Abstract
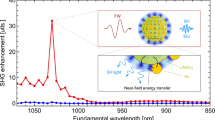
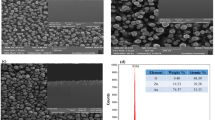
The nonlinear optical properties of single gold nanorods (GNRs) with a large diameter of ∼200 nm and a long length of ∼800 nm were investigated by using a focused femtosecond (fs) laser light with tunable wavelength. While the linear and nonlinear optical properties of small-sized GNRs have been extensively studied, the nonlinear optical properties of large-sized GNRs and the effects of high-order surface plasmon resonances remain unexplored. Second harmonic generation (SHG) or/and two-photon-induced luminescence (TPL) were observed in the nonlinear response spectra, and their dependences on excitation wavelength and polarization were examined. The scattering and absorption spectra of the small- and large-sized GNRs were compared by using the discrete dipole approximation method. It was found that the extinction of large-sized GNRs is dominated by scattering rather than absorption, which is dominant in small-sized GNRs. In addition, it was revealed that the excitation wavelength-dependent SHG of a GNR is governed by the linear scattering of the GNR and the maximum SHG is achieved at the valley of the scattering spectrum. In comparison, the excitation wavelength dependence of TPL is determined by the absorption spectrum of the GNR. The polarization-dependent SHG of a GNR exhibits a strong dependence on the dimension of the GNR, and it may appear as bipolar distributions parallel or perpendicular to the long axis of the GNR or multipole distributions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raether H (1988) Surface plasmons on smooth and rough surfaces and on gratings. Springer, Berlin
Prasad PN (2004) Nanophotonics. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Brongersma ML, Kik PG (2007) Surface plasmon nanophotonics. Springer, Netherlands
Nie S, Emory SR (1997) Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 275:1102–1106
Qian X, Peng X, Ansari DO, Yin-Goen Q, Chen GZ, Shin DM, Yang L, Young AN, Wang MD, Nie S (2008) In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat Biotechnol 26:83–90
Huang X, El-Sayed IH, Qian W, El-Sayed MA (2007) Cancer cells assemble and align gold nanorods conjugated to antibodies to produce highly enhanced, sharp, and polarized surface raman spectra: a potential cancer diagnostic marker. Nano Lett 7:1591–1597
Link S, El-Sayed MA (1999) Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. J Phys Chem B 103:8410–8426
Canfield BK, Husu H, Laukkanen J, Bai B, Kuittinen M, Turunen J, Kauranen M (2007) Local field asymmetry drives second-harmonic generation in noncentrosymmetric nanodimers. Nano Lett 7:1251–1255
Link S, Mohamed MB, El-Sayed MA (1999) Simulation of the optical absorption spectra of gold nanorods as a function of their aspect ratio and the effect of the medium dielectric constant. J Phys Chem B 103:3073–3077
Ming T, Zhao L, Yang Z, Chen H, Sun L, Wang J, Yan C (2009) Strong polarization dependence of plasmon-enhanced fluorescence on single gold nanorods. Nano Lett 9:3896–3903
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Chon JWM, Bullen C, Zijlstra P, Gu M (2007) Spectral encoding on gold nanorods doped in a silica sol–gel matrix and its application to high-density optical data storage. Adv Funct Mater 17:875–880
Zijlstra P, Chon JWM, Gu M (2009) Five-dimensional optical recording mediated by surface plasmons in gold nanorods. Nature 459:410–413
Li X, Lan TH, Tien CH, Gu M (2012) Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam. Nat Commun 3:998
Zijlstra P, Paulo PMR, Orrit M (2012) Optical detection of single non-absorbing molecules using the surface plasmon resonance of a gold nanorod. Nat Nanotechnol 7:379–382
Shao L, Fang C, Chen H, Man YC, Wang J, Lin HQ (2012) Distinct plasmonic manifestation on gold nanorods induced by the spatial perturbation of small gold nanospheres. Nano Lett 12:1424–1430
Chen L, Li GY, Liu GC, Dai QF, Lan S, Tie SL, Deng HD (2013) Sensing the moving direction, position, size, and material type of nanoparticles with the two-photon-induced luminescence of a single gold nanorod. J Phys Chem C 117:20146–201453
Sönnichsen C, Alivisatos AP (2005) Gold nanorods as novel nonbleaching plasmon-based orientation sensors for polarized single-particle microscopy. Nano Lett 5:301–304
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir 20:6414–6420
