Abstract
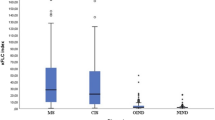
Increased intrathecal IgG and oligoclonal bands (OCB) are seminal features of multiple sclerosis (MS). Although no such differences in MS blood total IgG antibodies have been reported, serum OCB are a common and persistent finding in MS and have a systemic source. Recent studies showed that IgG3+ B cells and higher levels of serum IgG3 are linked to the development of MS. Additionally, intrathecal IgG synthesis in MS is associated with IgG3 heavy chain gene single nucleotide polymorphisms, and there is a strong relationship between susceptibility to MS and an IgG3 restriction fragment length polymorphism. These studies support the role of IgG3 in disease pathogenesis. Using multiple immunoassays, we investigated levels of total IgG, IgG1, and IgG3 in sera and CSF of 102 MS patients (19 paired CSF and sera), 76 patients with other neurological disorders (9 paired CSF and sera), and 13 healthy controls. We show that higher levels of total IgG and IgG3 antibodies were detected in MS serum, but not in CSF, which distinguishes MS from other inflammatory and non-inflammatory neurological disorders, with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves 0.79 for both IgG3 & total IgG. Our data support the notion that IgG3 antibodies may be a potential candidate for MS blood biomarker development.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankoti J, Apeltsin L, Hauser SL, Allen S, Albertolle ME, Witkowska HE, Von Büdingen HC (2014) In multiple sclerosis, oligoclonal bands connect to peripheral B-cell responses. Ann Neurol 75:266–276
Bakshi R, Yeste A, Patel B, Tauhid S, Tummala S, Rahbari R, Chu R, Regev K, Kivisäkk P, Weiner HL, Quintana FJ (2016) Serum lipid antibodies are associated with cerebral tissue damage in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 3:e200
Bankoti J, Apeltsin L, Hauser SL, Allen S, Albertolle ME, Witkowska HE, Von Büdingen HC (2014) In multiple sclerosis, oligoclonal bands connect to peripheral B-cell responses. Ann Neurol 75:266–276
Beseler C, Vollmer T, Graner M, Yu X (2017) The complex relationship between oligoclonal bands, lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid, and immunoglobulin G antibodies in multiple sclerosis: Indication of serum contribution PLoS One 12: e0186842
Brandle SM, Obermeier B, Senel M, Bruder J, Mentele R, Khademi M, Olsson T, Tumani H, Kristoferitsch W, Lottspeich F, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R, Dornmair K (2016) Distinct oligoclonal band antibodies in multiple sclerosis recognize ubiquitous self-proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:7864–7869
Buck, D., Albrecht, E., Aslam, M., Goris, A., Hauenstein, N., Jochim, A., International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C., Wellcome Trust Case Control, C., Cepok, S., Grummel, V., Dubois, B., Berthele, A., Lichtner, P., Gieger, C., Winkelmann, J., and Hemmer, B (2013) Genetic variants in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus are associated with the IgG index in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 73:86–94
Damelang T, Rogerson SJ, Kent SJ, Chung AW (2019) Role of IgG3 in Infectious Diseases. Trends Immunol 40:197–211
Delic-Sarac M, Izetbegovic S, Karamehic J, Subasic D, Saban A, Jukic T, Coric J, Panjeta M (2013) Detection methods of immunoglobulin IgG in CSF and serum. Med Arch 67:368–371
Delmotte P, Demonty L (1976) Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis. II. A detailed study of the serum IgA, IgG and IgM levels of 772 MS patients compared with 226 neurological controls. J Neurol 211:135–142
Di Pauli F, Gredler V, Kuenz B, Lutterotti A, Ehling R, Gneiss C, Schocke M, Deisenhammer F, Reindl M, Berger T (2010) Features of intrathecal immunoglobulins in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 288:147–150
Farina G, Magliozzi R, Pitteri M, Reynolds R, Rossi S, Gajofatto A, Benedetti MD, Facchiano F, Monaco S, Calabrese M (2017) Increased cortical lesion load and intrathecal inflammation is associated with oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis patients: a combined CSF and MRI study. J Neuroinflammation 14:40
Ferreira D, Voevodskaya O, Imrell K, Stawiarz L, Spulber G, Wahlund LO, Hillert J, Westman E, Karrenbauer VD (2014) Multiple sclerosis patients lacking oligoclonal bands in the cerebrospinal fluid have less global and regional brain atrophy. J Neuroimmunol 274:149–154
