Abstract
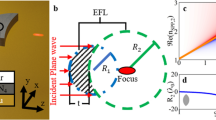
In this work, we investigate the interaction of surface plasmons with a plasmonic Lüneburg lens using near field scanning optical microscopy. Gray-scale electron beam lithography is used to prepare a dome-shaped resist structure on top of a gold film. This particular shape yields the effective refractive index profile of a Lüneburg lens for surface plasmons propagating at the film surface at an energy of \(\hbar \omega ={1.72}\) eV. Next to the Lüneburg lens a grating coupler is milled into the gold film with focused ion beam. The surface plasmons are launched to propagate through the lens and the near field pattern is scanned. We clearly identify a focal spot in the near field signal at the outer perimeter of the lens. In addition, we observe a beating pattern arising from further plasmon waves excited by higher orders of the grating coupler. The emergence of this beating pattern allows the detection of the plasmon’s wave fronts. An analytical model was used to retrieve the properties of the participating wave components. The measured near-field pattern could be modeled very well with electromagnetic simulations applying the effective refractive index approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozbay E (2006). Science (New York N Y) 311(5758):189. doi:10.1126/science.1114849
Gramotnev D K, Bozhevolnyi S I (2010). Nat Photonics 4(2):83. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2009.282
Schuller J a , Barnard E S, Cai W, Jun Y C, White J S, Brongersma M L (2010). Nat Mater 9 (3):193. doi:10.1038/nmat2630
Raether H (1988) Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings, Springer Tracts in Modern Physics, vol 111. Springer, Berlin
Anker J N, Hall W P, Lyandres O, Shah N C, Zhao J, Van Duyne R P (2008). Nat Mater 7 (6):442. doi:10.1038/nmat2162
Homola J, Yee S S, Gauglitz G (1999). Sensors Actuators B Chem 54 (1-2):3. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00321-9
Rottler A, Harland M, Bröll M, Klingbeil M, Ehlermann J, Mendach S (2013). Phys Rev Lett 111(25). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.253901
Pillai S, Catchpole K R, Trupke T, Green M a (2007). J Appl Phys 101(9):093105. doi:10.1063/1.2734885
Atwater H A, Polman A (2010). Nat Mater 9(3):205. doi:10.1038/nmat2629
Willets K a, Van Duyne R P (2007). Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.58.032806.104607
Kawata S, Inouye Y, Verma P (2009). Nat Photonics 3(7):388. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2009.111
Boltasseva A, Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Kjaer K, Larsen M, Bozhevolnyi S (2005). J Lightwave Technol 23(1):413. doi:10.1109/JLT.2004.835749
Engheta N (2007). Science (New York N Y) 317(5845):1698. doi:10.1126/science.1133268
Lal S, Link S, Halas N J (2007). Nat Photonics 1(11):641. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2007.223
Maier S, Atwater H (2005). Journal of Applied Physics 98(1):011101. doi:10.1063/1.1951057
Bozhevolnyi S I, Volkov V S, Devaux E, Laluet J Y, Ebbesen T W (2006). Nature 440(7083):508. doi:10.1038/nature04594
Liu Z, Steele J M, Srituravanich W, Pikus Y, Sun C, Zhang X (2005). Nano Lett 5(9):1726. doi:10.1021/nl051013j
Zentgraf T, Liu Y, Mikkelsen M H, Valentine J, Zhang X (2011). Nat Nanotechnol 6(3):151. doi:10.1038/nnano.2010.282
Leonhardt U (2006). Science (New York, N Y) 312(5781):1777. doi:10.1126/science.1126493
Pendry J B, Schurig D, Smith D R (2006). Science (New York, N Y) 312 (5781):1780. doi:10.1126/science.1125907
Chen H , Chan C T, Sheng P (2010). Nat Mater 9(5):387. doi:10.1038/nmat2743
Liu Y, Zentgraf T, Bartal G, Zhang X (2010). Nano Lett 10(6):1991. doi:10.1021/nl1008019
Huidobro P a, Nesterov M L, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J (2010). Nano lett 10(6):1985. doi:10.1021/nl100800c
Drezet A, Hohenau A, Koller D, Stepanov A., Ditlbacher H, Steinberger B, Aussenegg F R, Leitner A, Krenn JR (2008). Mater Sci Eng B 149(3):220. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2007.10.010
Ditlbacher H, Krenn J R, Felidj N, Lamprecht B, Schider G, Salerno M, Leitner A, Aussenegg F R (2002). Appl Phys Lett 80(3):404. doi:10.1063/1.1435410
Betzig E, Trautman J K (1992). Science (New York, N Y) 257(5067):189. doi:10.1126/science.257.5067.189
Luneburg R K (1944) Mathematical Theory of Optics. University of California Press
Geissler M, Xia Y (2004). Adv Mater 16(15):1249. doi:10.1002/adma.200400835
Zienkiewicz O C, Taylor R L, Zhu JZ (2005) The Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals: Its Basis and Fundamentals. Elsevier Science
Noginov M A, Podolskiy V A, Zhu G, Mayy M, Bahoura M, Adegoke J A, Ritzo B A, Reynolds K (2008). Opt Express 16(2):1385. doi:10.1364/OE.16.001385
Paul A, Zhen Y r, Wang Y, Chang W s, Xia Y, Nordlander P, Link S (2014). Nano Lett 14(6):3628. doi:10.1021/nl501363s
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft via ME 3600/1-1 and Graduiertenkolleg 1286 “Functional Metal-Semiconductor Hybrid Systems.” Furthermore, we thank Detlef Heitmann for fruitful discussions, Björn Beyersdorff for the fabrication of the FIB structure, and the Blick-Group at the University of Hamburg for additional funding.
Funding
This study was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grant numbers: Graduiertenkolleg 1286 and ME 3600/1-1) and by the Blick-Group at the University of Hamburg.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehlermann, J., Vu, H. & Mendach, S. Near Field Investigation of a Plasmonic Lüneburg Lens. Plasmonics 10, 1513–1518 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9960-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9960-z