Abstract
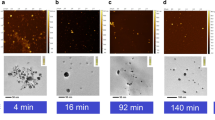
Metallic nanoparticles display distinct localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) properties that depend on their size, shape, and composition and that can be monitored to characterize their growth. Utilizing LSPR properties, we report the first investigation of ambient temperature formation of trioctylamine (TOA)-stabilized spherical silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) of ∼3.0-nm diameter by mild reduction of AgClO4 with the weak reducing agent heptamethyltrisiloxane in organic solvent. The appropriate choice of experimental conditions caused slow reduction, which allowed the study of the nanoparticle growth process by time-resolved UV–visible spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The linear nanoparticle growth kinetics from 50 min to end of the reaction derived from LSPR changes, the absence of a bimodal size distribution during the initial stage of the reduction process from TEM analysis, and the single crystallinity of the resulting AgNPs suggested a diffusion-controlled Ostwald-ripening growth process. It was also found that in addition to its stabilizing ability, TOA acted as a catalyst and facilitated Ag+ reduction. Furthermore, a modest increase in reaction temperature caused a substantial enhancement in the AgNP formation rate, and low concentration of stabilizing ligand yielded an increase in size and dispersity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Sayed MA (2001) Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Accounts of Chemical Research 34(4):257–264. doi:10.1021/ar960016n
Daniel M-C, Astruc D (2003) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104(1):293–346. doi:10.1021/cr030698+
Mayer KM, Hafner JH (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111(6):3828–3857. doi:10.1021/cr100313v
Brewer KE, Aikens CM (2010) TDDFT investigation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering of HCN and CN- on Ag20. J Phys Chem A 114(33):8858–8863. doi:10.1021/jp1025174
Johnson HE, Aikens CM (2009) Electronic structure and TDDFT optical absorption spectra of silver nanorods. J Phys Chem A 113(16):4445–4450. doi:10.1021/jp811075u
Aikens CM, Li S, Schatz GC (2008) From discrete electronic states to plasmons: TDDFT optical absorption properties of Ag n (n = 10, 20, 35, 56, 84, 120) tetrahedral clusters. J Phys Chem C 112(30):11272–11279. doi:10.1021/jp802707r
Provorse MR, Aikens CM (2010) Origin of intense chiroptical effects in undecagold subnanometer particles. J Am Chem Soc 132(4):1302–1310. doi:10.1021/ja906884m
Murray RW (2008) Nanoelectrochemistry: metal nanoparticles, nanoelectrodes, and nanopores. Chem Rev 108(7):2688–2720. doi:10.1021/cr068077e
Ivanova OS, Zamborini FP (2009) Size-dependent electrochemical oxidation of silver nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 132(1):70–72. doi:10.1021/ja908780g
Mendes MJ, Luque A, Tobias I, Marti A (2009) Plasmonic light enhancement in the near-field of metallic nanospheroids for application in intermediate band solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 95(7):071105
Standridge SD, Schatz GC, Hupp JT (2009) Distance dependence of plasmon-enhanced photocurrent in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 131(24):8407–8409. doi:10.1021/ja9022072
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Accounts of Chem Res 41(12):1578–1586. doi:10.1021/ar7002804
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang X, Murphy CJ, El-Sayed MA (2012) The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2740–2779
Sun L, Song Y, Wang L, Guo C, Sun Y, Liu Z, Li Z (2008) Ethanol-induced formation of silver nanoparticle aggregates for highly active SERS Substrates and application in DNA detection. J Phys Chem C 112(5):1415–1422. doi:10.1021/jp075550z
