Abstract
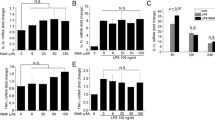
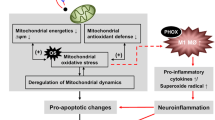
Methamphetamine (METH) is a drug of abuse, the acute and chronic use of which induces neurotoxic responses in the human brain, ultimately leading to neurocognitive disorders. Our goals were to understand the impact of METH on microglial mitochondrial respiration and to determine whether METH induces the activation of the mitochondrial-dependent intrinsic apoptosis pathway in microglia. We assessed the expression of pro- apoptosis genes using qPCR of RNA extracted from a human microglial cell line (HTHU). We examined the apoptosis-inducing effects of METH on microglial cells using digital holographic microscopy (DHM) to quantify real-time apoptotic volume decrease (AVD) in microglia in a noninvasive manner. METH treatment significantly increased AVD, activated Caspase 3/7, increased the gene expression levels of the pro- apoptosis proteins, APAF-1 and BAX, and decreased mitochondrial DNA content. Using immunofluorescence analysis, we found that METH increased the expression of the mitochondrial proteins cytochrome c and MCL-1, supporting the activation of mitochondrion-dependent (intrinsic) apoptosis pathway. Cellular bio-energetic flux analysis by Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer revealed that METH treatment increased both oxidative and glycolytic respiration after 3 h, which was sustained for at least 24 h. Several events, such as oxidative stress, neuro-inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial dysfunction, may converge to mediate METH-induced apoptosis of microglia that may contribute to neurotoxicity of the CNS. Our study has important implications for therapeutic strategies aimed at preserving mitochondrial function in METH abusing patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman SM, Kuczenski R, McCracken JT, London ED (2009) Potential adverse effects of amphetamine treatment on brain and behavior: a review. Mol Psychiatry 14(2):123–142
Brand MD, Nicholls DG (2011) Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochem J 435(2):297–312
Brown JM, Quinton MS, Yamamoto BK (2005) Methamphetamine-induced inhibition of mitochondrial complex II: roles of glutamate and peroxynitrite. J Neurochem 95:429–436
Cadet JL, Krasnova IN (2007) Interactions of HIV and methamphetamine: cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity potentiation. Neurotox Res 12(3):181–204
Cadet JL, Krasnova IN (2009) Molecular bases of methamphetamine-induced neurodegeneration. Int Rev Neurobiol 88:101–119
Cadet JL, Jayanthi S, Deng X (2003) Speed kills: cellular and molecular bases of methamphetamine-induced nerve terminal degeneration and neuronal apoptosis. FASEB J 17(13):1775–1788
Cadet JL, Jayanthi S, Deng X (2005) Methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis involves the activation of multiple death pathways. Review. Neurotox Res 8(3-4):199–206
Cao L, Walker MP, Vaidya NK, Fu M, Kumar S, Kumar A (2015) Cocaine-mediated autophagy in astrocytes involves sigma 1 receptor, PI3K, mTOR, Atg5/7, Beclin-1 and induces type II programed cell death. Mol Neurobiol 53:4417–4413
Castino R, Lazzeri G, Lenzi P, Bellio N, Follo C, Ferrucci M et al (2008) Suppression of autophagy precipitates neuronal cell death following low doses of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 106:1426–1439
Coelho-Santos V, Gonçalves J, Fontes-Ribeiro C, Silva AP (2012) Prevention of methamphetamine-induced microglial cell death by TNF-α and IL-6 through activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. J Neuroinflammation 6(9):103 https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-103
Cubells JF, Rayport S, Rajendran G, Sulzer D (1994 Apr) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity involves vacuolation of endocytic organelles and dopamine-dependent intracellular oxidative stress. J Neurosci 14(4):2260–2271
Davidson C, Gow AJ, Lee TH, Ellinwood EH (2001) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity: necrotic and apoptotic mechanisms and relevance to human abuse and treatment. Brain Res Rev 36(1):1–22
Dean AC, Groman SM, Morales AM, London ED (2013) An evaluation of the evidence that methamphetamine abuse causes cognitive decline in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(2):259–274
Deng X, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL (2007) Methamphetamine administration causes death of dopaminergic neurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Biol Psychiatry 61(11):1235–1243
Deng X, Cai NS, McCoy MT, Chen W, Trush MA, Cadet JL (2002) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in an immortalized rat striatal cell line by activating the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Neuropharmacology 42(6):837–845
