psychological well-being among older persons in peninsular Malaysia that was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momtaz, Y.A., Hamid, T.A., Yahaya, N. et al. Effects of Chronic Comorbidity on Psychological Well-being Among Older Persons in Northern Peninsular Malaysia. Applied Research Quality Life 5, 133–146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-010-9098-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-010-9098-2