Abstract
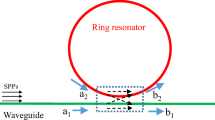
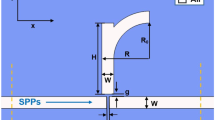
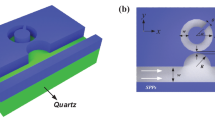
A high sensitive plasmonic refractive index sensor based on metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguides with embedding metallic nano-rods in racetrack resonator has been proposed. The refractive index changes of the dielectric material inside the resonator together with temperature changes can be acquired from the detection of the resonance wavelength, based on their linear relationship. With optimum design and considering a tradeoff among detected power, structure size, and sensitivity, the finite difference time domain simulations show that the refractive index and temperature sensitivity values can be obtained as high as 2610 nm per refractive index unit (RIU) and 1.03 nm/°C, respectively. In addition, resonance wavelengths of resonator are obtained experimentally by using the resonant conditions. The effects of nano-rods radius and refractive index of racetrack resonator are studied on the sensing spectra, as well. The proposed structure with such high sensitivity will be useful in optical communications that can provide a new possibility for designing compact and high-performance plasmonic devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier SA, Kik PG, Atwater HA, Meltzer S, Harel E, Koel BE, Requicha AA (2003) Local detection of electromagnetic energy transport below the diffraction limit in metal nanoparticle plasmon waveguides. Nature Mater 2(4):229–232
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, New York
Genet C, Ebbesen TW (2007) Light in tiny holes. Nature 445(7123):39–46
Chen Z, Cao X, Song X, Wang L, Yu L (2016) Side-coupled cavity-induced Fano resonance and its application in nanosensor. Plasmonics 11(1):307–313
Lu H, Liu X, Wang L, Gong Y, Mao D (2011) Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt Express 19(4):2910–2915
Gao Y, Ren G, Zhu B, Huang L, Li H, Yin B, Jian S (2016) Tunable plasmonic filter based on graphene split-ring. Plasmonics 11(1):291–296
Li-Ping X, Fa-Qiang W, Rui-Sheng L, Shi-Wei Z, Miao H (2015) A high-sensitivity refractive-index sensor based on plasmonic waveguides asymmetrically coupled with a nanodisk resonator. Chinese Phys Lett 32(7):070701-1–070701-4
Kwon SH (2013) Deep subwavelength-scale metal–insulator–metal plasmonic disk cavities for refractive index sensors. IEEE Photonics Journal 5(1):4800107-1–4800107-7
Vafapour Z, Zakery A (2015) New approach of plasmonically induced reflectance in a planar metamaterial for plasmonic sensing applications. Plasmonics 11(2):609–618
Wu T, Liu Y, Yu Z, Peng Y, Shu C, Ye H (2014) The sensing characteristics of plasmonic waveguide with a ring resonator. Opt Express 22(7):7669–7677
Rakhshani MR, Mansouri-Birjandi MA (2016) Dual wavelength demultiplexer based on metal–insulator–metal plasmonic circular ring resonators. J Mod Opt 63(11):1078–1086
Wu YD (2014) High transmission efficiency wavelength division multiplexer based on metal–insulator–metal plasmonic waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 32(24):4242–4246
Wang X, Wang P, Chen C, Chen J, Lu Y, Ming H, Zhan Q (2010) Plasmonic racetrack resonator with high extinction ratio under critical coupling condition. J Appl Phys 107(12):124517
Chen Z, Cui L, Song X, Yu L, Xiao J (2015) High sensitivity plasmonic sensing based on Fano interference in a rectangular ring waveguide. Opt Commun 340:1–4
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang L, Duan G, Zhao Y, Xiao J (2015) Sharp asymmetric line shapes in a plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. J Lightwave Technol 33(15):3250–3253
Rakhshani MR, Mansouri-Birjandi MA (2016) High sensitivity plasmonic sensor based on metal–insulator–metal waveguide and hexagonal-ring cavity with round-corners. Sensors Journal, IEEE 16(9):3041–3046