Fernandes NC, Sriram U, Gofman L, Cenna JM, Ramirez SH, Potula R (2016) Methamphetamine alters microglial immune function through P2X7R signaling. J Neuroinflammation 13:91
Ferrick DA, Neilson A, Beeson C (2008) Advances in measuring cellular bioenergetics using extracellular flux. Drug Discov Today 13(5–6):268–274
Friend DM, Keefe KA (2013) Glial reactivity in resistance to methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 125:566–574
Garcia-Mesa Y, Jay TR, Checkley MA, Luttge B, Dobrowolski C, Valadkhan S, Landreth GE, Karn J, Alvarez-Carbonell D (2017) Immortalization of primary microglia: a new platform to study HIV regulation in the central nervous system. J Neuro-Oncol 23(1):47–66
Gonçalves J, Baptista S, Martins T, Milhazes N, Borges F, Ribeiro CF, Malva JO, Silva AP (2010) Methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction in the mice hippocampus: preventive effect of indomethacin. Eur J Neurosci 31:315–326
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Bordelon M, McCoy MT, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-death Bcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex. FASEB J 15(10):1745–1752
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Noailles PA, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2004) Methamphetamine induces neuronal apoptosis via cross-talks between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria-dependent death cascades. FASEB J 18(2):238–251
Khmaladze A, Kim MK, Lo CM (2008) Phase imaging of cells by simultaneous dual-wavelength reflection digital holography. Opt Express 16:10900–10911
Khmaladze A, Matz RL, Epstein T, Jasensky J, Banaszak Holl MM, Chen Z (2012) Cell volume changesduring apoptosis monitored in real time using digital holographic microscopy. J Struct Biol 178:270–278
Lang F, Shumilina E, Ritter M, Gulbins E, Vereninov A, Huber SM (2006) Ion channels and cell volume in regulation of cell proliferation and apoptotic cell death. Contrib Nephrol 152:142–160
LaVoie MJ, Card JP, Hastings TG (2004) Microglial activation precedes dopamine terminal pathology in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Exp Neurol 187:47–57
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Loftis JM, Choi D, Hoffman W, Huckans MS (2011) Methamphetamine causes persistent immune dysregulation: a cross-species, translational report. Neurotox Res 20:59–68
Lull ME, Block ML (2010) Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):354–365
Ma J, Wan J, Meng J, Banerjee S, Ramakrishnan S, Roy S (2014) Methamphetamine induces autophagy as a pro-survival response against apoptotic endothelial cell death through the Kappa opioid receptor. Cell Death Dis 5:e1099
Maltese WA, Overmeyer JH (2015) Non-apoptotic cell death associated with perturbations of macropinocytosis. Front Physiol 6:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00038
Marshall BD, Werb D (2010) Health outcomes associated with methamphetamine use among young people: a systematic review. Addiction 105(6):991–1002
Marshall JF, O'Dell SJ (2012) Methamphetamine influences on brain and behavior: unsafe at any speed? Trends Neurosci 35(9):536–545
Matsumoto RR, Shaikh J, Wilson LL, Vedam S, Coop A (2008) Attenuation of methamphetamine induced effects through the antagonism of sigma (sigma) receptors: evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:871–881
McCann UD, Kuwabara H, Kumar A, Palermo M, Abbey R, Brasic J, Ye W, Alexander M, Dannals RF, Wong DF, Ricaurte GA (2008) Persistent cognitive and dopamine transporter deficits in abstinent methamphetamine users. Synapse 62:91–100
Núñez R, Sancho-Martínez SM, Novoa JM, López-Hernández FJ (2010) Apoptotic volume decrease as a geometric determinant for cell dismantling into apoptotic bodies. Cell Death Differ 17(11):1665–1671
Nguyen EC, McCracken KA, Liu Y, Pouw B, Matsumoto RR (2005) Involvement of sigma (sigma) receptors in the acute actions of methamphetamine: receptor binding and behavioral studies. Neuropharmacology 49:638–645
O'Callaghan JP, Sriram K, Miller DB (2008) Defining ‘neuroinflammation’: lessons from MPTP- and methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139(10):318–330
Pasantes-Morales H, Tuz K (2006) Volume changes in neurons: hyperexcitability and neuronal death. Contrib Nephrol 152:221–240
Pasquali L, Lazzeri G, Isidoro C, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008 Oct) Role of autophagy during methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:191–196
