Abstract
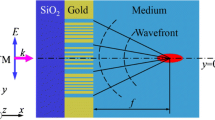
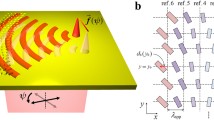
The novel plasmonic lenses based on slanted nanoslits have been proposed theoretically. The slanted nanoslits with different slant angles can provide unequal propagation distances for the surface plasmon polaritons excited by incident light. The phase retardation for wavefront shaping can be obtained to realize constructive interference on a preset single spot. We can actively modulate the position of the optical focus by adjusting the slits slant angles properly. The simulation results of the finite element method are used to verify our proposals.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raether H (1988) Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings. Springer Berlin Heidelberg 111(1):1–133
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Shalaev VM (2007) Optical negative-index metamaterials. Nat Photonics 1(1):41–48
Lopez-Tejeira F, Rodrigo SG, Martin-Moreno L, Garcia-Vidal FJ, Devaux E, Ebbesen TW, Krenn JR, Radko IP, Bozhevolnyi SI, Gonzalez MU, Weeber JC, Dereux A (2007) Efficient unidirectional nanoslit couplers for surface plasmons. Nat Phys 3(5):324–328
Xu T, Zhao Y, Gan D, Wang C, Du C, Luo X (2008) Directional excitation of surface plasmons with subwavelength slits. Appl Phys Lett 92(10):101501–101501–3
Wang Y, Wang J, Gao S, Liu C (2013) Two-way directional plasmonic excitation with two unsymmetrical metallic slits. Appl Phys Express 6(2):263–270
Xia X, Wang J, Liang X, Tang B, Song C, Qu S, Wang Y, Liu C (2015) A dual-way directional surface-plasmon-polaritons launcher based on asymmetric slanted nanoslits. J Mod Opt 62(5):358–363
Kim S, Lim Y, Kim H, Park J, Lee B (2008) Optical beam focusing by a single subwavelength metal slit surrounded by chirped dielectric surface gratings. Appl Phys Lett 92(1):013103–013103–3
Wang B, Wu X, Zhang Y (2013) Multiple-wavelength focusing and demultiplexing plasmonic lens based on asymmetric nanoslit arrays. Plasmonics 8(4):1535–1541
Lin J, Mueller JPB, Wang Q, Yuan G, Antoniou N, Yuan X, Capasso F (2013) Polarization-controlled tunable directional coupling of surface plasmon polaritons. Science 340(6130):331–334
Wang X, Xia X, Wang J, Zhang F, Hu ZD, Liu C (2015) Tunable plasmonically-induced transparency with unsymmetrical graphene-rings resonators. J Appl Phys 118(1):013101
Zhang J, Guo Z, Li R, Wang W, Zhang A, Liu J, Qu S, Gao J (2015) Circular polarization analyzer based on the combined coaxial Archimedes’ spiral structure. Plasmonics 10(6):1255–1261
Khorasaninejad M, Aieta F, Kanhaiya P, Kats MA, Genevet P, Rousso D, Capasso F (2015) Achromatic metasurface lens at telecommunication wavelengths. Nano Lett 15(8):5358–5362
Maklizi MEI, Hendawy M, Swillam MA (2014) Super-focusing of visible and UV light using a meta surface. J Opt 16(10):105007
Sun ZJ, Kim HK (2004) Refractive transmission of light and beam shaping with metallic nano-optic lenses. Appl Phys Lett 85(4):642–644
Shi H, Wang C, Du C, Luo X, Dong X, Gao H (2005) Beam manipulating by metallic nano-slits with variant widths. Opt Express 13(18):6815–6820
Gao Y, Liu J, Guo K, Gao Y, Liu S (2014) A side-illuminated plasmonic planar lens. Opt Express 22(1):699–706
Lieven V, Catrysse PB, Zongfu Y, White JS, Barnard ES, Brongersma ML, Fan S (2009) Planar lenses based on nanoscale slit arrays in a metallic film. Nano Lett 9(1):235–238
Lin L, Goh XM, McGuinness LP, Roberts A (2010) Plasmonic lenses formed by two-dimensional nanometric cross-shaped aperture arrays for Fresnel region focusing. Nano Lett 10(5):1936–1940
Gao H, Hyun JK, Lee MH, Yang JC, Lincoln JL, Odom TW (2010) Broadband plasmonic microlenses based on patches of nanoholes. Nano Lett 10(10):4111–4116
Ishii S, Kildishev AV, Shalaev VM, Kuo-Ping C, Drachev VP (2011) Metal nanoslit lenses with polarization-selective design. Opt Lett 36(4):451–453
Jiang X, Ye J, He J, Wang X, Hu D, Feng S, Kan Q, Zhang Y (2013) An ultrathin terahertz lens with axial long focal depth based on metasurfaces. Opt Express 21(24):30030–30038
Ni X, Ishii S, Alexander VK, Vladimir MS (2013) Ultra-thin, planar, Babinet-inverted plasmonic metalenses. Light Sci Appl 2(4):e72–e77
Hu D, Wang X, Feng S, Ye J, Sun W, Kan Q, Klar PJ, Zhang Y (2013) Ultrathin terahertz planar elements. Adv Opt Mater 1(2):186–191
Pors A, Nielsen MG, Eriksen RL, Bozhevolnyi SI (2013) Broadband focusing flat mirrors based on plasmonic gradient metasurfaces. Nano Lett 13(2):829–834
Wang W, Guo Z, Zhou K, Sun Y, Shen F, Li Y, Qu S, Liu S (2015) Polarization-independent longitudinal multifocusing metalens. Opt Express 23(23):29855–29866
De AF, Liberale C, Coluccio ML, Cojoc G, Di FE (2011) Emerging fabrication techniques for 3D nano-structuring in plasmonics and single molecule studies. Nanoscale 3(7):2689–2696
De AF, Malerba M, Patrini M, Miele E, Das G, Toma A, Zaccaria RP, Di FE (2013) 3D hollow nanostructures as building blocks for multifunctional plasmonics. Nano Lett 13(8):3553–3558
Han Z, Forsberg E, He S (2007) Surface plasmon Bragg gratings formed in metal–insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 19(2):91–93
Lin X, Huang X (2009) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33(23):2874–2876
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11504139, 11504140), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant Nos. BK20140167, BK20140128), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. JUSRP115A15, JUSRP51517), and the Nature Science Foundation of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (Grant No. XKY2014206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, H., Wang, J., Liu, D. et al. Plasmonic Planar Lens Based on Slanted Nanoslit Array. Plasmonics 12, 361–367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0272-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0272-8