Fischer-Williams M, Roberts RC (1971) Cerebrospinal fluid proteins and serum immunoglobulins. Occurrence in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases: comparative measurement of gamma-globulin and the IgG class. Arch Neurol 25:526–534
Gaiser CN, Johnson MJ, De Lange G, Rassenti L, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Steinman L (1987) Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis associated with an immunoglobulin gamma 3 restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Clin Invest 79:309–313
García-Merino A, Persson MA, Ernerudh J, Díaz-Gil JJ, Olsson T (1986) Serum and cerebrospinal fluid antibodies against myelin basic protein and their IgG subclass distribution in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1066–1070
Gilden DH (2005) Infectious causes of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 4:195–202
Glynn P, Gilbert HM, Newcombe J, Cuzner ML (1982) Analysis of immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis brain: quantitative and isoelectric focusing studies. Clin Exp Immunol 48:102–110
Graner M, Pointon T, Manton S, Green M, Dennison K, Davis M, Braiotta G, Craft J, Edwards T, Polonsky B, Fringuello A, Vollmer T, Yu X (2020). Oligoclonal IgG antibodies in multiple sclerosis target patient-specific peptides. PLoS One 15:e0228883
Greve B, Magnusson CG, Melms A, Weissert R (2001) Immunoglobulin isotypes reveal a predominant role of type 1 immunity in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 121:120–125
Grimaldi LM, Maimone D, Reggio A, Raffaele R (1986) IgG1,3 and 4 oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Ital J Neurol Sci 7:507–513
Joseph FG, Hirst CL, Pickersgill TP, Ben-Shlomo Y, Robertson NP, Scolding NJ (2009) CSF oligoclonal band status informs prognosis in multiple sclerosis: a case control study of 100 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:292–296
Karrenbauer VD, Bedri SK, Hillert J, Manouchehrinia A (2021) Cerebrospinal fluid oligoclonal immunoglobulin gamma bands and long-term disability progression in multiple sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep 11:14987
Kaschka WP, Theilkaes L, Eickhoff K, Skvaril F (1979) Disproportionate elevation of the immunoglobulin G1 concentration in cerebrospinal fluids of patients with multiple sclerosis. Infect Immun 26:933–941
Keir G, Walker RW, Johnson MH, Thompson EJ (1982) Nitrocellulose immunofixation following agarose electrophoresis in the study of immunoglobulin G subgroups in unconcentrated cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chim Acta 121:231–236
Kennedy PGE, Graner M, Pointon T, Li X, Tanimoto K, Dennison K, Im G, Fringuello A, Zhou W, Graner A, Sillau S, Vollmer T, Yu X (2021) Aberrant Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation in Multiple Sclerosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol
Kwon YN, Kim B, Kim JS, Mo H, Choi K, Oh SI, Kim JE, Nam TS, Sohn EH, Heo SH, Kim SB, Park KC, Yoon SS, Oh J, Baek SH, Kim BJ, Park KS, Sung JJ, Jung JH, Kim SJ, Park SH, Waters P, Kim SM (2022) Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-Immunoglobulin G in the CSF: Clinical Implication of Testing and Association With Disability. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 9
Lambin P, Gervais A, Levy M, Defendini E, Dubarry M, Lebon P, Rouger P, Schuller E (1991) Intrathecal synthesis of IgG subclasses in multiple sclerosis and in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Neuroimmunol 35:179–189
Long Y, Gao C, Qiu W, Hu X, Peng F, Lu Z (2013) Antibodies target microvessels in neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis patients. Neurol Res 35:922–929
Losy J, Michałowska-Wender G, Wender M (1992) IgG1-IgG4 subclasses in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood serum and their synthesis in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Neurochir Pol 26:297–303
Lumsden CE (1971) The immunogenesis of the multiple sclerosis plaque. Brain Res 28:365–390
Marsh-Wakefield F, Ashhurst T, Trend S, Mcguire HM, Juillard P, Zinger A, Jones AP, Kermode AG, Hawke S, Grau GE, Hart PH, Byrne SN (2020) IgG3 (+) B cells are associated with the development of multiple sclerosis. Clin Transl Immunology 9:e01133.
