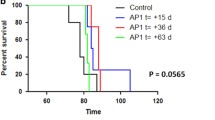
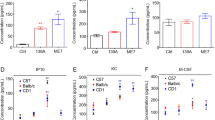
Abstract
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE) are neurodegenerative diseases caused by an infectious agent with viral properties. Host prion protein (PrP), a marker of late stage TSE pathology, is linked to a similar protein called Shadoo (Sho). Sho is reduced in mice infected with the RML scrapie agent, but has not been investigated in other TSEs. Although PrP is required for infection by TSE agents, it is not known if Sho is similarly required. Presumably Sho protects cells from toxic effects of misfolded PrP. We compared Sho and PrP changes after infection by very distinct TSE agents including sporadic CJD, Asiatic CJD, New Guinea kuru, vCJD (the UK epidemic bovine agent) and 22L sheep scrapie, all passaged in standard mice. We found that Sho reductions were agent-specific. Variable Sho reductions in standard mice could be partly explained by agent-specific differences in regional neuropathology. However, Sho did not follow PrP misfolding in any quantitative or consistent way. Tga20 mice with high murine PrP levels revealed additional agent-specific differences. Sho was unaffected by Asiatic CJD yet was markedly reduced by the kuru agent in Tga20 mice; in standard mice both agents induced the same Sho reductions. Analyses of neural GT1 cells demonstrated that Sho was not essential for TSE infections. Furthermore, because all infected GT1 cells appeared as healthy as uninfected controls, Sho was not needed to protect infected cells from their “toxic” burden of abundant abnormal PrP and intracellular amyloid.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akowitz A, Sklaviadis T, Manuelidis L (1994) Endogenous viral complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nucleic Acids Res 22:1101–1107
Arjona A, Simarro L, Islinger F, Nishida N, Manuelidis L (2004) Two Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agents reproduce prion protein-independent identities in cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:8768–8773
Baker CA, Manuelidis L (2003) Unique inflammatory RNA profiles of microglia in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:675–679
Baker CA, Martin D, Manuelidis L (2002) Microglia from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease-infected brains are infectious and show specific mRNA activation profiles. J Virol 76:10905–10913
Baker CA, Lu ZY, Manuelidis L (2004) Early induction of interferon-responsive mRNAs in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurovirol 10:29–40
Barron RM, Campbell SL, King D, Bellon A, Chapman KE, Williamson RA, Manson JC (2007) High titers of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy infectivity associated with extremely low levels of PrPSc in vivo. J Biol Chem 282:35878–35886
Comoy EE, Casalone C, Lescoutra-Etchegaray N, Zanusso G, Freire S, Marce D, Auvre F, Ruchoux MM, Ferrari S, Monaco S, Sales N, Caramelli M, Leboulch P, Brown P, Lasmezas CI, Deslys JP (2008) Atypical BSE (BASE) transmitted from asymptomatic aging cattle to a primate. PLoS ONE 3:e3017
Fischer M, Rulicke T, Raeber A, Sailer A, Moser M, Oesch B, Brandner S, Aguzzi A, Weissmann C (1996) Prion protein (PrP) with amino-proximal deletions restoring susceptibility of PrP knockout mice to scrapie. EMBO J 15:1255–1264
Forloni G, Angeretti N, Chiesa R, Monzani E, Salmona M, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F (1993) Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 362:543–546
Gossner AG, Bennet N, Hunter N, Hopkins J (2009) Differential expression of Prnp and Sprn in scrapie infected sheep also reveals Prnp genotype specific differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:862–866
Hunter N, Cairns D (1998) Scrapie-free Merino and Poll Dorset sheep from Australia and New Zealand have normal frequencies of scrapie-susceptible PrP genotypes. J Gen Virol 79(Pt 8):2079–2082
Lloyd SE, Grizenkova J, Pota H, Collinge J (2009) Shadoo (Sprn) and prion disease incubation time in mice. Mamm Genome 20:367–374
Lu ZY, Baker CA, Manuelidis L (2004) New molecular markers of early and progressive CJD brain infection. J Cell Biochem 93:644–652
Manuelidis L (1994) The dimensions of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Transfusion 34:915–928
Manuelidis L (1998) Vaccination with an attenuated Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease strain prevents expression of a virulent agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2520–2525
Manuelidis L (2006) A 25 nm virion is the likely cause of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J Cell Biochem 100:897–915