Bantz KC, Haynes CL (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates fabricated using electroless plating on polymer-templated nanostructures. Langmuir 24(11):5862–5867. doi:10.1021/la800103b
Freeman RG, Grabar KC, Allison KJ, Bright RM, Davis JA, Guthrie AP, Hommer MB, Jackson MA, Smith PC, Walter DG, Natan MJ (1995) Self-assembled metal colloid monolayers: an approach to SERS substrates. Science 267(5204):1629–1632. doi:10.1126/science.267.5204.1629
Solarska R, Królikowska A, Augustyński J (2010) Silver nanoparticle induced photocurrent enhancement at WO3 photoanodes. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(43):7980–7983. doi:10.1002/anie.201002173
Gao Y, Shan D, Cao F, Gong J, Li X, Ma H-Y, Su Z-M, Qu L-Y (2009) Silver/polyaniline composite nanotubes: One-Step Synthesis and electrocatalytic activity for neurotransmitter dopamine. J Phys Chem C 113(34):15175–15181. doi:10.1021/jp904788d
Jones MR, Osberg KD, Macfarlane RJ, Langille MR, Mirkin CA (2011) Templated techniques for the synthesis and assembly of plasmonic nanostructures. Chem Rev 111(6):3736–3827. doi:10.1021/cr1004452
Rycenga M, Cobley CM, Zeng J, Li W, Moran CH, Zhang Q, Qin D, Xia Y (2011) Controlling the synthesis and assembly of silver nanostructures for plasmonic applications. Chem Rev 111(6):3669–3712. doi:10.1021/cr100275d
Joshi GK, McClory PJ, Dolai S, Sardar R (2012) Improved localized surface plasmon resonance biosensing sensitivity based on chemically synthesized gold nanoprisms as plasmonic transducers. J Mater Chem 22(3):923–931
Joshi GK, McClory PJ, Muhoberac BB, Kumbhar A, Smith KA, Sardar R (2012) Designing efficient localized surface plasmon resonance-based sensing platforms: optimization of sensor response by controlling the edge length of gold nanoprisms. J Phys Chem C 116(39):20990–21000. doi:10.1021/jp302674h
Xia Y, Xiong Y, Lim B, Skrabalak SE (2009) Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew Chem Int Ed 48(1):60–103. doi:10.1002/anie.200802248
Richards VN, Rath NP, Buhro WE (2010) Pathway from a molecular precursor to silver nanoparticles: the prominent role of aggregative growth. Chem Mater 22(11):3556–3567. doi:10.1021/cm100871g
Polte J, Ahner TT, Delissen F, Sokolov S, Emmerling F, ThuÃànemann AF, Kraehnert R (2010) Mechanism of gold nanoparticle formation in the classical citrate synthesis method derived from coupled in situ XANES and SAXS evaluation. J Am Chem Soc 132(4):1296–1301. doi:10.1021/ja906506j
Sardar R, Shumaker-Parry JS (2011) Spectroscopic and microscopic investigation of gold nanoparticle formation: ligand and temperature effects on rate and particle size. J Am Chem Soc 133(21):8179–8190. doi:10.1021/ja107934h
Van Hyning DL, Klemperer WG, Zukoski CF (2001) Silver nanoparticle formation: predictions and verification of the aggregative growth model. Langmuir 17(11):3128–3135. doi:10.1021/la000856h
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss of the Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspension. Nat Phys Sci 241:20–22
Ji X, Song X, Li J, Bai Y, Yang W, Peng X (2007) Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: the third role of citrate. J Am Chem Soc 129(45):13939–13948. doi:10.1021/ja074447k
Chow MK, Zukoski CF (1994) Gold sol formation mechanisms: role of colloidal stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 165(1):97–109
Brust M, Walker M, Bethell D, Schiffrin DJ, Whyman R (1994) Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase liquid–liquid system. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 7:801–802
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW (2009) Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25(24):13840–13851. doi:10.1021/la9019475
