Abstract
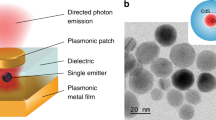
Nanoantenna-enhanced ultrafast emission from colloidal quantum dots as quantum emitters is required for fast quantum communications. On-chip integration of such devices requires a scalable and high-throughput technology. We report self-assembly lithography technique of preparing hybrid of gold nanorods antenna over a compact CdSe quantum dot monolayer. We demonstrate resonant and nonresonant gold nanorod antenna-enhanced radiative and anisotropic decay. Extensive simulations explain the mechanism of the decay rates and the role of antenna in both random and compact monolayers of quantum dots. The study could find applications in quantum dot display and quantum communication devices.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoang TB, Akselrod GM, Mikkelsen MH (2016) Ultrafast room-temperature single photon emission from quantum dots coupled to plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 16:270
Giannini V, Fernandez-Dominguez AI, Heck SC, Maier SA (2011) Plasmonic nanoantennas: fundamentals and their use in controlling the radiative properties of nanoemitters. Chem Rev 111:3888
Novotny L, van Hulst N (2011) Antennas for light. Nat Photonics 5:83
Eggleston MS, Messer K, Zhang L, Yablonovitch E, Wu MC (2015) Optical antenna enhanced spontaneous emission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:1704
Novotny L, Hecht B (2006) Principles of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bharadwaj P, Deutsch B, Novotny L (2009) Optical antennas. Advances in Optics and Photonics 1:438
Neogi A, Morkoç H, Kuroda T, Tackeuchi A (2005) Coupling of spontaneous emission from GaN–AlN quantum dots into silver surface plasmons. Opt Lett 30:93
Haridas M, Basu JK, Gosztola DJ, Wiederrecht GP (2010) Photoluminescence spectroscopy and lifetime measurements from self-assembled semiconductor-metal nanoparticle hybrid arrays. Appl Phys Lett 97:83307
Russell KJ, Liu T-L, Cui S, Hu EL (2012) Large spontaneous emission enhancement in plasmonic nanocavities. Nat Photonics 6:459
Tripathi LN, Praveena M, Basu JK (2013) Plasmonic tuning of photoluminescence from semiconducting quantum dot assemblies. Plasmonics 8:657
Haridas M, Tripathi LN, Basu JK (2011) Photoluminescence enhancement and quenching in metal-semiconductor quantum dot hybrid arrays. Appl Phys Lett 98:063305
Tripathi LN, Praveena M, Valson P, Basu JK (2014) Long range emission enhancement and anisotropy in coupled quantum dots induced by aligned gold nanoantenna. Appl Phys Lett 105:163106
Peng ZA, Peng XG (2001) Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J Am Chem Soc 123:183
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir 20:6414
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer, Berlin
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370
Chandrasekhar S (1943) Stochastic problems in physics and astronomy. Rev Mod Phys 15:1
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology (Nanomission), India, for the financial support and Advanced Facility for Microscopy and Microanalysis, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, for access to TEM measurements. M. Praveena acknowledges UGC, India, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, L.N., Praveena, M., Johns, B. et al. Nanoantenna-Enhanced Radiative and Anisotropic Decay Rates in Monolayer-Quantum Dots. Plasmonics 13, 1811–1816 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0695-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0695-5