Abstract
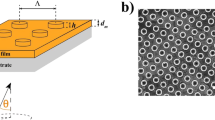
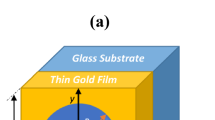
The relation between the enhanced optical transmission and the unit structural features is studied by changing the unit structural features. 3D finite-difference time-domain method is employed to study the enhanced optical transmission of periodic subwavelength circular-sharps shaped hole arrays in metallic films which are deposited on a quartz substrate. The influences of the unit structural features on the enhanced optical transmission are investigated. It is found that the enhanced optical transmission strongly depends on the unit structural edge sharp features: the sharp acuity, numbers, and distributions. The sharp acuity and numbers influence the enhanced optical transmission via localized surface plasmon resonance mode. The sharp distributions affect the enhanced optical transmission equaling to the effect of polarization properties. The results show that the surface plasmons strongly depend on unit structure edge sharp features. Changing the unit structural edge sharp features, the properties of the enhanced optical transmission can be tailored. This paper provides theoretical support for building the various functions of new plasmonic devices.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, et al. (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through subwavelength hole arrays. Nature 391:667–669
Wang GX, Lu H, Liu XM, et al. (2011) Tunable multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on MIM plasmonic nanodisk resonators at telecommunication regime. Opt Express 19:3513–3518
Lerose D, Siaw HEK, Ching BC, et al. (2013) CMOS-integrated geometrically tunable optical filters. Appl Opt 52:1655–1662
Bulgarevich DS, Watanabe M, Shiwa M, et al. (2010) Highly-efficient aperture array terahertz band-pass filtering. Opt Express 18:25250–25255
Yuan MH, Zhao D (2015) A tunable terahertz bandpass filter with a slit aperture flanked by symmetrically distributed parallel grooves on both sides. Acta Phtonica Sin 44:323003–0323007
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Pala RA, Shimizu KT, Melosh NA, et al. (2008) A nonvolatile plasmonic switch employing photochromic molecules. Nano Lett 8:1506–1510
Liu M, Zentgraf T, Liu YM, et al. (2010) Light-driven nanoscale plasmonic motors. Nat Nanotechnol 5:570–573
Atwater H A (2007) The promise of plasmonics. Sci Am 296:56–62
Xu T, Wu YK, Luo XG, et al. (2010) Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging. Nat Commun 1:59
Chen Q, Cumming DRS (2010) High transmission and low color cross-talk plasmonic color filters using triangular-lattice hole arrays in aluminum films. Opt Express 18:14056–14062
Martin-Moreno L, Garcia-Vidal FJ, Lezec HJ, et al. (2001) Theory of extraordinary optical transmission through subwavelength hole arrays. Phys Rev Lett 86:1114–1117
Wang XL, Liu H, Luo H, et al. (2015) Optical filtering properties of subwavelength Tai-chi-shaped metal hole arrays. Opt Commun 340:56–62
Koerkamp KJK, Enoch S, Segerink FB, et al. (2004) Strong influence of hole shape on extraordinary transmission through periodic arrays of subwavelength holes. Phys Rev Lett 92:183901–183904
Wang YK, Qin Y, Zhang ZY et al (2014) Extraordinary optical transmission property of X-shaped plasmonic nanohole arrays. Plasmonics 9:203–207
Gao HT, Shi HF, Wang CT, et al. (2005) Surface plasmon polariton propagation and combination in Y-shaped metallic channels. Opt Express 13:10795–10800
Sun M, Xing SX, Chen YY, et al. (2010) Enhanced transmission through periodic H-shaped arrays. Acta Phtonica Sin 39:1602–1605
Lee JW, Seo MA, Kim DS, et al. (2009) Polarization dependent transmission through asymmetric C-shaped holes. Appl Phys Lett 94:081102–081104
Rodrigo SG, Mahboub O, Degiron A, et al. (2010) Holes with very acute angles: a new paradigm of extraordinary optical transmission through strongly localized modes. Opt Express 18:23691–23697
Besbes M, Hugonin JP, Lalanne P, et al. (2007) Numerical analysis of a slit-groove diffraction problem. J Eur Opt Soc Rapid Publ 2:1–17
Ruan ZC, Qiu M (2006) Enhanced transmission through periodic arrays of subwavelength holes: the role of localized waveguide resonances. Phys Rev Lett 96:233901–233904
Degiron A, Ebbesen TW (2005) The role of localized surface plasmon modes in the enhanced transmission of periodic subwavelength apertures. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 7:S90–S96
Zhang ZY, Zhao YP (2007) Extinction spectra and electrical field enhancement of Ag nanorods with different topologic shapes. Appl Phys 102:113308–113310
Sepúlveda B, Alaverdyan Y, Alegret J, et al. (2008) Shape effects in the localized surface plasmon resonance of single nanoholes in thin metal films. Opt Express 16:5609–5616
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 11174119) and the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (grant no. CX2015B403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, J., Yuan, Z., Chen, Z. et al. Dependence of Surface Plasmons on Unit Structure Edge Sharp Features. Plasmonics 12, 795–801 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0326-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0326-y