Underwood S, Mulvaney P (1994) Effect of the solution refractive index on the color of gold colloids. Langmuir 10(10):3427–3430. doi:10.1021/la00022a011
Polte J, Erler R, Thunemann AF, Sokolov S, Ahner TT, Rademann K, Emmerling F, Kraehnert R (2010) Nucleation and growth of gold nanoparticles studied via in situ small angle x-ray scattering at millisecond time resolution. ACS Nano 4(2):1076–1082. doi:10.1021/nn901499c
Polte J, Tuaev X, Wuithschick M, Fischer A, Thuenemann AF, Rademann K, Kraehnert R, Emmerling F (2012) Formation mechanism of colloidal silver nanoparticles: analogies and differences to the growth of gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6(7):5791–5802. doi:10.1021/nn301724z
Wang Y-C, Gunasekaran S (2012) Spectroscopic and microscopic investigation of gold nanoparticle nucleation and growth mechanisms using gelatin as a stabilizer. J Nanopart Res 14(10):1–11. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1200-2
Yuk JM, Park J, Ercius P, Kim K, Hellebusch DJ, Crommie MF, Lee JY, Zettl A, Alivisatos AP (2012) High-resolution EM of colloidal nanocrystal growth using graphene liquid cells. Science 336(6077):61–64. doi:10.1126/science.1217654
Zheng H, Smith RK, Y-w J, Kisielowski C, Dahmen U, Alivisatos AP (2009) Observation of single colloidal platinum nanocrystal growth trajectories. Science 324(5932):1309–1312. doi:10.1126/science.1172104
Dharmaratne AC, Krick T, Dass A (2009) Nanocluster size evolution studied by mass spectrometry in room temperature Au25(SR)18 synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 131(38):13604–13605. doi:10.1021/ja906087a
Novo C, Funston AM, Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzan LM, Mulvaney P (2007) Influence of the medium refractive index on the optical properties of single gold triangular prisms on a substrate. J Phys Chem C 112(1):3–7. doi:10.1021/jp709606u
Mulvaney P (1996) Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nano sized metal particles. Langmuir 12(3):788–800. doi:10.1021/la9502711
Sardar R (2006) PhD Thesis CUNY, Graduate Center
Bootharaju MS, Pradeep T (2010) Uptake of toxic metal ions from water by naked and monolayer protected silver nanoparticles: an x-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation. J Phys Chem C 114(18):8328–8336. doi:10.1021/jp101988h
Ferraria AM, Boufi S, Battaglini N, Botelho do Rego AM, ReiVilar M (2009) Hybrid systems of silver nanoparticles generated on cellulose surfaces. Langmuir 26(3):1996–2001. doi:10.1021/la902477q
Qian H, Zhu M, Wu Z, Jin R (2012) Quantum sized gold nanoclusters with atomic precision. Accounts of Chem Res 45(9):1470–1479. doi:10.1021/ar200331z
Alvarez MM, Khoury JT, Schaaff TG, Shafigullin MN, Vezmar I, Whetten RL (1997) Optical absorption spectra of nanocrystal gold molecules. The J of Phys Chem B 101(19):3706–3712. doi:10.1021/jp962922n
Gronbeck H (2012) The bonding in thiolate protected gold nanoparticles from Au4f photoemission core level shifts. Nanoscale 4(14):4178–4182
Hakkinen H (2012) The gold-sulfur interface at the nanoscale. Nat Chem 4(6):443–455
Carney RP, Kim JY, Qian H, Jin R, Mehenni H, Stellacci F, Bakr OM (2011) Determination of nanoparticle size distribution together with density or molecular weight by 2D analytical ultracentrifugation. Nat Commun 2:335, http://www.nature.com/ncomms/journal/v2/n6/suppinfo/ncomms1338_S1.html
Skrdla PJ (2012) Roles of nucleation, denucleation, coarsening, and aggregation kinetics in nanoparticle preparations and neurological disease. Langmuir 28(10):4842–4857. doi:10.1021/la205034u