Manuelidis L (2010) Transmissible encephalopathy agents: virulence, geography and clockwork. Virulence 1:1–4
Manuelidis L, Fritch W (1996) Infectivity and host responses in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Virology 216:46–59
Manuelidis L, Lu ZY (2000) Attenuated Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agents can hide more virulent infections. Neurosci Lett 293:163–166
Manuelidis EE, Kim J, Angelo JN, Manuelidis L (1976) Serial propagation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in guinea pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73:223–227
Manuelidis EE, Gorgacz EJ, Manuelidis L (1978) Transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with scrapie-like syndromes to mice. Nature 271:778–779
Manuelidis L, Sklaviadis T, Akowitz A, Fritch W (1995) Viral particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5124–5128
Manuelidis L, Fritch W, Xi YG (1997) Evolution of a strain of CJD that induces BSE-like plaques. Science 277:94–98
Manuelidis L, Yu ZX, Banquero N, Mullins B (2007) Cells infected with scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agents produce intracellular 25-nm virus-like particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1965–1970
Manuelidis L, Chakrabarty T, Miyazawa K, Nduom NA, Emmerling K (2009a) The kuru infectious agent is a unique geographic isolate distinct from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13529–13534
Manuelidis L, Liu Y, Mullins B (2009b) Strain-specific viral properties of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) are encoded by the agent and not by host prion protein. J Cell Biochem 106:220–231
Massignan T, Stewart RS, Biasini E, Solomon IH, Bonetto V, Chiesa R, Harris DA (2009) A novel, drug-based, cellular assay for the activity of neurotoxic mutants of the prion protein. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.064949
Nishida N, Katamine S, Manuelidis L (2005) Reciprocal interference between specific CJD and scrapie agents in neural cell cultures. Science 310:493–496
Premzl M, Sangiorgio L, Strumbo B, Marshall Graves JA, Simonic T, Gready JE (2003) Shadoo, a new protein highly conserved from fish to mammals and with similarity to prion protein. Gene 314:89–102
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13363–13383
Sakaguchi S, Katamine S, Yamanouchi K, Kishikawa M, Moriuchi R, Yasukawa N, Doi T, Miyamoto T (1993) Kinetics of infectivity are dissociated from PrP accumulation in salivary glands of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent-inoculated mice. J Gen Virol 74(Pt 10):2117–2123
Silveira JR, Raymond GJ, Hughson AG, Race RE, Sim VL, Hayes SF, Caughey B (2005) The most infectious prion protein particles. Nature 437:257–261
Sklaviadis T, Dreyer R, Manuelidis L (1992) Analysis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease infectious fractions by gel permeation chromatography and sedimentation field flow fractionation. Virus Res 26:241–254
Sklaviadis T, Akowitz A, Manuelidis EE, Manuelidis L (1993) Nucleic acid binding proteins in highly purified Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:5713–5717
Sun R, Liu Y, Zhang H, Manuelidis L (2008) Quantitative recovery of scrapie agent with minimal protein from highly infectious cultures. Viral Immunol 21:293–302
Tateishi J, Ohta M, Koga M, Sato Y, Kuroiwa Y (1979) Transmission of chronic spongiform encephalopathy with kuru plaques from humans to small rodents. Ann Neurol 5:581–584
Watts JC, Drisaldi B, Ng V, Yang J, Strome B, Horne P, Sy MS, Yoong L, Young R, Mastrangelo P, Bergeron C, Fraser PE, Carlson GA, Mount HT, Schmitt-Ulms G, Westaway D (2007) The CNS glycoprotein Shadoo has PrP(C)-like protective properties and displays reduced levels in prion infections. EMBO J 26:4038–4050
Xi YG, Ingrosso L, Ladogana A, Masullo C, Pocchiari M (1992) Amphotericin B treatment dissociates in vivo replication of the scrapie agent from PrP accumulation. Nature 356:598–601
Acknowledgements
We thank Kaitlin Emmerling and Carolyn Brokowski for manuscript improvements. This work was supported by Neurological Disorders and Stroke Grant RO1 012674 and National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Grant R21 A1076645.
Conflict of Interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant support: NINDS RO1 012674; NIAID R21 A1076645
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazawa, K., Manuelidis, L. Agent-specific Shadoo Responses in Transmissible Encephalopathies. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 5, 155–163 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-010-9191-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-010-9191-1