Rau TF, Kothiwal AS, Rova AR, Brooks DM, Poulsen DJ (2012) Treatment with low-dose methamphetamine improves behavioral and cognitive function after severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 73(2 Suppl 1):S165–S172
Rau TF, Kothiwal AS, Zhang L, Ulatowski S, Jacobson S, Brooks DM, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Chopp M, Poulsen DJ (2011) Low dose methamphetamine mediates neuroprotection through a PI3K-AKT pathway. Neuropharmacology 61(4):677–686
Roohbakhsh A, Shirani K, Karimi G (2016) Methamphetamine-induced toxicity: the role of autophagy? Chem Biol Interact 260:163–167
Rusyniak DE (2011) Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Neurol Clin 29(3):641–655
Sekine Y, Ouchi Y, Sugihara G, Takei N, Yoshikawa E, Nakamura K, Iwata Y, Tsuchiya KJ, Suda S, Suzuki K, Kawai M, Takebayashi K, Yamamoto S, Matsuzaki H, Ueki T, Mori N, Gold MS, Cadet JL (2008) Methamphetamine causes microglial activation in the brains of human abusers. J Neurosci 28:5756–5761
Shen K, Zhang Y, Lv X, Chen X, Zhou R, Nguyen LK, Wu X, Yao H (2016) Molecular mechanisms involving sigma-1 receptor in cell apoptosis of bv-2 microglial cells induced by methamphetamine. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15:857–865
Smith KJ, Butler TR, Prendergast MA (2010) Inhibition of sigma-1 receptor reduces N-methyl-D-aspartate induced neuronal injury in methamphetamine-exposed and -naive hippocampi. Neurosci Lett 481:144–148
Thiriet N, Jayanthi S, McCoy M, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine increases expression of the apoptotic c-myc and L-myc genes in the mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 90(2):202–204
Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, Simon SL, Geaga JA, Hong MS, Sui Y, Lee JY, Toga AW, Ling W, London ED (2004) Structural abnormalities in the brains of human subjects who use methamphetamine. J Neurosci 24:6028–6036
Tong J, Fitzmaurice P, Furukawa Y, Schmunk GA, Wickham DJ, Ang LC, Sherwin A, McCluskey T, Boileau I, Kish SJ (2014) Is brain gliosis a characteristic of chronic methamphetamine use in the human? Neurobiol Dis 67:107–118
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2005) Another way to die: autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1528–1534
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Shumay E, Telang F, Thanos PK, Alexoff D (2010) Distribution and pharmacokinetics of methamphetamine in the human body: clinical implications. PLoS One 5(12):e15269
Wang J, Silva JP, Gustafsson CM, Rustin P, Larsson NG (2001) Increased in vivo apoptosis in cells lacking mitochondrial DNA gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(7):4038–4043
Wang J, Qian W, Liu J, Zhao J, Yu P, Jiang L, Jing Z, Gao R, Xiao H (2014) Effect of methamphetamine on the microglial damage: role of potassium channel Kv1.3. PLoS One 9(2):e88642
Wu CW, Ping YH, Yen JC, Chang CY, Wang SF, Yeh CL, Chi CW, Lee HC (2007) Enhanced oxidative stress and aberrant mitochondrial biogenesis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells during methamphetamine induced apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 220:243–251
Xu E, Liu J, Liu H, Wang X, Xiong H (2017) Role of microglia in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 9(3):84–100
Yamamoto BK, Moszczynska A, Gudelsky GA (2010) Amphetamine toxicities: classical and emerging mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1187:101–121
Yu S, Zhu L, Shen Q, Bai X, Di X (2015) Recent advances in methamphetamine neurotoxicity mechanisms and its molecular pathophysiology. Behav Neurol volume 2015, Article ID 103969, 11 pages, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/103969
Zhang Y, Lv X, Bai Y, Zhu X, Wu X, Chao J, Duan M, Buch S, Chen L, Yao H (2015) Involvement of sigma-1 receptor in astrocyte activation induced by methamphetamine via up-regulation of its own expression. J Neuroinflammation 12:29
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge grant support from the Dr. Louis Sklarow Memorial Trust (SDM) and the Troup Fund of the Kaleida Health Foundations (SAS). The authors are grateful to Dr. Jonathan Karn, Chairman and Reinberger Professor of Molecular Biology, and Director of the CASE Center for AIDS Research, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH for the generous donation of the HTHU cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharikova, A.V., Quaye, E., Park, J.Y. et al. Methamphetamine Induces Apoptosis of Microglia via the Intrinsic Mitochondrial-Dependent Pathway. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 13, 396–411 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-018-9787-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-018-9787-4