Shankar R, Shahi V, Sahoo U (2010) Comparative study of linear poly(alkylarylsilane)s as reducing agents toward Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions‚ synthesis of polymer‚ metal nanocomposites with variable size domains of metal nanoparticles. Chem Mater 22(4):1367–1375. doi:10.1021/cm902039r
Shields SP, Richards VN, Buhro WE (2010) Nucleation control of size and dispersity in aggregative nanoparticle growth. A study of the coarsening kinetics of thiolate-capped gold nanocrystals. Chem of Mater 22(10):3212–3225. doi:10.1021/cm100458b
Chuit C, Corriu RJP, Reye C, Young JC (1993) Reactivity of penta- and hexacoordinate silicon compounds and their role as reaction intermediates. Chem Rev 93(4):1371–1448. doi:10.1021/cr00020a003
Yamamura M, Kano N, Kawashima T, Matsumoto T, Harada J, Ogawa K (2008) Crucial Role of N¬∑¬∑¬∑Si interactions in the solid-state coloration of disilylazobenzenes. J Org Chem 73(21):8244–8249. doi:10.1021/jo801334a
Kano N, Komatsu F, Yamamura M, Kawashima T (2006) Reversible photoswitching of the coordination numbers of silicon in organosilicon compounds bearing a 2-(Phenylazo)phenyl group. J Am Chem Soc 128(21):7097–7109. doi:10.1021/ja060926s
Hiramatsu H, Osterloh FE (2004) A simple large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold and silver nanoparticles with adjustable sizes and with exchangeable surfactants. Chem Mater 16(13):2509–2511. doi:10.1021/cm049532v
Zheng N, Fan J, Stucky GD (2006) One-step one-phase synthesis of monodisperse noble-metallic nanoparticles and their colloidal crystals. J Am Chem Soc 128(20):6550–6551. doi:10.1021/ja0604717
Smetana AB, Wang JS, Boeckl J, Brown GJ, Wai CM (2007) Fine-tuning size of gold nanoparticles by cooling during reverse micelle synthesis. Langmuir 23(21):10429–10432. doi:10.1021/la701229q
Yeshchenko O, Dmitruk I, Alexeenko A, Kotko A, Verdal J, Pinchuk A (2012) Size and temperature effects on the surface plasmon resonance in silver nanoparticles. Plasmonics 7(4):685–694. doi:10.1007/s11468-012-9359-z
Sardar R, Heap TB, Shumaker-Parry JS (2007) Versatile solid phase synthesis of gold nanoparticle dimers using an asymmetric functionalization approach. J Am Chem Soc 129(17):5356–5357. doi:10.1021/ja070933w
Ojea-Jimenez I, Bastus NG, Puntes V (2011) Influence of the sequence of the reagents addition in the citrate-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115(32):15752–15757. doi:10.1021/jp2017242
Ojea-Jimenez I, Romero FM, Bastus NG, Puntes V (2010) Small gold nanoparticles synthesized with sodium citrate and heavy water: insights into the reaction mechanism. J Phys Chem C 114(4):1800–1804. doi:10.1021/jp9091305
Bastus NG, Comenge J, Puntes V (2011) Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 27(17):11098–11105. doi:10.1021/la201938u
Njoki PN, Luo J, Kamundi MM, Lim S, Zhong C-J (2010) Aggregative growth in the size-controlled growth of monodispersed gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 26(16):13622–13629. doi:10.1021/la1019058
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by start-up funds provided by IUPUI. N.W. D. and J. C. N. acknowledge MURI fellowship from Center for Research and Learning, IUPUI. Authors would also like to acknowledge Dr. Carrie Donley (CHANL) for helping with XPS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Histogram for particle size analysis at early stages, XPS data, and UV–visible spectra. (DOCX 907 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dennis, N.W., Muhoberac, B.B., Newton, J.C. et al. Correlated Optical Spectroscopy and Electron Microscopy Studies of the Slow Ostwald-Ripening Growth of Silver Nanoparticles under Controlled Reducing Conditions. Plasmonics 9, 111–120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9603-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9603-1