Wen K, Hu Y, Chen L, Zhou J, Lei L, Meng Z (2016) Single/dual Fano resonance based on plasmonic metal-dielectric-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 11(1):315–321
Yu X, Shi L, Han D, Zi J, Braun PV (2010) High quality factor metallodielectric hybrid plasmonic–photonic crystals. Adv Funct Mater 20(12):1910–1916
Nezhad MP, Simic A, Bondarenko O, Slutsky B, Mizrahi A, Feng L, Lomakin V, Fainman Y (2010) Room-temperature subwavelength metallo-dielectric lasers. Nat Photonics 4(6):395–399
Maksymov IS (2011) Optical switching and logic gates with hybrid plasmonic–photonic crystal nanobeam cavities. Phys Lett A 375(5):918–921
Taflove A, Hagness SC (2000) Computational electrodynamics. Artech house publishers
Masi M, Orobtchouk R, Fan G, Fedeli JM, Pavesi L (2010) Towards a realistic modelling of ultra-compact racetrack resonators. J Lightwave Technol 28(22):3233–3242
Ma N, Li C, Poon AW (2004) Laterally coupled hexagonal micropillar resonator add-drop filters in silicon nitride. Photonics Technology Letters, IEEE 16(11):2487–2489
Wang TB, Wen XW, Yin CP, Wang HZ (2009) The transmission characteristics of surface plasmon polaritons in ring resonator. Opt Express 17(26):24096–24101
Sulliran DM (1996) Exceeding the courant condition with the FDTD method. IEEE Microw Guided Wave Lett 6(8):289–291
Wei PK, Huang YC, Chieng CC, Tseng FG, Fann W (2005) Off-angle illumination induced surface plasmon coupling in subwavelength metallic slits. Opt Express 13(26):10784–10794
Zhang Q, Huang XG, Lin XS, Tao J, Jin XP (2009) A subwavelength coupler-type MIM optical filter. Opt Express 17(9):7549–7555
Chen L, Liu Y, Yu Z, Wu D, Ma R, Zhang Y, Ye H (2016) Numerical analysis of a near-infrared plasmonic refractive index sensor with high figure of merit based on a fillet cavity. Opt Express 24(9):9975–9983
Li Z, Zhang S, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Xu H (2011) Coherent modulation of propagating plasmons in silver-nanowire-based structures. Small 7(5):593–596
Chen S, Meng L, Hu J, Yang Z (2015) Fano interference between higher localized and propagating surface plasmon modes in nanovoid arrays. Plasmonics 10(1):71–76
Dolatabady A, Granpayeh N, Nezhad VF (2013) A nanoscale refractive index sensor in two dimensional plasmonic waveguide with nanodisk resonator. Opt Commun 300:265–268
Raza S, Toscano G, Jauho AP, Mortensen NA, Wubs M (2013) Refractive-index sensing with ultrathin plasmonic nanotubes. Plasmonics 8(2):193–199
Zafar R, Salim M (2015) Enhanced figure of merit in Fano resonance-based plasmonic refractive index sensor. IEEE Sensors J 15(11):6313–6317
Ren M, Pan C, Li Q, Cai W, Zhang X, Wu Q, Fan S, Xu J (2013) Isotropic spiral plasmonic metamaterial for sensing large refractive index change. Opt Lett 38(16):3133–3136
Xie YY, Huang YX, Zhao WL, Xu WH, He C (2015) A novel plasmonic sensor based on metal–insulator–metal waveguide with side-coupled hexagonal cavity. IEEE Photonics Journal 7(2):1–12
Chen Z, Yu L (2014) Multiple Fano resonances based on different waveguide modes in a symmetry breaking plasmonic system. IEEE Photonics Journal 6(6):1–8
Binfeng Y, Ruohu Z, Guohua H, Yiping C (2016) Ultra sharp Fano resonances induced by coupling between plasmonic stub and circular cavity resonators. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-0154-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakhshani, M.R., Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A. Utilizing the Metallic Nano-Rods in Hexagonal Configuration to Enhance Sensitivity of the Plasmonic Racetrack Resonator in Sensing Application. Plasmonics 12, 999–1006 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0351-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0351-x