Abstract
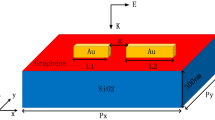
We study an active modulation of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of Au nanoparticles based on highly doped graphene in visible and near-infrared regions. We find that compared to the traditional metal SPR, the SPR of Au nanoparticles based on graphene causes a remarkable blue shift. The field intensity in the gap is redistributed to standing wave. The field intensity of standing wave is about one order of magnitude higher than the traditional model. Moreover, the SPR of Au nanoparticles can be actively modulated by varying the graphene Fermi energy. We find the maximum modulation of field intensity of absorption spectra is more than 21.6 % at λ = 822 nm and the amount of blue shift is 17.4 nm, which is about 2.14 % of the initial wavelength λ 0 = 813.4 nm, with increasing monolayer graphene Fermi energy from 1.0 to 1.5 ev. We find that the SPR sensitivity to the refractive index n of the environment is about 642 nm per refractive index unit (RIU). The SPR wavelengths have a big blue shift, which is about 33 nm, with increasing number of graphene layers from 1 to 3, and some shoulders on the absorption spectra are observed in the models with multilayer graphene. Finally, we study the Au nanorod array based on monolayer graphene. We find that the blue shift caused by the graphene increases from 14 to 24 nm, with increasing gap g y from 10 to 20 nm. Then, it decreases from 24 to 14 nm, with increasing gap g y from 20 to 50 nm. This study provides a new way for actively modulating the optical and optoelectronic devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bukasov R, Shumaker-Parry JS (2007) Highly tunable infrared extinction properties of gold nanocrescents. Nano Lett 7(5):1113–1118
Sherry LJ, Chang SH, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP, Wiley BJ, Xia YN (2005) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver nanocubes. Nano Lett 5(10):2034–2038
Sherry LJ, Jin RC, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver triangular nanoprisms. Nano Lett 6(9):2060–2065
Zhou X, Fu Y, Li K, Wang S, Cai Z (2008) Coupling mode-based nanophotonic circuit device. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 91:373–376
Endo T, Yamamura S, Nagatani N, Morita Y, Takamura Y, Tamiya E (2005) Localized surface plasmon resonance based optical biosensor using surface modified nanoparticle layer for label-free monitoring of antigen–antibody reaction. Sci and tech. Adv Mater 6(5):491–500
Zhao J, Zhang XY, Youzon CR, Haes AJ, Van Duyne RP (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanomedicine 1(2):219–228
Haes AJ, Hall WP, Chang L, Klein WL, Van Duyne RP (2004) A localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor: first steps toward an assay for Alzheimer’s disease. Nano Lett 4(6):1029–1034
Haynes CL, Van Duyne RP (2001) Nanosphere lithography: a versatile nanofabrication tool for studies of size-dependent nanoparticle optics. J Phys Chem B 105(24):5599–5611
Nehl CL, Liao HW, Hafner JH (2006) Optical properties of star-shaped gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 6(4):683–388
Sun YG, Xia YN (2003) Gold and silver nanoparticles: a class of chromophores with colors tunable in the range from 400 to 750 nm. Analyst 128:686–691
Kinkhabwala A, Yu ZF, Fan SH, Avlasevich Y, Müllen K, Moerner WE (2009) Large single-molecule fluorescence enhancements produced by a bowtie nanoantenna. Nature Photon 3:654–657
KH S, Wei QH, Zhang X (2006) Tunable and augmented plasmon resonances of Au/SiO2/Au nanodisks. Appl Phys Lett 88:063118
Miller MM, Lazarides AA (2005) Sensitivity of metal nanoparticle surface plasmon resonance to the dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 109:21556–21565
Dridi M, Vial A (2010) FDTD modeling of gold nanoparticles in a nematic liquid crystal: quantitative and qualitative analysis of the spectral tunability. J Phys Chem C 114:9541–9545
Qian HL, Ma YG, Yang Q, Chen BG, Liu Y, Guo X, Lin SS, Ruan JL, Liu X, Tong LM, Wang ZL (2014) Electrical tuning of surface plasmon polariton propagation in graphene nanowire hybrid structure. ACS Nano 8(3):2584–2589
Gao WL, Shu J, Qiu CY, QF X (2012) Excitation of plasmonic waves in graphene by guided-mode resonances. ACS Nano 6(9):7806–7813
Yan HG, Low T, Zhu WJ, Wu YQ, Freitag M, Li XS, Guinea F, Avouris P, Xia FN (2013) Damping pathways of mid-infrared plasmons in graphene nanostructures. Nature Photon 7:394–399
Swathi Iyer GR, Wang J, Wells G, Guruvenket S, Payne S, Bradley M, Borondics F (2014) Large-area, freestanding, single-layer graphene-gold: a hybrid plasmonic nanostructure. ACS Nano 8(6):6353–6362
Radko IP, Bozhevolnyi SI, Grigorenko AN (2016) Maximum modulation of plasmon-guided modes by graphene gating. Opt Express 24(8):8266–8279
Yao Y, Kats MA, Genevet P, NF Y, Song Y, Kong J, Capasso F (2013) Broad electrical tuning of graphene-loaded plasmonic antennas. Nano Lett 13:1257–1264
Li ZQ, Henriksen EA, Jiang Z, Hao Z, Martin MC, Kim P, Stormer HL, Basov DN (2008) Dirac charge dynamics in graphene by infrared spectroscopy. Nature Phys 4:532–535
Nair RR, Blake P, Grigorenko AN, Novoselov KS, Booth TJ, Stauber T, Peres NMR, Geim AK (2008) Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 320(5881):1308
Efetov DK, Kim P (2010) Controlling electron-phonon interactions in graphene at ultrahigh carrier densities. Phys Rev Lett 105(25):256805
Gómez-Díaz JS, Perruisseau-Carrier J (2013) Graphene-based plasmonic switches at near infrared frequencies. Opt Express 21(13):15490
RW Y, Pruneri V, de Abajo F JG (2015) Resonant visible light modulation with graphene. ACS Photonics 2015(2):550–558
Palik ED (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, New York
Kim JY, Lee C, Bae S, Kim KS, Hong BH, Choi EJ (2011) Far-infrared study of substrate-effect on large scale graphene. Appl Phys Lett 98:201907
Gotschy W, Vonmetz K, Leitnev A, Aussenegg FR (1996) Thin films by regular patterns of metal nanoparticles: tailoring the optical properties by nanodesign. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 63:381–384
Ditlbacher H, Krenn JR, Lamprecht B, Leitner A, Aussenegg FR (2000) Spectrally coded optical data storage by metal nanoparticles. Opt Lett 25(8):563
Zhang MJ, Zhou XL, YQ F (2010) Plasmonic resonance excited extinction spectra of cross-shaped Ag nanoparticles. Plasmonics 5:355–361
Baek IH, Ahn KJ, Kang BJ, Bae S, Hong BH, Yeom DI, Lee K, Jeong YU, Rotermund F (2013) Terahertz transmission and sheet conductivity of randomly stacked multi-layer graphene. Appl Phys Lett 102(19):191109
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11474021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Y., Deng, L., Wang, L. et al. Modulation of Visible and Near-Infrared Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au Nanoparticles Based on Highly Doped Graphene. Plasmonics 12, 1317–1324 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0389-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0389-9