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2003) Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater 15:1957–1962
Grzelczak M, Pérez-Juste J, Mulvaney P, Liz-Marzán LM (2008) Shape control in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Chem Soc Rev 37:1783–1791
Khanal BP, Zubarev ER (2007) Rings of nanorods. Angew Chem Ed 46:2195–2198
Van der Zande BMI, Koper GJM, Lekkerkerker HNW (1999) Alignment of rod-shaped gold particles by electric fields. J Phys Chem B 103:5754–5760
Khatua S, Chang W, Swanglap P, Olson J, Link S (2011) Active modulation of nanorod plasmons. Nano Lett 11:3797–3802
Pelton M, Liu M, Kim HY, Smith G, Guyot-Sionnest P, Scherer NF (2006) Optical trapping and alignment of single gold nanorods by using plasmon resonances. Opt Lett 31:2075–2077
Zins I, Schubert O, Sönnichsen C, Oddershede LB (2008) Quantitative optical trapping of single gold nanorods. Nano Lett 8:2998–3003
Mohamed MB, Volkov V, Link S, El-Sayed MA (2000) The ‘lightning’ gold nanorods: fluorescence enhancement of over a million compared to the gold metal. Chem Phys Lett 317:517–523
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2005) Aspect ratio dependence of the enhanced fluorescence intensity of gold nanorods: experimental and simulation study. J Phys Chem B 109:16350–16356
Wang H, Huff TB, Zweifel DA, He W, Low PS, Wei A, Cheng J (2005) In vitro and in vivo two-photon luminescence imaging of single gold nanorods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15752–15756
Hubert C, Billot L, Adam PM, Bachelot R, Royer P, Grand J, Gindre D, Dorkenoo KD, Ford A (2007) Role of surface plasmon in second harmonic generation from gold nanorods. Appl Phys Lett 90:181105–181107
Butet J, Duboisset J, Bachelier G, Russier-Antoine I, Benichou E, Jonin C, Brevet P (2010) Optical second harmonic generation of single metallic nanoparticles embedded in a homogeneous medium. Nano Lett 10:1717–1721
Link S, Burda C, Mohamed MB, Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2000) Femtosecond transient absorption dynamics of colloidal gold nanorods: shape independence of the electron-phonon relaxation time. Phys Rev B 61:6066–6090
Deng HD, Li GC, Dai QF, Ouyang M, Lan S, Trofimov VA, Lysak TM (2013) Size dependent competition between second harmonic generation and two-photon luminescence observed in gold nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 24:075201
Payne EK, Shuford KL, Park S, Schatz GC, Mirkin CA (2006) Multipole plasmon resonances in gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 110:2150–2154
Okamoto H, Imura K (2009) Near-field optical imaging of enhanced electric fields and plasmon waves in metal nanostructures. Prog Surf Sci 84:199–229
Yurkin MA, Maltsev VP, Hoekstra AG (2007) The discrete dipole approximation: an overview and recent developments. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 106:558–589
Draine BT, Flatau PJ (2009) User guide to the giscrete dipole approximation code, DDSCAT 7.0. http://arxiv.org/abs/0809.0337
The information on the refractive indices of materials are available on website http://refractiveindex.info/
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110:7238–7248
Dadap JI, Shan J, Heinz TF (2004) Theory of optical second-harmonic generation from a sphere of centrosymmetric material: small-particle limit. J Opt Soc Am B 21:1328–1347
Dadap JI, Shan J, Eisenthal KB, Heinz TF (1999) Second-harmonic rayleigh scattering from a sphere of centrosymmetric material. Phys Rev Lett 83:4045–4048
Bachelier G, Butet J, Russier-Antoine I, Jonin C, Benichou E, Brevet PF (2010) Origin of optical second-harmonic generation in spherical gold nanoparticles: local surface and nonlocal bulk contributions. Phys Rev B 82:235403
Bachelier G, Russier-Antoine I, Benichou E, Jonin C, Brevet P (2008) Multipolar second-harmonic generation in noble metal nanoparticles. J Opt Soc Am B 25:955–960
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51171066 and 11374109), the Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 20114407110002), and the project for high-level professionals in the universities of Guangdong province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Deng, H., Li, G. et al. Nonlinear Optical Properties of Large-Sized Gold Nanorods. Plasmonics 9, 1471–1480 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9766-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9766-4