Mehta PD (1988) Quantitation of IgG subclasses in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 540:261–263
Raknes G, Fernandes Filho JA, Pandey JP, Myhr KM, Ulvestad E, Nyland H, Vedeler CA (2000) IgG allotypes and subclasses in Norwegian patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 175:111–115
Salier JP, Glynn P, Goust JM, Cuzner ML (1983) Distribution of nominal and latent IgG (Gm) allotypes in plaques of multiple sclerosis brain. Clin Exp Immunol 54:634–640
Shimizu F, Tasaki A, Sano Y, Ju M, Nishihara H, Oishi M, Koga M. Kawai M, Kanda T (2014) Sera from remitting and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis patients disrupt the blood-brain barrier. PLoS One 9:e92872
Trend S, Jones AP, Cha L, Byrne SN, Geldenhuys S, Fabis-Pedrini MJ, Carroll WM, Cole JM, Booth DR, Lucas RM, Kermode AG, French MA, Hart PH (2018) Higher Serum Immunoglobulin G3 Levels May Predict the Development of Multiple Sclerosis in Individuals With Clinically Isolated Syndrome. Front Immunol 9:1590
Vartdal F, Vandvik B (1982) Multiple sclerosis. Electrofocused “bands” of oligoclonal CSF IgG do not carry antibody activity against measles, varicella-zoster or rotaviruses. J Neurol Sci 54:99–107
Vidarsson G, Dekkers G, Rispens T (2014) IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Front Immunol 5:520
Yu X, Graner M, Kennedy PGE, Liu Y (2020) The Role of Antibodies in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Front Neurol 11:533388
Zeman AZ, Keir G, Luxton R, Thompson EJ (1996) Serum oligoclonal IgG is a common and persistent finding in multiple sclerosis, and has a systemic source. QJM 89:187–193
Zoehner G, Miclea A, Salmen A, Kamber N, Diem L, Friedli C, Bagnoud M, Ahmadi F, Briner M, Sédille-Mostafaie N, Kilidireas C, Stefanis L, Chan A, Hoepner R, Evangelopoulos ME (2019) Reduced serum immunoglobulin G concentrations in multiple sclerosis: prevalence and association with disease-modifying therapy and disease course. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 12:1756286419878340
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Neurosurgery Nervous System Biorepository in the Department of Neurosurgery of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus (https://medschool.cuanschutz.edu/neurosurgery/research-and-innovation) for providing control samples from healthy donors and patients with brain tumors and other non-inflammatory neurological disorders. We thank Accelerated Cure Project (https://www.acceleratedcure.org/) for providing MS and HC samples.
Funding
This work was supported by the Department of Neurosurgery Research Funds, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus. Additional support was from NIH NIMH (5R21MH118174-02) for MWG & XY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PGEK, MWG, and XY analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. AF, TP, KA, SB, TC performed experiments. DL provided samples and the revision of the manuscript. XY designed the studies, did data analysis, prepared figures, and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial Interests
The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennedy, P.G.E., Graner, M.W., Fringuello, A. et al. Higher Levels of IgG3 Antibodies in Serum, But Not in CSF, Distinguish Multiple Sclerosis From Other Neurological Disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 17, 526–537 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10048-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10048-x