Abstract
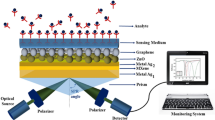
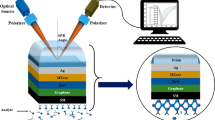
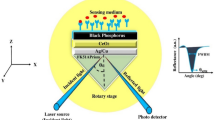
A proposed surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor inclusion of black phosphorus (BP) nanomaterial is presented in this paper. The performance of the sensor is compared with sensors based on graphene, MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2. The optimal thickness of the Cu-Ni layer with BP is determined using the angular interrogation method, resulting in the highest sensitivity of 525°/RIU at a wavelength of 633 nm. The results indicate that the proposed sensor outperforms other 2D nanomaterial-based sensors in terms of sensitivity. Furthermore, the sensor is used for detecting glucose levels in urine samples. By optimizing the thickness of the Cu layer, a maximum sensitivity of 430.10°/RIU is achieved for glucose level detection. It is observed that the proposed configuration with other 2D nanomaterials enhances the sensitivity at a lower thickness of Ni.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data set generated is already presented in the manuscript.
References
Homola J (2003) Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 377(3):528–539
Wolfbe is OS (2006) Fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 78(12):3859–3874
Boisde G, Harmer A (1996) Chemical and biochemical sensing with optical fibers and waveguides
Karlsson R, Fält A (1997) Experimental design for kinetic analysis of protein-protein interactions with surface plasmon resonance biosensors. J Immunol Methods 200(1–2):121–133
Patching SG (2014) Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for characterization of membrane protein–ligand interactions and its potential for drug discovery. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bio membranes 1838(1):43–55
Song SY, Choi HG, Hong JW, Kim BW, Sim SJ, Yoon HC (2008) Selective antigen–antibody recognition on SPR sensor based on the heat-sensitive conformational change of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). Colloids Surf, A 313:504–508
Jabbari S, Dabirmanesh B, Arab SS, Amanlou M, DaneshjouS GS, Khajeh K (2016) A novel enzyme based SPR-biosensor to detect bromocriptine as anergoline derivative drug. Sensor Actuator B Chem 240:519–527
Vaisocherova H, Homola J (2006) SPR biosensors for medical diagnostics. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 229–247
Pal S, Prajapati YK, Saini JP (2020) Influence of graphene’s chemical potential on SPR biosensor using ZnO for DNA hybridization. Opt Rev 27:57–64
Jena SC, Shrivastava S, Saxena S, Kumar N, Maiti SK, Mishra BP, Singh RK (2019) Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for label-free detection of BIRC5 biomarker in spontaneously occurring canine mammary tumours. Sci Rep 9:13485
Otto A (1968) Excitation of surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection, Springer Z. Phys 216:398–410
Sharma N (2012) Performances of different metals in optical fibre-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Indian Acad Sci 78(3):417–427
Kumar R, Pal S, Prajapati YK, Saini JP (2021) Sensitivity enhancement of MXene based SPR sensor using silicon: theoretical analysis. SILICON 13:1887–1894
Kumar R, Pal S, Pal N, Mishra V, Prajapati YK (2021) High-performance bimetallic surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor using a black phosphorus–MXene hybrid structure. Appl Phys A 127(4):259
Srivastava T, Jha R, Das R (2011) High-performance bimetallic SPR sensor based on periodic-multilayer-waveguides. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 23(20):1448–1450
Rahman M, Abdulrazak LF, Ahsan M, Based MA, Rana MM, AnowerM S, Rikta KA, Haider J, Gurusamy S (2021) 2D nanomaterial-based hybrid structured (Au-WSe 2-PtSe 2-BP) surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor with improved performance. IEEE Access 10:689–698
Akjouj A, Mir A (2022) Performance evaluation of multifunctional SPR bimetallic sensor using hybrid 2D-nanomaterials layers. Optik 269:169857
Alagdar M, Yousif B, Areed NF, Elzalabani M (2020) Improved the quality factor and sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance sensor with transition metal dichalcogenide 2D nanomaterials. J Nanopart Res 22:1–13
Xu Y, Ang YS, Wu L, Ang LK (2019) High sensitivity surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional MXene and transition metal dichalcogenide: a theoretical study. Nanomaterials 9(2):165
Singh MK, Pal S, Verma A, Mishra V, Prajapati YK (2021) Sensitivity enhancement using anisotropic black phosphorus and antimonene in bi-metal layer-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Superlattices Microstruct 156:106969
Pal S, Verma A, Prajapati YK, Saini JP (2020) Sensitive detection using heterostructure of black phosphorus, transition metal di-chalcogenides and MXene in SPR sensor. Appl Phys A 126(10):809
Yuan Y, Yu X, Ouyang Q, Shao Y, Song J, Qu J, Yong KT (2018) Highly anisotropic black phosphorous-graphene hybrid architecture for ultrassensitive plasmonic biosensing: theoretical insight. 2D Materials 5(2):15
Maurya JB, Prajapati YK, Raikwar S, Saini JP (2018) A silicon-black phosphorous based surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of NO2 gas. Optik 160:428–433
Srivastava A, Verma A, Das R, Prajapati YK (2020) A theoretical approach to improve the performance of SPR biosensor using MXene and black phosphorus. Optik 203:163430
Jawad A, Arifuzzaman S, Anower MS, Ferdous AI, Anwer TMK, Ahammad SH, Hossain A, Rashed ANZ (2023) Modeling and performance analysis of an advanced hybrid surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor employing indium tin oxide-phosphorene hetero structure. Plasmonics 1–11
Singh MK, Pal S, Prajapati YK, Saini JP (2020) Sensitivity enhancement using antimonene and BlueP/MoS2 heterostructure in SPR sensor. IEEE Sensors Letters 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/lsens.2020.3005942
Alagdar M, Yousif B, Areed NF, Elzalabani M (2020) Highly sensitive fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor employing 2D nanomaterials. Appl Phys A 126:1–16
LinZ CS, Lin C (2020) Sensitivity improvement of a surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional materials hybrid structure in visible region: a theoretical study. Sensors 20(9):2445
Kasani S, Curtin K, Wu N (2019) A review of 2D and 3D plasmonic nanostructure array patterns: fabrication, light management and sensing applications. Nanophotonics 8(12):2065–2089
Mostufa S, Paul AK, Chakrabarti K (2021) Detection of hemoglobin in blood and urine glucose level samples using a graphene-coated SPR based biosensor. OSA Continuum 4(8):2164–2176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rajeev Kumar: conceptualization, simulation, formal analysis, design, simulation, modeling, writing—original draft, M. K. Singh: modeling, writing—original draft, formal analysis, Lalit Garia: formal analysis, B. D. Patel: formal analysis, Mridula: writing—original draft, formal analysis, B. M. Singh: formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Ethical approval is not required as the data presented here is based on numerical study.
Consent for Publication
All authors of this draft express their consent to publish this theoretical research.
Consent to Participate
No consent is required.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Singh, M.K., Garia, L. et al. Refractive Index Sensing–Based Ultra Sensitive Black Phosphorus Configured Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor for the Detection of Glucose Level. Plasmonics 19, 203–213 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01972-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01972-0