Abstract
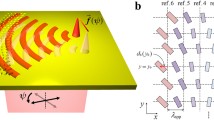
We report plasmonic lenses consisting of coupled nanoslits immersed in a high-index medium to obtain the robustly efficient superfocusing. Based on the geometrical optics and the wavefront reconstruction theory, an array of nanoslits perforated in a gold film and a series of spacings between adjacent nanoslits are optimally designed to realize the desired phase modulation for light focusing. The numerical results verify the design of each plasmonic lens in excellent agreement. For the given total phase difference of 2π, the immersion plasmonic lenses with smaller lens aperture can have much better focusing performance than the non-immersion one. A superfocusing spot of λ/4.39 is achieved using an oil immersion plasmonic lens with an aperture size of 4.97λ, resulting in a resolution improvement of 68.9 % compared with the non-immersion lens. Moreover, such superfocusing performance can be still well kept when the structural parameters of the lens, e.g., nanoslit width and metal film thickness, are deviated from the original design, making the final implementation of the superfocusing lenses much easier.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J, Li Z, Zhang X, Xiao J, Gong Q (2013) Submicron bidirectional all-optical plasmonic switches. Sci Rep 3:1451
Zhang X, Liu Z (2008) Superlenses to overcome the diffraction limit. Nat Mater 7:435–441
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Lin L, Goh XM, McGuinness LP, Roberts A (2010) Plasmonic lenses formed by two-dimensional nanometric cross-shaped aperture arrays for Fresnel-region focusing. Nano Lett 10:1936–1940
Kawata S, Inouye Y, Verma P (2009) Plasmonics for near-field nano-imaging and superlensing. Nat Photonics 3:388–394
Liu Z, Durant S, Lee H, Pikus Y, Fang N, Xiong Y, Sun C, Zhang X (2007) Far-field optical superlens. Nano Lett 7:403–408
Fu Y, Zhou X (2010) Plasmonic lenses: a review. Plasmonics 5:287–310
Hao F, Wang R, Wang J (2010) A novel design method of focusing-control device by modulating SPPs scattering. Plasmonics 5:45–49
Cheng B, Chang K, Lan Y, Tsai D (2015) Achieving planar plasmonic subwavelength resolution using alternately arranged insulator-metal and insulator-insulator-metal composite structures. Sci Rep 5:7996
Cheng B, Chen H, Chang K, Lan Y, Tsai D (2015) Magnetically controlled planar hyperbolic metamaterials for subwavelength resolution. Sci Rep 5:18172
Yu Y, Zappe H (2011) Effect of lens size on the focusing performance of plasmonic lenses and suggestions for the design. Opt Express 19:9434–9444
Yu Y, Zappe H (2012) Theory and implementation of focal shift plasmonic of lenses. Opt Lett 37:1592–1594
Shi H, Wang C, Du C, Luo X, Dong X, Gao H (2005) Beam manipulating by metallic nano-slits with variant widths. Opt Express 13:6815–6820
Ishii S, Kildishev AV, Shalaev VM, Chen K, Drachev VP (2011) Metal nanoslit lenses with polarization-selective design. Opt Lett 36:451–453
Chen Q, Cumming DRS (2010) Visible light focusing demonstrated by plasmonic lenses based on nano-slits in an aluminum film. Opt Express 18:14788–14793
Verslegers L, Catrysse PB, Yu Z, White JS, Barnard ES, Brongersma ML, Fan S (2009) Planar lenses based on nanoscale slit arrays in a metallic film. Nano Lett 9:235–238
Verslegers L, Catrysse PB, Yu Z, Fan S (2009) Planar metallic nanoscale slit lenses for angle compensation. Appl Phys Lett 95:071112
Zhu Y, Yuan W, Yu Y, Diao J (2015) Metallic planar lens formed by coupled width-variable nanoslits for superfocusing. Opt Express 23:20124–20131
Smith BW, Bourov A, Kang H, Cropanese F, Fan Y, Lafferty NV, Zavyalova LV (2004) Water immersion optical lithography at 193 nm. J Micro/Nanolith MEMS MOEMS 3(1):44–51
Mansfield SM, Kino GS (1990) Solid immersion microscope. Appl Phys Lett 57:2615
Karrai K, Lorenz X, Novotny L (2000) Enhanced reflectivity contrast in confocal solid immersion lens microscopy. Appl Phys Lett 77:3459
Rogers ET, Lindberg J, Roy T, Savo S, Chad JE, Dennis MR, Zheludev NI (2012) A super-oscillatory lens optical microscope for subwavelength imaging. Nat Mater 11:432–435
Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF (2006) Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313:1642–1645
Klar TA, Jakobs S, Dyba M, Egner A, Hell SW (2000) Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:8206–8210
Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang X (2006) Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods 3:793–796
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51375400), the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2013ZC53036), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 3102014JC02020504), the Program for the New Star of Science and Technology of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2014KJXX-38), the Specific Project for the National Excellent Doctorial Dissertations (201430), and the Program for the New Century Excellent Talents in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Yuan, W., Yu, Y. et al. Robustly Efficient Superfocusing of Immersion Plasmonic Lenses Based on Coupled Nanoslits. Plasmonics 11, 1543–1548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0208-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0208-3